Today, environmental issues are at the head of the table at almost every meeting of World Governments. It's no secret that ecology has become the new religion of the 21st century. 2017 was declared the year of environmental protection in Russia, and therefore environmental education is one of the tasks for this year.
Why purify water?
Of the total stock of the World Ocean, only 3% is fresh water, of which 68% are glaciers (not suitable for drinking), 30% are underground sources (often contaminated from soils), and only 2% are terrestrial water sources. From the global picture of the world it is clear that the presence of clean fresh water is not just a necessity, but sometimes a luxury.
Wastewater generated during the economic activities of enterprises contain a large amount of pollutants in concentrations exceeding the permissible and regulatory levels. As a rule, we are talking about heavy metals (iron, nickel, copper, lead, mercury, cadmium, etc.), petroleum products, suspended solids, aluminum, surfactants (synthetic surfactants, for the average person this is all that foam). These substances, falling into water bodies, disrupt the normal functioning of aquatic biogeocenoses, poison the soil, provoke the growth of blue-green algae, and are toxic to animals. These pollutants are also toxic to humans.
A large amount of pollutants is also generated from human activities in residential multi-apartment and private houses. Basically, these are surfactants and organic waste, but metal salts also enter the sewers.
What is a sewage treatment skimmer?
A flotator is a device designed to remove fine impurities from water by the physicochemical method. Relatively speaking, this is the mechanism of one of the main processing modules in engineering and technology for wastewater treatment. It is on the flotator that the main separation of dissolved substances and water purification to standard values take place.
Industrial flotators can be designed for both large plants and car washes, differing in size and material.
The main task of the flotator is to isolate and remove from the water pollutants dissolved in it, translating them into an insoluble form. At the same time, air is supplied to the device to increase the cleaning effect.
The principle of operation of the flotator for wastewater treatment
The principle of operation of the flotator is based on passing air bubbles through the cleaned medium in order to form a foam. This foam is called sludge, which is removed and discharged to special dewatering devices. In order for the bubbles to capture and take away pollution, it is necessary to add special substances - coagulants and flocculants. These substances have high adhesion, that is, they help pollutants stick together with each other and with air bubbles, forming the so-called flocculi.
The bubble, passing from the nozzle or nozzle of the distributor up, captures sticky contaminants with it. This process is carried out until the water reaches the desired cleaning effect.
The complexity of the process is to accurately select the dose of coagulant and flocculant so that the adhesion force is high enough to stick to the bubble, but the flakes formed are not too heavy so as not to damage the air bubble.
Scheme including a flotator for wastewater treatment
Technology, involving a flotator as the main processing module, always includes a reagent farm and a device for creating air bubbles. The reagent farm is a container with reagents (coagulants, flocculants, alkali to adjust the pH) and a reactor for mixing the reagent with water.
As a device for creating air bubbles, as a rule, a saturator is used, which is a chamber for mixing air with water in order to create a water-air mixture. Next, this mixture is sent to the flotator. The saturation device is equipped with a powerful air pump.
The flotator is never used separately; it is always included in the general water treatment scheme. The complete scheme, as a rule, consists of the stages of preliminary sedimentation, physico-chemical treatment (flotator or coagulator) and subsequent mechanical cleaning on filters.
In other words, the flotator can not provide all the cleaning, it is only a separate unit that requires pre-treatment and subsequent. If sand or other coarse impurities enter the skimmer, this will damage the device. Also, this device cannot provide disinfection and complete cleaning of oil products. Therefore, after it, an ultraviolet installation and sorption (or mechanical) filters are needed.
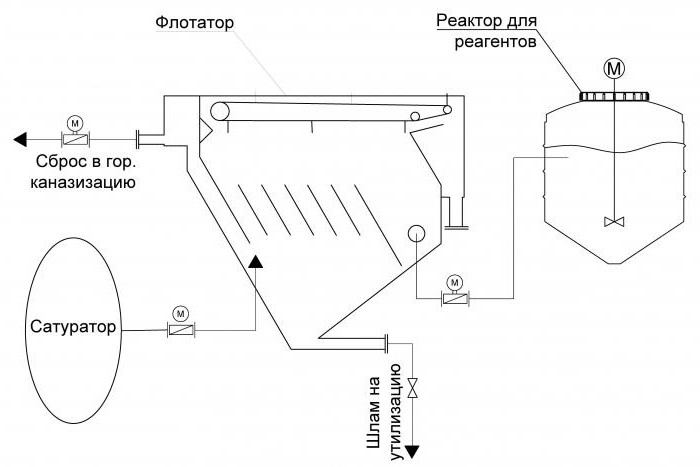
The circuit diagram is based on the flotation process. Flotation is the treatment of wastewater with air bubbles in order to extract soluble and emulsified substances. Water flows to the main processing module. There, in the pressure (or non-pressure) mode, a pre-prepared reagent is fed in the reactor. Air bubbles are also fed into the flotator using a saturation device. In a flotator for water purification , wastewater is treated with reagents and air bubbles, and most of the flocs emerge in the form of flocculent water. The floated sludge is removed from the water surface by a scraper conveyor into the sludge collector.
