While a person is alive, he breathes. What is breathing? These are processes that continuously supply all organs and tissues with oxygen and remove carbon dioxide from the body resulting from the work of the metabolic system. The respiratory system that directly interacts with the cardiovascular system performs these vital processes. To understand how gas exchange occurs in the human body, one should study the structure and function of the lungs.
Why is a person breathing?
The only way to get oxygen is by breathing. It is not possible to delay it for a long time, since the body requires another portion. Why is oxygen needed at all? Without it, there will be no metabolism, the brain and all other human organs will work. With the participation of oxygen, nutrients are broken down, energy is released, and each cell is enriched with them. Breath is commonly called gas exchange. And this is fair. After all, the features of the respiratory system are to take oxygen from the air that has entered the body, and remove carbon dioxide.
What are human lungs
Their anatomy is quite complex and variable. This organ is paired. Its location is the chest cavity. The lungs are adjacent to the heart on both sides - right and left. Nature made sure that both of these critical organs were protected from squeezing, shock, etc. The chest is the front barrier for damage , the vertebral column is behind, and the ribs are on the sides.
The lungs are literally pierced by hundreds of branches of the bronchi, with pinhead-sized alveoli located at their ends. There are up to 300 million of them in the body of a healthy person. Alveoli play an important role: they supply blood vessels with oxygen and, having a branched system, are able to provide a large area for gas exchange. Just imagine: they can cover the entire surface of a tennis court!
In appearance, the lungs resemble semi-cones, the bases of which are adjacent to the diaphragm, and the tips with rounded ends protrude 2-3 cm above the collarbone. A rather peculiar organ is the human lungs. The anatomy of the right and left lobes is different. So, the first is slightly larger in volume than the second, while it is somewhat shorter and wider. Each half of the organ is covered with pleura, consisting of two leaves: one is fused with the chest, the other with the surface of the lung. The external pleura contains glandular cells, due to which fluid is produced in the pleural cavity.
The inner surface of each lung has a recess, which is called the gate. They include the bronchi, the base of which looks like a branching tree, and the pulmonary artery, and a couple of pulmonary veins come out.
Human lungs. Their functions
Of course, in the human body there are no secondary organs. Important in ensuring human activity are the lungs. What work do they do?
- The main functions of the lungs are to carry out the respiratory process. Man lives while breathing. If the supply of oxygen to the body stops, death will occur.
- The work of the human lungs is to remove carbon dioxide, due to which the acid-base balance is maintained in the body. Through these organs, a person gets rid of volatile substances: alcohol, ammonia, acetone, chloroform, and ether.
- The functions of the human lungs are not limited to this. The paired organ is still involved in the purification of blood, which comes in contact with air. The result is an interesting chemical reaction. Oxygen molecules in the air and carbon dioxide molecules in dirty blood are interchanged, that is, oxygen replaces carbon dioxide.
- Various functions of the lungs allow them to participate in the water metabolism that occurs in the body. Through them, up to 20% of the liquid is removed.
- Lungs are active participants in the process of heat regulation. They give off 10% of the heat to the atmosphere when air is exhaled.
- Regulation of blood coagulation is not complete without the participation of the lungs in this process.
How do lungs work?
The functions of the human lungs are to transport the oxygen contained in the air to the blood, use it, and remove carbon dioxide from the body. Lungs - fairly large soft organs with spongy tissue. Inhaled air enters the air sacs. They are separated by thin walls with capillaries.
Between blood and air there are only small cells. Therefore, for inhaled gases, the thin walls do not constitute obstacles, which contributes to good passability through them. In this case, the functions of the human lungs are to use the necessary and remove unnecessary gases. Lung tissue is very elastic. When you inhale, there is an expansion of the chest and an increase in lung volume.
