Anus is the final part of the intestine through which the body ejects feces (that is, the remnants of waste food).
The structure of the anus of man
The anus is limited by sphincters, which are formed by muscles. Such muscle rings are necessary to control the opening and closing of the anus. In the human body, two anorectal sphincters:
- Internal, consisting of thickenings of smooth muscles of the rectum and not subject to consciousness. Its length is from one and a half to three and a half centimeters.
- External, consisting of striated muscles and controlled by consciousness. Its length varies from two and a half to five centimeters.
The anus ends with the anal edge, which is a sharp transition of the scaly mucosa of the lining of the distal anorectal canal into the skin of the perineum. The skin in the anus is usually more pigmented (i.e. darker in color) and wrinkled due to the presence of an external sphincter.
In childhood, the anus is located more dorsally than in adults, about twenty millimeters from the tailbone. The diameter of the anus, as a rule, is three to six centimeters, and the length of the channel varies from three to five centimeters. In addition to the sphincters, the rectal obturator apparatus includes muscles that lift the anus and muscles of the pelvic diaphragm.
In the structure of the anus, three departments can be distinguished:
- The mucosa in this department is equipped with longitudinal folds, between which crypts (anal sinuses) are found, where the holes of the anal glands exit.
- Area covered by squamous epithelium.
- This department is covered with stratified keratinized flat epithelium and is equipped with numerous sebaceous and sweat glands, as well as hair.
The area of the anus and rectum has a developed circulatory network, as well as many nerve endings, which deliberately delays the act of defecation and is often the cause of neurogenic constipation.
Anus topography
The structures that directly interact with the anal canal are the rectal ampoule and the sigmoid colon. The anal canal is located in the perineum. In the front, the rectum is adjacent to the seminal vesicles, vials of the vas deferens, the bladder and prostate gland in men. In women, the vagina and uterus are located in front. The channel terminates in the anus. At the back, the external sphincter is attached to the coccyx using the anal coccygeal ligament.
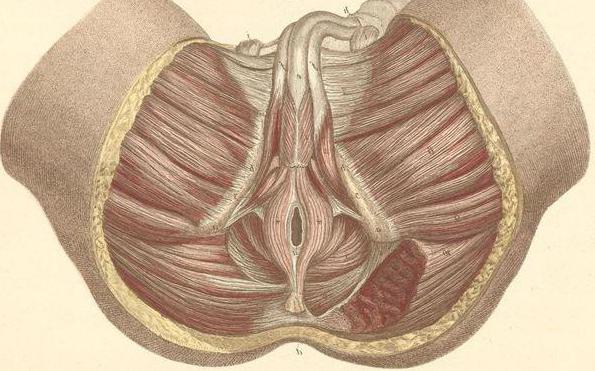
In the area of the perineum behind and on the sides of the anus there are paired sciatic-rectal fossae, shaped like a prism and filled with fatty tissue, in which the nerves and blood vessels pass. With a frontal section, the pits have the shape of triangles. The lateral wall of the fossa is formed by the obstructive muscle and sciatic tubercle (inner surface), the medial - by the external sphincter and muscle, which raises the anus. The posterior wall of the fossa is formed by the coccygeal muscle and its posterior bundles, which raises the anus, and the anterior one - by the transverse muscles of the perineum. Fatty tissue, which is located in the cavity of the sciatic-rectal fossa, performs the function of an elastic elastic pillow.
The structure of the female anus
In the female body, the rectum in front is adjacent to the vagina and is separated from the latter by a thin layer of Denovilje-Salishchev. Due to this structural feature of the anus and rectum in women, both infectious and tumor agents easily penetrate from one cavity to another, which leads to the formation of rectal-vaginal fistula as a result of various injuries or ruptures of the perineum during childbirth.
The structure of the anus in women determines its shape in the form of a flat or slightly protruding formation. This is due to the fact that in the process of delivery, the muscles of the perineum relax, and the muscles that lift the anus lose their ability to contract.
Features of the anus in men
The structure of the male anus has some differences. In men (especially muscular ones), the anus looks like a funnel. The anterior wall of the anal canal is adjacent to the bulb of the urethra and the apex of the prostate gland. In addition, the internal sphincter of men is thicker than that of women.
Functions of the anus and rectum
The rectum is responsible for the removal of waste substances from the body. In addition, fluid is absorbed in it. So, with dehydration and pressing of feces, about four liters of fluid are returned to the body per day. Together with the liquid, trace elements are reabsorbed. The rectal ampoule is a reservoir for feces, the accumulation of which leads to overstretching of the walls of the intestine, the formation of a nerve impulse and, as a result, the urge to defecate (defecate).
