Arabian deserts - the general name of the desert complex, which is located on the peninsula of the same name. This natural zone is located on the territories of all countries that are located on the peninsula, and also captures the corners of some continental powers. Different names are given to the local deserts by local residents, and in the understanding of Western people, all this is a single zone covered with almost impassable sands that are fried every day under the scorching sun.
Geographical position
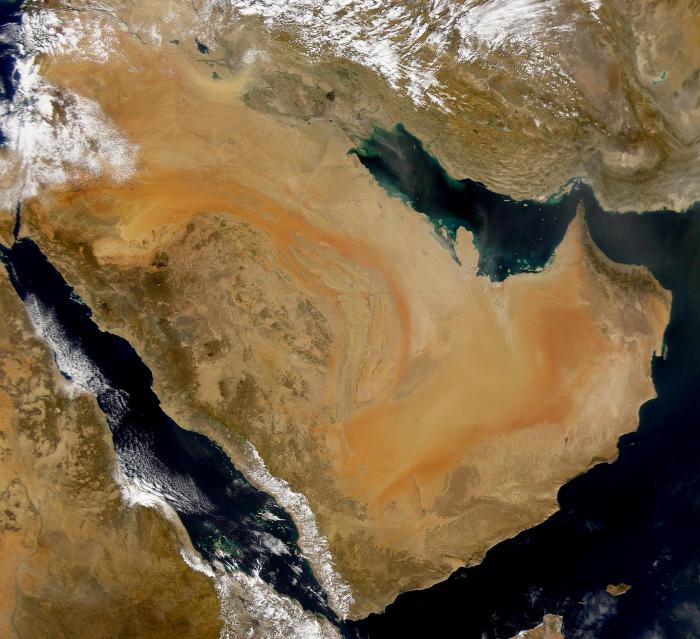
To begin with, we will consider in what part of the world and in which climatic zone the Arabian Peninsula is located. The map shows that these lands are located in the tropical zone, and in the north they begin at about 30 degrees parallel. The area of the peninsula is 3.25 million square kilometers, and at the same time its outlines are very straightforward. For this reason, there are very few convenient bays here, which does not allow many countries (with the exception of the UAE) to organize a tourism business here. From a geological point of view, the Arabian desert on the map occupies its own separate plate of the same name. However, earlier this tectonic rock was part of Africa, which is perfectly noticeable by the similar climatic and geological features of these two places.
Maritime issue
Now consider what kind of seas the bays washed the Arabian Peninsula. The map of this area is not full of names, since there are very few bays here. Basically, all adjacent seas to this part of the world are formed by the nearby continents - Eurasia and Africa, as well as islands that are nearby. So, the east of the peninsula is washed by the Persian and Omani gulfs. South bathes in the Gulf of Aden and the Arabian Sea. The western shores of Arabia are washed by the Red Sea, where the water border with Egypt passes. In the north, this desert zone passes into the main part of the mainland.
Climatic conditions
In their weather conditions, the Arabian deserts differ little from each other. The average rainfall that falls on the peninsula per year is 100 mm. It should be noted that in areas located closer to the mountains, this number grows to 500-600 mm, and up to 200 mm increases where the sands approach the sea bays. In summer, the average daily temperature here is about 45-50 degrees, at night it drops to 15 Celsius. In winter, in some regions, even in the afternoon, the thermometer does not rise above 15, and at night frosts occur. Those deserts that lie in the more southern tropics, even in January, warm up to 35 degrees.
Political situation
All countries of the Arabian Peninsula are fully or partially located in the desert zone. Among these political units are the following: Saudi Arabia, Oman, Yemen, UAE, Qatar, Bahrain and Kuwait. All of them have access to the sea, and some of them (Bahrain and Kuwait) are located on the islands. As for the division of the peninsula into deserts, which is accepted by local residents, it consists of seven units. The largest desert here is called Rub al-Khali, and it occupies the entire south of Saudi Arabia, the northern parts of Oman and Yemen, as well as the west of the UAE. It is followed by the Dehna Desert, which is located in the heart of Saudi Arabia. This natural zone is replete with oases, as it stretches along the bed of a dried river, where, according to scientists, the underground sources are still preserved. The Arabian deserts of Tijama and Big Nefood are located in the South and North of the peninsula, respectively. In the first one you can find low mountains, and also it goes to the shores of the Red Sea, which makes it not very arid. Big Nefood is a zone of red sands. The most windy point of the peninsula, where very sharp daily temperature jumps are also traced. All other deserts of the Arabian Peninsula are very small in size and do not have an individual landscape.
The largest plain of the region
Rub al-Khali, as we have already found out, is the most extensive desert-type natural zone on Arabian lands. This desert is located on a plateau that rises above sea level by 500 meters with a gradual descent to the south. Almost all other Arabian deserts are adjacent to this main one, because their flora, fauna and relief are very similar. The entire territory, which occupies more than 500,000 square meters. km, sheltered by numerous varieties of sand. In the south, they turn into salt marshes, indicating the proximity of the sea. The terrain is absolutely lifeless, there are no insects or reptiles. Rub al-Khali is a vivid representative of the eolian types of relief. There are both single dunes and dunes, which form long ridges, stretching for hundreds of meters or even kilometers. It is also noteworthy that on these lands you can find quick white sands.
Fauna of this world
In principle, the Arabian Desert on the map is located in a very favorable region for living. However, all kinds of mammals (except three) are absent because nature did not reward the region with precipitation, the necessary amount of moisture, and did not protect it from strong winds. Among those “brave men” who live in the desert, we will name a wolf, a sand fox and ferrets. In the northern regions of the peninsula, where there are many herbaceous plants, one can meet ungulates and rodents. In the sand zone there are numerous reptiles - lizards and snakes - all poisonous. At night, tarantulas and tarantulas, as well as other insects that live in the sand, are activated. Numerous birds soar above the dunes. These are larks, sparrows, grouse, eagles and goats, as well as several other species of birds.