The respiratory throat, represented by the nose, pharynx, larynx, trachea, has the appearance of a tube 10-15 cm long, divided into two parts, which are called bronchi. Air passing through them enters the air sacs. And when you exhale, there is a decrease in lung volume, a decrease in the chest size, partial closure of the pulmonary valve, which allows air to come out again. This is how the human lungs work.
Their structure and functions are such that the capacity of this organ is measured by the amount of inhaled and exhaled air. So, in men it is equal to seven pints, in women - five. Lungs are never empty. The air remaining after exhalation is called residual. When inhaled, it mixes with fresh air. Therefore, breathing is a conscious and at the same time unconscious process that occurs constantly. A person breathes when he sleeps, but he does not think about it. In this case, if desired, you can briefly interrupt your breathing. For example, being under water.
Interesting facts about lung function
They are able to pump 10 thousand liters of inhaled air per day. But it is not always crystal clear. Together with oxygen, dust, a lot of microbes and foreign particles enter our body. Therefore, the lungs function protection against all unwanted impurities in the air.
The walls of the bronchi have many tiny villi. They are needed to trap germs and dust. And the mucus, which is produced by the cells of the walls of the airways, lubricates these villi, and then is excreted during coughing.
The structure of the respiratory system
It consists of organs and tissues that fully provide ventilation and respiration. In the implementation of gas exchange - the main link in the metabolism - are the functions of the respiratory system. The latter is responsible only for pulmonary (external) respiration. It includes:
1. The airways, consisting of the nose and its cavity, larynx, trachea, bronchi.
The nose and its cavity are heated, moisturized and the inhaled air is filtered. Its cleansing is achieved through numerous hard hairs and goblet cells with cilia.
The larynx lies between the root of the tongue and the trachea. Its cavity is divided by the mucous membrane in the form of two folds. In the middle, they are not completely fused. The gap between them is called the voice.
Trachea originates from the larynx. In the chest, it is divided into bronchi: right and left.
2. Lungs with densely branched vessels, bronchioles and alveolar sacs. They begin the gradual division of the main bronchi into small tubes called bronchioles. They consist of the smallest structural elements of the lung - lobules.
In the pulmonary artery, blood carries the right ventricle of the heart. It is divided into left and right. Arterial branching follows the bronchi, braiding the alveoli and forming small capillaries.
3. The musculoskeletal system, thanks to which a person is not limited in respiratory movements.
These are ribs, muscles, diaphragm. They monitor the integrity of the airways and maintain them during various postures and body movements. Muscles, contracting and relaxing, contribute to a change in the volume of the chest. The diaphragm is designed to separate the chest cavity from the abdominal cavity. It is the main muscle involved in normal inspiration.
A man breathes through his nose. Further, the air passes through the airways and enters the human lungs, the structure and functions of which provide further work of the respiratory system. This is a purely physiological factor. Such breathing is called nasal breathing. In the cavity of this organ, heating, moisturizing and purification of air occur. If the mucous membrane of the nose is irritated, the person sneezes and protective mucus begins to stand out. Nasal breathing can be difficult. Then air passes through the mouth into the throat. Such breathing is said to be oral and, in fact, pathological. In this case, the functions of the nasal cavity are disturbed, which causes various diseases of the respiratory tract.
