The human spine, the structure of which meets the basic tasks of life, is the basis of the whole organism, the support of the bones of the skeleton, skull, numerous internal organs, muscle mass and fatty deposits. The load on the spinal column is significant, but the body weight is distributed evenly, part of the load falls on the ribs of the chest and pelvic bones. Thus, a conditional balance of weight is maintained.
Main departments
The main sections of the human spine : lumbar and sacral, thoracic and cervical. The upper part, cervical, consists of 7 vertebrae of different configurations and sizes. Below are 12 pieces of the chest, they are much larger than the neck and are connected to the ribs of the chest. The thoracic part passes into the lumbar region of five vertebrae, they account for the main load. Then comes the sacrum of five inactive vertebrae.
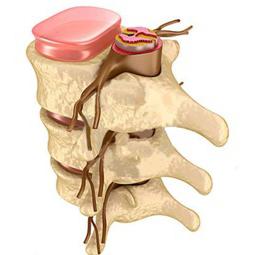
The structure of the human spine is quite complex, multi-component. It has a curved shape that allows you to maintain balance, and also gives the whole body the cushioning properties necessary for quick and sharp movements. The human spine, the structure of which we are considering, is one of the most complex organs. It begins with the first and second vertebra of the cervical spine . The first, called "atlas" consists of bone arches and articulates directly with the base of the skull. The next “epistrophy” partially enters the “atlas”. Thanks to this pair, a person’s head can turn in different directions and tilt.
Vulnerability
The remaining vertebrae are identical in shape and differ only in size. All of them are surrounded by muscles of the chest, abdomen, pelvis and back.
Human spine, structure which is due to the many functions that he has to perform, is a vulnerable part of the human body. Even being protected by the immune system from attacks of various viral infections, it is subject to mechanical effects. Even a mild, sometimes even insignificant injury caused from the outside can disrupt its functionality. Not to mention severe injuries with damage to the intervertebral joints, which inevitably result in disability.
Spinal cord
The vertebrae are rounded with several processes, through which the body of this vertebra articulates with neighboring ones. The combination principle allows them to move in a certain amplitude. The cartilage discs serve as an elastic gasket between the vertebrae, which ensures the separation of bone surfaces. Inside the spine along the entire length there passes a special hole-channel for the spinal cord - the basis of the hematopoietic system of the body. Any displacement can compress the brain or even destroy it. The human spine, whose structure is impeccable in terms of functionality, is still not immune to damage. Therefore, overloads and traumatic body movements should be avoided.