Blood, like any tissue, consists of cells and their intercellular substance metabolism . Moreover, their ratio is such that it is more like a suspension of shaped elements (cells) in a liquid medium.
The formation of cells in the bone marrow from red and white sprouts, and then through multiple sinusoidal capillaries, they enter the general bloodstream, where they perform their highly specialized functions. However, before that, they undergo multistage differentiation from a common progenitor cell of a pluripotent stem cell to mature cells: leukemia, thrombotic and red blood cells, the norm of all these cells can fluctuate as a manifestation of compensation or pathology. The last of them are the main transporters of oxygen, while the remaining
white blood cells (leukocytes, consist of 5 classes) and plate bodies (platelets) carry out multifaceted protective reactions. So, lymphocytes provide immunity, neutrophils and monocytes - phagocytosis and proteolysis, baso-and eisonophils - the secretion of biologically active substances: histamine, thromboxanes, prostaglandins and leukotrienes, FAT, promoting vasoconstriction and activation of other cells. Platelets form a kind of “plug” in case of damage to the vascular wall.
Red blood cells, norm: structure and functions
Red blood cells are one of the most highly specialized cells. Their young predecessors are called reticulocytes, when they mature, the cell gradually loses the nucleus and replaces it with hemoglobin - a quaternary structure protein that can form a weak compound with oxygen to easily capture it in the pulmonary capillaries and also easily transfer to tissues. Red blood cells normally have a biconcave shape, since it gives them a number of advantages, increasing the surface area to bind more oxygen and allowing them to “fold” when passing through the vessels of the smallest caliber of the microvasculature. Since men spend more energy and, accordingly, oxygen, red blood cells also have a high concentration in their blood.
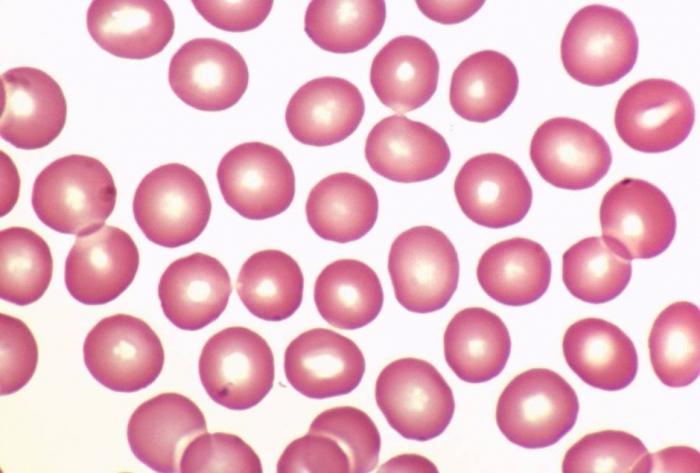
The norm for women is 3.9 - 4.7 * 10 ^ 12 / l, for men the same norm is 4.0-5.0 * 10 ^ 12 / l. This is also explained by a higher level of androgens, which have a stimulating effect on erythropoiesis. Another important component of OAK is the level of hemoglobin, since with a decrease in its concentration per unit volume of blood, the pathological state of "anemia" occurs, accompanied by increasing hypoxia and ischemia of organs. The color indicator reflects how saturated red blood cells are with hemoglobin. The norm of this indicator is 0.8-1.05 units, and when it is reduced, we can talk about hypochromic anemia. Anemia can also be normochromic, as with increased hemolysis, when it is the erythrocytes, the norm of which is maintained by the balance of their synthesis in CMC, that undergo an increased destruction in the tissues, destruction occurs in the liver and spleen after 90-110 days. Hyperchromic anemia is observed with the so-called. megaloblastic anemia, developing with a lack of vitamin B12 or H4 folate, the most important components of erythropoiesis.