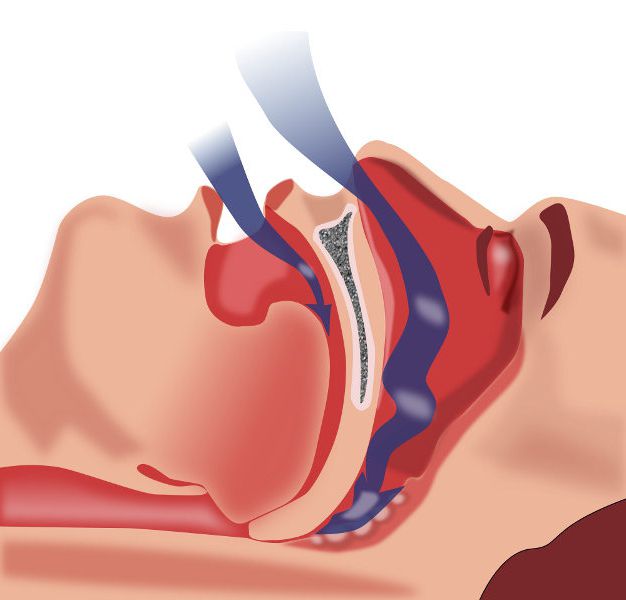
From the pharynx, air is sent to the larynx, which performs other functions, in addition to carrying oxygen further into the respiratory tract, in particular, reflexogenic. If irritation of this organ occurs, a cough or spasm appears. In addition, the larynx is involved in sound production. This is important for any person, as his communication with other people occurs through speech. Tracheas and bronchi continue to heat and moisturize the air, but this is not their main function. Performing a certain work, they regulate the volume of inhaled air.
Respiratory system. Functions
The air surrounding us contains oxygen in its composition, which can penetrate our body and through the skin. But its quantity is not enough to support life. There is a respiratory system for this. The transportation of the necessary substances and gases is carried out by the circulatory system. The structure of the respiratory system is such that it is able to supply oxygen to the body and removes carbon dioxide from it. It performs the following functions:
- Regulates, conducts, moisturizes and degreases air, removes dust particles.
- Protects the airways from ingestion of food.
- Conducts air into the trachea from the larynx.
- Improves gas exchange between the lungs and blood.
- Carries out the transportation of venous blood to the lungs.
- Saturates oxygen with blood and removes carbon dioxide.
- It has a protective function.
- Delays and resolves blood clots, particles of foreign origin, emboli.
- Carries out an exchange of necessary substances.
An interesting fact is that with age, there is a limitation of the functional capabilities of the respiratory system. The level of ventilation of the lungs and respiratory work is reduced. The reasons for such violations can be various changes in the bones and muscles of a person. As a result, the shape of the chest changes, its mobility decreases. This leads to a decrease in the capabilities of the respiratory system.
Respiratory phases
When inhaled, oxygen from the alveoli of the lungs enters the bloodstream, namely red blood cells. From here, on the contrary, carbon dioxide passes into the air in which oxygen was contained. From the moment it enters and until the air leaves the lungs, its pressure in the organ rises, which stimulates the diffusion of gases.
During exhalation, pressure in the alveoli of the lungs is created that exceeds atmospheric pressure. The diffusion of gases: carbon dioxide and oxygen begins to take place more actively.
Each time after exhalation, a pause is created. This is because there is no diffusion of gases, since the pressure of the air remaining in the lungs is negligible, much lower than atmospheric.
While I breathe, I live. Breathing process
- To a child in the womb, oxygen enters through her blood, so the baby’s lungs do not participate in the process, they are filled with liquid. When the baby is born and takes its first breath, the lungs begin to work. The structure and functions of the respiratory system are such that they are able to provide the human body with oxygen and remove carbon dioxide.
- The signals about the amount of oxygen required for a specific period of time are provided by the respiratory center, which is located in the brain. So, during sleep, oxygen is required much less than during hours of operation.
- The volume of air entering the lungs is regulated by the messages that the brain sends.

- During the arrival of this signal, the diaphragm straightens, which leads to stretching of the chest. This maximizes the volume occupied by the lungs when expanding during inspiration.
- During exhalation, the diaphragm and intercostal muscles relax, the chest volume decreases. This leads to the expulsion of air from the lungs.
Types of breathing
- Clavicular. When a person is hunched, his shoulders are raised, and his stomach is squeezed. This indicates an insufficient supply of oxygen to the body.
- Breast breathing. It is characterized by chest expansion due to intercostal muscles. Such functions of the respiratory system contribute to the saturation of the body with oxygen. This method, purely physiological, is more suitable for pregnant women.
