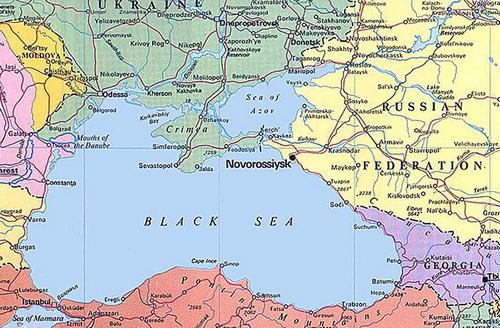
The Sea of Azov on the map is a semi-enclosed water area of the Atlantic Ocean. The facility is located in the eastern part of Europe. Two countries have on their territory the Sea of Azov - Ukraine and the Russian Federation.
general information
The Sea of Azov is considered the smallest in the world. Its maximum depth is not more than thirteen and a half meters, and the average (according to various estimates) is within 6.8–8 m. In the area where the Sea of Azov is located, other objects connecting the water area with the Atlantic Ocean are located. Among them, the straits of Kerch and Gibraltar, the Bosphorus and the Dardanelles should be noted. In addition, the connecting links are the Mediterranean, Aegean and Black Seas.
History
Previously, in antiquity, where the Sea of Azov is now, there was no water. The filling of the water area supposedly began in 5600 BC. e. At that time, the Don River flowed directly into the Black Sea in the area of the current Kerch Strait. In the area where the Sea of Azov is located, there are different settlements. The names of many of them went in the name of the reservoir. For example, the villages of Priazovskaya and Azov, the city of Azov, which is located in the lower reaches of the river. Don, Novoazovsk and others.
Title
In ancient times, different nationalities called the water area in their own way. It should be said that the sea was renamed quite a few times. Until today, the exact origin of the name has not been established. There are several hypotheses on the etymology of the original word "basics":
- named after Prince Azum, who was killed in 1067;
- by the name of the tribe "assy", which, in turn, is supposedly derived from the Avestan and means "fast";
- in Circassian "uzev", which means "neck";
- in the Turkic word "azan" - "lower".
Back in the distant I century. n e. in his writings Pliny, listing the Scythian tribes, speaks of the settlement "Asoki". The name is similar to the word "basics". It is believed that the modern name of the water area has been used in Russian toponymy since the beginning of the 17th century, thanks to the chronicler Pimen. At the same time, it must be said that not all of the Sea of Azov originally received the name (the city of Taganrog is located on a map of Russia not far from the part that received the name) And only by the 2nd half of the 18th century the name was assigned to the entire water area.
Research
The history of the study of the region where the Sea of Azov is conditionally divided into several stages.
- Geographical (ancient), continuing from the time of Herodotus to the beginning of the 19th century.
- Geological and geographical. It lasted from the 19th century to the 40s of the 20th century.
- Complex. This period began in the mid-20th century and continues to this day.
Claudius Ptolemy compiled the first map of the coast of the Sea of Azov. Ukraine as such did not exist then, and the position of the reservoir itself relative to other objects was not entirely clear. Ptolemy established the first geographical coordinates for estuaries, cities, bays and capes. Subsequently, Gleb Svyatoslavovich, who ruled in 1068 in Tmutarakan, measured the distance from Kerch to Taman on ice. It was at that time approximately 20 kilometers. Already from the 12-14th centuries, the Venetians and Genoese began to draw up maps and locations of the Azov and Black Seas.
Geographical position
The region where the Sea of Azov is located lies between 45 ° 12′30 ″ and 47 ° 17′30 ″ s. w. and 33 ° 38 ′ and 39 ° 18 ′ in. The maximum length of the reservoir reaches 380 kilometers, and the width is 200 kilometers. The coastline has a length of 2686 km, the surface of the water area covers an area of 37,800 square meters. km (this figure does not include braids and islands, which are spread over a territory of 107.9 sq. km). In accordance with morphological characteristics, the object is classified as flat seas. The reservoir is considered shallow, with low coastal slopes. The Sea of Azov (this is clearly visible on the map of Russia) is quite distant from the ocean. In this regard, the object belongs to the group of continental reservoirs. In winter, the Sea of Azov can completely or partially freeze. The ice is carried out along the Kerch Strait. Typically, ice formation begins in January. In cold years, it can occur a month earlier.