And now about the functions of the anus. Being in constant tension, its sphincters control the release of feces (defecation) and the exit of gases from the intestines (flutulence).
Pathology of the anus
- Tumors
- Hemorrhoids.
- Hernias.
- Various defects of the mucosa (cysts, anal fissures, ulcers).
- Inflammatory processes (abscesses, paraproctitis, proctitis, fistulas).
- Congenital conditions (atresia of the anus).
Sphincter spasm
In accordance with the structure of the anus, the manifestations of pathologies of this section of the intestine are also characteristic. Among the symptoms, the most common sphincter spasm (external or internal), which is pain and discomfort in the anus.
The causes of this condition are:
- mental problems;
- prolonged constipation;
- chronic inflammation in the area of the internal or external sphincter;
- excessive innervation.
Accordingly, the duration is distinguished:
- A prolonged spasm, characterized by severe pain, which is not removed by the use of ordinary analgesics.
- Short-term spasm - sharp short-term acute pains in the anus, extending to the pelvic joints or tailbone.
Depending on the cause, the spasm may be:
- primary (due to neurological problems);
- secondary (due to problems in the gut itself).
The manifestations of this symptom are:
- the appearance of pain due to stress;
- pain relief during bowel movements or with the help of warm water is stopped;
- the pain is acute, localized in the anus and gives to the coccyx, pelvis (perineum) or abdomen.
Diagnosis of pathological processes
- Computed tomography can detect polyps and other pathological formations.
- A biopsy is used to determine the malignancy of tumor processes.
- Anoscopy (sigmoidoscopy) is used to assess the condition of the mucous membrane of the anus, as well as taking material for a biopsy.
- Anorectal manometry. In accordance with the structure of the anus (photo above), a diagnosis is made of the muscular apparatus (sphincters) of the anus. Most of the time, the anal muscles are as stressed as possible to control defecation and flatulence. Up to eighty-five percent of the basal anal tone is carried out by the internal anal sphincter. With insufficient or absent coordination between the muscles of the pelvic floor and the sphincters of the anus, dyshesia develops, which is manifested by difficult bowel movements and constipation.
- Rectal research. This method allows to detect hernias, prolapse of the intestines, uterus, hemorrhoids, fistulas, fissures, and other pathologies of the anus and rectum.
- Ultrasound of the anus. Based on this study, we can assume the presence of neoplasms, determine their location and size, detect hemorrhoidal nodes, and so on.
Anorectal Discomfort
The anatomical structure of the anus is such that the skin in this area is especially sensitive, and pathogenic bacteria can settle in its folds if hygiene is not observed, frequent constipation or diarrhea, which can lead to discomfort, irritation, itching, unpleasant odor and pain.
To reduce these manifestations and their prevention should:
- Wash the anus and the skin around it with water without soap (the latter can dry the skin and, as a result, lead to even greater discomfort). It is necessary to give preference to the Cavilon spray or the use of alcohol-free wet wipes (since toilet paper irritates the skin).
- The skin in the anus should be dry.
- It is necessary to create a barrier to moisture. For example, it is recommended to use Dimethicon cream, which creates a protective film on the skin around the anus.
- Use of pharmaceutical powders (e.g. talcum powder or corn starch). They should be applied to pre-cleaned and dried skin.
- The use of disposable underwear or moisture-absorbing pads.
- The use of "breathable" linen and clothes made from natural materials of free cut, which does not constrain movements.
- In case of fecal incontinence, immediately need to replace underwear.
Treatment
The purpose of a particular therapy depends on the nature of the disease. With spasms of the sphincters, first of all, they eliminate the reasons that they were caused. In addition, laxatives, antibacterial, painkillers and antispasmodics are prescribed in the form of ointments / suppositories, as well as physiotherapy, electrosleep, applications, massage, microclysters. With the ineffectiveness of conservative treatment, surgical operations are performed.
Hemorrhoids are treated with special suppositories and ointments, as well as surgical methods. Congenital abnormalities (atresia of the anus) require immediate surgery. Anus tumors are treated with a combination of radiation and chemotherapy, as well as surgical removal of the neoplasm. Cracks in the area of the anus are very treatable with the use of special baths, dieting, healing candles and creams, as well as surgically. Hernias and prolapses of the rectum are removed by surgical methods.