A dielectric is a material or substance that practically does not pass electric current. Such conductivity is obtained due to the small number of electrons and ions. These particles are formed in a non-conductive material only when high temperature properties are achieved. About what is a dielectric and will be discussed in this article.
Description
Each electronic or radio conductor, semiconductor or charged dielectric passes electric current through itself, but the peculiarity of the dielectric is that a small current will flow in it even with a high voltage above 550 V. An electric current in a dielectric is the movement of charged particles in a certain direction (it can be positive and negative).
Types of currents
The dielectric conductivity is based on:
- Absorption currents - a current that flows in a dielectric at constant current until it reaches an equilibrium state, changing direction when turning on and applying voltage to it and when it is turned off. With alternating current, the voltage in the dielectric will be present in it all the time while it is in the action of an electric field.
- Electronic conductivity - the movement of electrons under the influence of a field.
- Ionic conductivity - is the movement of ions. It is found in solutions of electrolytes - salts, acids, alkali, as well as in many dielectrics.
- Mionic conductivity is the movement of charged particles called molions. It is found in colloidal systems, emulsions and suspensions. The phenomenon of movement of molions in an electric field is called electrophoresis.
Electrical insulation materials are classified by their state of aggregation and chemical nature. The former are divided into solid, liquid, gaseous and hardening. By chemical nature they are divided into organic, inorganic and organoelemental materials.
The conductivity of dielectrics in the state of aggregation:
- Electrical conductivity of gases. Gaseous substances have a fairly low current conductivity. It can occur in the presence of free charged particles, which appears due to the influence of external and internal, electronic and ionic factors: X-ray and radioactive species, collision of molecules and charged particles, thermal factors.
- Electrical conductivity of a liquid dielectric. Dependence factors: molecular structure, temperature, impurities, the presence of large charges of electrons and ions. The electrical conductivity of liquid dielectrics is largely dependent on the presence of moisture and impurities. The conductivity of the electricity of polar substances is also created using a liquid with dissociated ions. When comparing polar and nonpolar liquids, the former have a clear advantage in conductivity. If you clean the liquid from impurities, then this will contribute to a decrease in its conductive properties. With an increase in the conductivity of a liquid substance and its temperature, a decrease in its viscosity arises, leading to an increase in the mobility of ions.
- Solid dielectrics. Their electrical conductivity is caused by the movement of charged particles of dielectric and impurities. In strong fields of electric current, electrical conductivity is detected.
Physical properties of dielectrics
With a specific material resistance of less than 10-5 Ohm * m, they can be attributed to conductors. If more than 108 Ohm * m - to dielectrics. There may be cases when the resistivity will be several times greater than the resistance of the conductor. In the range of 10-5-108 Ohm * m is a semiconductor. Metallic material is an excellent conductor of electric current.
Of the entire periodic table, only 25 elements belong to non-metals, and 12 of them will probably be with the properties of a semiconductor. But, of course, in addition to the substances in the table, there are many more alloys, compositions, or chemical compounds with the property of a conductor, semiconductor, or dielectric. Based on this, it is difficult to draw a certain line of values of various substances with their resistances. For example, at a lower temperature factor, the semiconductor will behave like a dielectric.
Application
The use of non-conductive materials is very extensive, because it is one of the popularly used classes of electrical components. It became clear enough that they can be used due to the properties in an active and passive form.
In a passive form, the properties of dielectrics are used for use in an insulating material.
In active form, they are used in ferroelectric, as well as in materials for emitters of laser technology.
Core dielectrics
Common species include:
- Glass.
- Rubber.
- Oil.
- Asphalt.
- China.
- Quartz.
- Air.
- Diamond.
- Pure water.
- Plastic.
What is a dielectric fluid?
Polarization of this type occurs in an electric current field. Liquid non-conductive substances are used in the technique for pouring or impregnating materials. There are 3 classes of liquid dielectrics:
Petroleum oils are weakly viscous and mostly non-polar. They are often used in high voltage equipment: transformer oil, high voltage water. Transformer oil is a non-polar dielectric. Cable oil has found application in the impregnation of insulating paper wires with a voltage of up to 40 kV, as well as coatings based on metal with a current of more than 120 kV. Compared to condenser oil, transformer oil has a cleaner structure. This type of dielectric is widely used in production, despite the high cost compared to analog substances and materials.
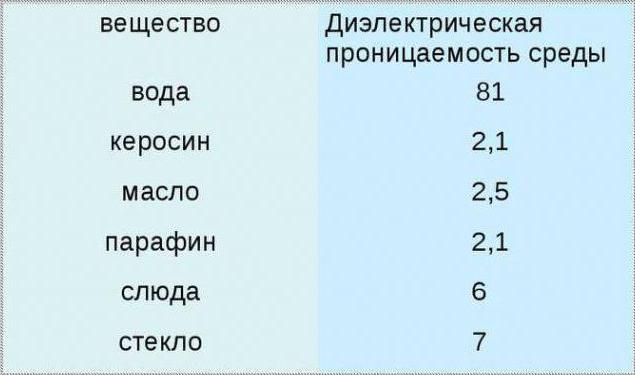
What is a synthetic dielectric? Currently, almost everywhere it is banned due to its high toxicity, as it is based on chlorinated carbon. And a liquid dielectric based on organic silicon is safe and environmentally friendly. This type does not cause metal rust and has the properties of low hygroscopicity. There is a liquefied dielectric containing an organofluorine compound, which is especially popular because of its incombustibility, thermal properties and oxidative stability.
And the last look is vegetable oils. They are weakly polar dielectrics, they include flaxseed, castor, tung, hemp. Castor oil is highly heated and is used in paper capacitors. The remaining oils are evaporated. Evaporation in them is caused not by natural evaporation, but by a chemical reaction called polymerization. Actively used in enamels and paints.
Conclusion
The article examined in detail what a dielectric is. Various species and their properties were mentioned. Of course, in order to understand the subtlety of their characteristics, we will have to study the physics section about them in more depth.