Bathymetry
The place where the Sea of Azov is located has a relatively simple underwater relief. In the course of removal from the coast, a smooth and slow increase in depths occurs. In the central part of the water area they reach 13 meters. Here the depths are maximum. The location of the isobaths, close to symmetrical, violates their small elongation towards the northeast to the Taganrog Bay. About two kilometers from the coast is isobath 5 meters. It moves away from the Taganrog Bay and near the mouth of the Don River. In this section, the depths increase towards the open part of the reservoir. At the border of the sea and the bay, they reach eight to nine meters. The bottom relief is characterized by the presence of underwater elevations. They are stretched along the western (banks of the Arabat and Morskaya) and eastern (Zhelezinsky bank) coasts. Depths above them are reduced from 8-9 to three to five meters. A fairly wide shallow water is characteristic of the coastal underwater slope on the northern coast. Here the depths are 6-7 m. The southern coast is distinguished by a steep underwater slope. The depths in this section are 11–13 meters. Sea shores are usually sandy and flat. In the southern section, however, one can find hills of volcanic origin, and in some places passing into the advanced steep mountains.
The catchment area in the basin is about 586,000 square meters. km The currents depend on the blowing strong winds of the north-east and south-west directions. The main movement occurs along the coast. Its direction is back clockwise.
Temperature mode
Shallow water bodies are characterized by a large seasonal temperature variability. In winter, the figures reach a minimum. In January-February, the values are close to freezing temperature. In the southern part of the reservoir, not far from the Kerch Strait, the thermometer column rises above zero. The temperature amplitude per year is + 27.5 ... + 28.5 degrees. In summer, fairly uniform indicators are observed over the entire surface of the sea - from +24 to +26 degrees. In July, in some areas (for example, such as Crimea), the Sea of Azov warms up to a maximum of +28 ... +28.5 degrees. The highest temperature was recorded in Primorsko-Akhtarsk. She was +32.5 degrees. As for the long-term average annual temperature, then on the surface it is within 11 ° C. In this case, interannual fluctuations are of the order of one degree.
Salinity
The Sea of Azov has hydrochemical features. They are formed mainly under the influence of abundant river inflow (about 12% of the total water volume). In addition, there is somewhat difficult water exchange with the Black Sea. Before the regulation of the Don, the salinity of the reservoir in question was lower than that of the ocean. three times. The indicators ranged from 1 ppm at the mouth of the river to 10.5 in the central part and to 11.5 in the Kerch Strait area. The salinity of the Sea of Azov began to increase after the construction of the Tsimlyansk hydroelectric complex. By 1977, average rates rose to 13.8 ppm; in the Gulf of Taganrog, the numbers were slightly lower - 11.2. During relatively high humidity, a rapid decrease in salinity was observed. She was at that time 10.9 ‰. However, by 2000, the indicators rose again, stabilizing at 11 ‰. It should be said that in the northern part of the reservoir there is little salt, unlike the site to which Crimea adjoins. The Sea of Azov (a map showing the location of the facility is presented below) in this area is rich in non-salt. It has been mined since ancient times. Until the end of the 19th century, salt from this site provided almost half of Russia's needs. The salinity of water reaches its highest value in the solution - brine Sivash and other lakes. This is due to intense evaporation from the surface of the water in the summer. All of these hypersaline areas are large renewable mineral salt deposits that the Sea of Azov is known for. Russia, having these facilities, provides itself with a significant amount of this mineral. Due to the connection with the sea, the composition of their brine is similar to the structure of sea water. Mostly in the brine are sulfates and chlorides of magnesium and sodium.
Water
The Sea of Azov is characterized by low transparency. In every season and in different areas, it is different. Indicators range from 0.5 to 8 meters. Low transparency is mainly due to the influx of a large amount of turbid river waters, sufficiently rapid agitation of bottom silts during waves, and the presence of planktonic masses in the reservoir. The lowest rates are observed in the Taganrog Bay. There, transparency is in the range of 0.5-0.9, in rare cases - 2 meters. The water in this area can change its color from greenish yellow to brownish yellow. In the central part of the reservoir, due to great depths and under the influence of the Black Sea currents, transparency can range from one and a half to two and a half to eight meters. Here the water has a greenish-blue color. Almost everywhere in the summer, there is an increase in transparency. And in some areas, due to the rather rapid development of the smallest animals and plant organisms in the upper layers, the indicators drop to zero. And the water at the same time becomes a bright green color. This phenomenon is called the "bloom of the sea."