One of the distinguishing features of representatives of the plant kingdom is the presence in their cells of special structures - plastids. These include chloroplasts, chromoplasts and leukoplasts, the structure and functions of which will be considered in our article.
What are plastids
Plastids are called organelles of plant cells, fungi, and some simple animals. These are round bodies that have a semi-autonomous structure. They are able to interconvert into each other. For example, leukoplasts, the structure and functions of which change under the influence of direct sunlight, are converted into chloroplasts. Many have observed that potato tubers turn green. This is the result of such an amazing transformation. But you should not eat such a product in food. Along with chloroplasts in tubers, poison accumulates - alkaloid solanine. It can cause severe food poisoning and is especially dangerous for children.
When fruits and vegetables ripen, plastids also interconvert. Only in this case, chromoplasts are formed from leukoplasts that determine the color of various parts of the plant: yellow, red, pink, purple, etc.
Types of Plastids
Leukoplasts, plastids, chromoplasts, chloroplasts differ both in structure and in function. But all of them play an important and irreplaceable role. The ability to color different parts of the plant is due to the fact that chromoplasts contain various pigments - dyes.
The bright petals of the corollas of most plants are typical proof of this. This color, along with the aroma of flowers, attracts insects for pollination, which precedes fertilization and the formation of fruits.
Green plastids contain the chlorophyll pigment, which determines their color. The presence of this substance (along with carbon dioxide, water and solar radiation) is a prerequisite for the photosynthesis process. In its course, plants form carbohydrates and oxygen. The former are for them a source of nutrition, growth and development. And oxygen, all living things, from bacteria to humans, use oxygen to breathe.
The structure of leukoplasts
Leukoplasts are colorless organelles. They have the correct spherical shape. The system of membranes inside is rather poorly developed. The shape can change to irregular only if sufficiently large starchy grains begin to form in their cytoplasm. Leukoplast plastids are found in the storage of the main plant tissue. It forms the basis of shoot modifications - tubers, bulbs, rhizomes. The function of leukoplasts is determined by such features of their structure. Many valuable nutrients can accumulate in the cavity of these organelles. Leukoplasts, like all plastids, are double-membrane organelles. However, the inner shell does not form pronounced outgrowths into the structure.
Leukoplasts are eukaryotic cells. This means that in their cytoplasm, DNA molecules that carry genetic information are contained in the formed nucleus.
Leukoplast function
These plastids are specialized. Depending on the species, they are able to accumulate and synthesize various types of organic substances. For example, carbohydrate starch contains amyloplasts. This substance is characteristic of all plants, since it is formed from glucose obtained during photosynthesis. Oleoplasts produce and store fats. Liquid fats are also found in the cells of some plants and are called oils. Proteinoplasts contain proteins. The structure of leukoplasts determines such functions. In addition to the cavity necessary for the supply and storage of various substances, they contain enzymes. These biological natural catalysts are able to accelerate chemical reactions, but are not part of their products. Under the influence, for example, of simple glucose carbohydrate, starch polysaccharide is formed. When conditions arise that are unfavorable for photosynthesis, it again breaks down to monomers and is used by the plant to carry out vital processes.
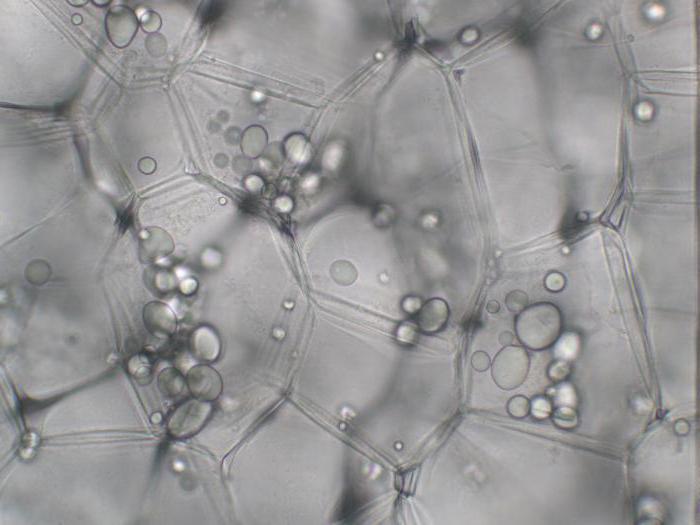
Where are the leukoplasts
Since the main function of leukoplasts is the accumulation of substances, these organelles are found in thickened and fleshy parts of plants. Potato tubers are especially rich in them. Each student is able to conduct a qualitative reaction to starch, which is contained in his leukoplasts. To do this, you just need to apply a few drops of iodine solution to a fresh slice. Under his influence, plastids, previously colorless, will acquire a saturated violet color. They can be examined under a microscope even at low magnification.
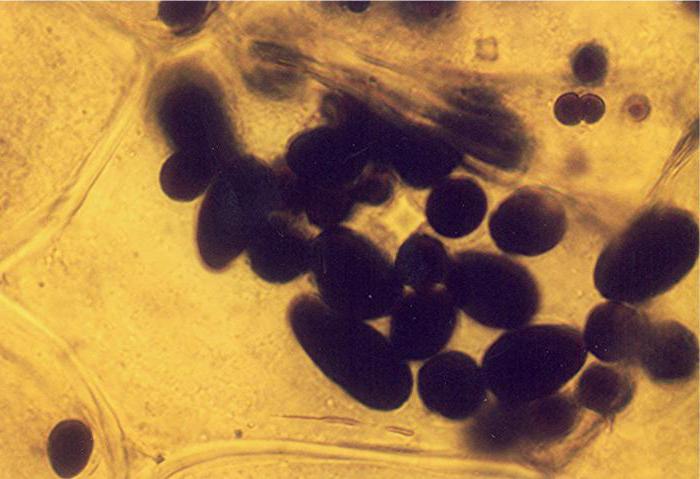
There are also many leukoplasts in the bulbs of plants. Due to the large supply of water and carbohydrates, such roots can carry unfavorable periods of drought, frost and heat underground. At the same time, the aboveground small part of the plant dies, and the modified shoot remains viable. For example, tulips manage to grow and bloom in a couple of weeks. And then in their bulb accumulate carbohydrates formed during photosynthesis by the green parts of this spring plant.
Rhizomes are no exception. Everyone knows how difficult it is to get rid of weeds. They are not afraid of even the most severe drought, and the leaves appear again above the surface of the soil. The thing is that the plant itself develops underground in the form of a thickened modified shoot with elongated internodes. It contains a significant amount of leukoplasts, and hence the supply of substances.
The endosperm of seeds, fungal spores, and ovules of higher plants perform their functions precisely due to the presence of these plastids.
The origin of leukoplastics
The presence of leukoplasts in the embryonic tissue of plant organisms has been proven. And they are formed from the so-called proplastids. These structures are the precursors of all types of similar organelles. Initially, they are located in the meristem - the educational tissue of plants. Proplastids are microscopic bodies up to 1 μm in size. It is with them that the entire chain of interconversions of these plant cell organelles begins.
Thus, the main function of leukoplasts is the synthesis, accumulation and storage of various types of organic substances necessary for the existence of living organisms.