This slurry is very unstable to mechanical movements, therefore, it is collected from the surface of the water carefully so as not to break the foam.
Flotator device
A skimmer is an open container made of steel or plastic, equipped with a scraper mechanism for collecting sludge and having a conical shape from the bottom. A flotator implies the presence of nozzles in it for supplying a water-air mixture from a saturator, for discharging flotation sludge and emergency emptying, for supplying wastewater and discharging purified water. The installation of the flotator is usually located at the service site for convenience.
Types of Flotators
Flotators for wastewater treatment are distinguished by the way in which water is saturated with bubbles and the nature of the bubbles. The most common methods are mechanical, pressure and electroflotation. Pressure flotation implies the presence of a saturation chamber and a pump group. In addition, reagents are often used in this method. Electroflotation does not need a reagent farm and a saturator, since it is based on the dissolution of electrodes in water.
Mechanical flotation
Mechanical (or impeller) implies the presence of an agitator, which at high speed of rotation breaks air bubbles in the water. This type of water treatment is suitable for water prone to foaming and saturated with gases. In the mechanical method, reagents cannot be used, since the turbulent flows created by the mixer simply break down the flocs of contaminants. At the moment, mechanical flotation is not common, as it rarely provides a sufficient cleaning effect.
As a rule, flotators for treating wastewater from oil products belong to this treatment segment .
Pressure flotation
In this case, flotators for wastewater treatment are equipped with a saturation device and a reagent farm. A saturator is a chamber in which air is injected under atmospheric pressure. The medium prepared in a saturator is called a water-air mixture. This is the most common type of flotation and most often used. The cleaning process occurs due to the preliminary treatment of water with a reagent (coagulant or flocculant) and subsequent treatment with the pressure of the water-air mixture. Each gas bubble attaches pollution to itself, since it has a large attractive force due to the phase boundary (water-air). Preliminary preparation of water with a reagent improves cleaning, as it creates flocculi (micelles), which also have a certain attractive force. The main part of the water is discharged through the pipe of purified water for further purification or discharge. From above, a special scraper device removes flotation sludge - pollution carried away with air bubbles up in concentrated form.

The main advantage of pressure flotation is a wide range of applications. The disadvantages include the availability of additional devices (reagent farm, saturator, pumps), which take up a lot of space, and they need to be automated (for example, selection of the dose of reagents). Determining the amount of reagent plays a large role, since a small dose will lead to insufficient cleaning (not all small dissolved particles will coarsen), and a large dose can cause the bubbles to not withstand the weight of the flakes and collapse, which will also reduce the cleaning effect.
Electroflotator
This type of flotator for wastewater treatment is laconic and easy to use. The essence of the method is the electrolysis of the liquid being purified and the evolution of gases from the electrodes. An electrolysis process takes place in the flotator: hydrogen is released at the cathode, and oxygen is released at the anode. When using soluble electrodes (for example, aluminum or iron), water is additionally saturated with metal ions with a high degree of oxidation, which plays the role of reagents for creating flocs of contaminants. This process helps isolate and land even more pollutants from the water. Since the space of the flotator is not large, under such conditions there is a good adhesion of flakes and air bubbles, which provides the highest cleaning effect.

The main advantage of such a device is the absence of a reagent farm and other bulky devices, with a high degree of water purification. The disadvantages include high energy consumption and the need for hydrogen removal equipment.
Nozzle flotation
In this case, special nozzles are used to introduce air into the processed water, which is fed to the flotator, where it is divided into a two-phase mixture. The advantage of this method will be less wear of the installation parts, and therefore a longer service life.
Reagent farm
Some flotation methods use the following reagents to improve the cleaning effect:
- pH adjustment reagents are acids and alkalis that are added to water to ensure normal working conditions of the coagulant and flocculant;
- coagulants - reagents that promote flocculation and are salts of iron and aluminum;
- flocculants - reagents that create larger and more stable flakes (flocs) and are polyacrylamide compounds.
The main disadvantages of having a reagent water treatment method are the need for the presence of personnel, as well as the area that must be allocated for tanks and reactors. It is also very important to choose the right dose of reagents, which is possible only empirically.