- Deep breathing fills the lower organs with air. Most often, athletes and men breathe this way. This method is convenient during exercise.
No wonder they say that breathing is a mirror of mental health. So, the psychiatrist Lowen noticed a striking relationship between the nature and type of emotional disturbance of a person. In people prone to schizophrenia, the upper chest is involved in breathing. A person with a neurotic type of character breathes more belly. Usually people use mixed breathing, in which both the chest and the diaphragm are involved.
Lungs of smokers
Smoking deals a severe blow to organs. Tobacco smoke contains tar, nicotine and hydrogen cyanide. These harmful substances have the ability to settle on the lung tissue, resulting in the death of the epithelium of the organ. The lungs of a healthy person are not affected by such processes.
Smokers have dirty gray or black lungs due to the accumulation of a huge number of dead cells. But this is not all the negative points. Pulmonary function is significantly reduced. Negative processes leading to inflammation begin. As a result, a person suffers from chronic obstructive pulmonary diseases that contribute to the development of respiratory failure. It, in turn, causes numerous disorders that occur due to a lack of oxygen in the tissues of the body.
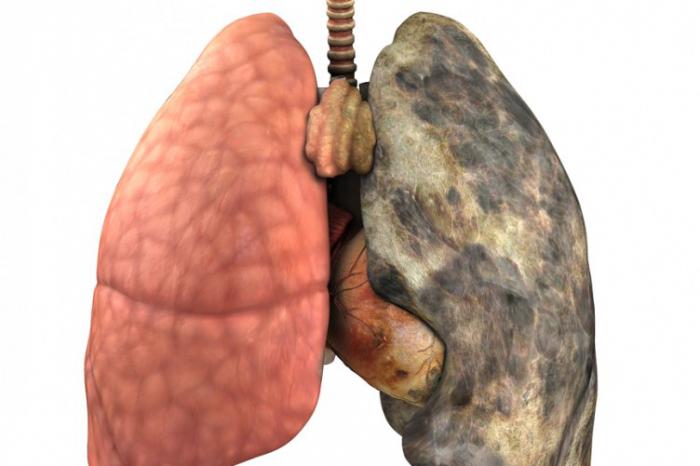
Social advertising constantly demonstrates clips, pictures with the difference between the lungs of a healthy and smoking person. And many people who have never picked up cigarettes sigh in relief. But do not reassure yourself so much, believing that the terrible sight that represents the lungs of a smoker has nothing to do with you. Interestingly, at first glance there is no particular external difference. Neither an X-ray, nor conventional fluorography will show whether the person being examined smokes or not. Moreover, not a single pathologist will be able to determine with absolute certainty whether a person had an addiction to smoking during his life until he found typical symptoms: the condition of the bronchi, yellowing of the fingers, and so on. Why so? It turns out that harmful substances floating in the gassed air of cities, getting into our body, just like tobacco smoke, get into the lungs ...
The structure and functions of this body are designed to protect the body. It is known that toxins destroy lung tissue, which subsequently, due to the accumulation of dead cells, acquires a dark color.
What is the essence of advertising? Just on posters with comparative inscriptions depict the organs of an adult and ... baby.
Interesting about breathing and the respiratory system
- The lungs are the size of a human palm.
- The volume of the paired organ is 5 liters. But it is not fully used. To ensure normal breathing, 0.5 l is enough. The volume of residual air is one and a half liters. If you count, then exactly three liters of air volume are always in reserve.
- The older the person, the less often his breathing. In one minute, a newborn inhales and exhales thirty-five times, a teenager - twenty, an adult - fifteen times.
- In one hour, a person takes a thousand breaths, in a day - twenty-six thousand, in a year - nine million. Moreover, men and women do not breathe equally. In one year, the former take 670 million breaths, and the latter 746.
- In one minute, it is vital for a person to get eight and a half liters of air volume.
Based on the foregoing, we conclude: the lungs need to be monitored. If in doubt about your respiratory system, consult your doctor.