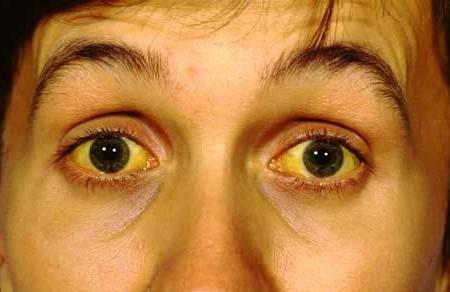
Jaundice is not an independent ailment, it is only a symptom of some pathologies. In many cases, it can be physiological, that is, unrelated to any disease (in newborns). The cause of this condition is an increase in bilirubin in the blood, which gives the icteric color to the skin, mucous membranes and sclera.
Jaundice: types
This condition is inextricably linked with the content of bilirubin in the blood. However, the reasons for its increase may be different. In some cases, the establishment of the cause allows one to suspect pathology in the body, which requires immediate treatment. Depending on the type of bilirubin metabolism disorder, several types of jaundice can be identified:
- Conjugation jaundice, which is a consequence of impaired bilirubin binding. It arises in newborns.
- Parenchymal jaundice, developing with a number of liver pathologies. The defeat of the parenchyma of this organ (the death of functional cells - hepatocytes) makes it impossible to capture bilirubin and its further exchange.
- Obstructive jaundice, which appears when there is a violation of the outflow of bile. It is associated with diseases that contribute to the closure or narrowing of the lumen of the bile duct. This phenomenon occurs with gallstone disease or the formation of a tumor.
- Hemolytic jaundice is a pathology associated with the breakdown of red blood cells. Bilirubin is a pigment that occurs during the breakdown of hemoglobin, therefore, increased lysis of red blood cells leads to an increase in its level.
- Nuclear jaundice is an independent and most dangerous species. It occurs if the fetus was prone to hypoxia during development or asphyxiation during childbirth. Also, the cause can be infections in a pregnant woman. The danger lies in the fact that the pigment accumulates in the nerve cells of the brain, which leads to various neurological disorders and can even cause death.
Conjugation jaundice in newborns
Jaundice that occurs in newborns is physiological, as it is not associated with a pathological process. It develops, as a rule, 3-5 days after birth. Normally, red blood cells are subject to constant renewal, which is accompanied by hemolysis - their destruction. In adults, the liver is fully formed, so bilirubin, which is released during the breakdown of these cells, manages to bind and does not accumulate in the blood.
The clinical picture in infants is associated with intensive renewal of red blood cells and relative liver failure. This organ is not yet fully formed, especially often such jaundice occurs in premature babies. Bilirubin begins to accumulate in the blood, and then accumulates in the skin and mucous membranes, giving them a characteristic color. The peak falls on the third or fifth day. Then these symptoms disappear, as the bilirubin metabolism gradually normalizes.
What is this condition?
Conjugation jaundice (ICD-10) is not allocated separately in the international classification. It is encoded P59.0 as neonatal jaundice, which is a consequence of premature delivery, and is associated with hyperbilirubinemia. This process is described in more detail above.
Conjugation form of the disease occurs more often in children. This is transient jaundice in newborns, as well as a condition that develops in premature infants and children undergoing asphyxiation. The causes of the problem are often endocrine pathology and heredity (for example, Lucy-Driscope and Gilbert syndromes). The same group also includes jaundice.
Bilirubin - what is it?
This name was given to the pigment, which is the decay product of hemoglobin. At a certain concentration, it leads to staining of the skin and mucous membranes. The level of bilirubin is the most important diagnostic criterion, since its increase allows you to identify any pathological process and begin treatment. The amount of pigment reflects the condition of the liver and biliary tract.
In the body, bilirubin occurs in two forms - direct and indirect. The first is the product of the transformation of the second. Indirect bilirubin is toxic and absorbed by fats. It is not excreted from the body. In metabolic disorders, this form can accumulate, having a toxic effect on the body. Normally, it turns into direct non-toxic bilirubin. Conjugation jaundice occurs due to a violation of its metabolism.
Bilirubin exchange
The source of this pigment is hemoglobin, the main component of red blood cells. With the breakdown of red blood cells, hemoglobin is released and is cleaved. This process is carried out by macrophages in specialized organs (bone marrow, liver and spleen). As a result of splitting, heme and globin are formed. The first is transformed into biliverdin - the precursor of indirect bilirubin. Its formation from biliverdin is associated with the activity of special enzymes, among which are cytochrome P-450, hemoxygenase. Next, indirect bilirubin is sent to the liver cells, where it binds to glucuronic acid. Thus, direct bilirubin is formed, which accumulates in the gallbladder, and then undergoes excretion into the duodenum. Intestinal microflora contributes to its restoration to urobilinogen. Part of it is susceptible to absorption, the remains are converted into stercobilinogen and excreted in the feces, giving it a characteristic color.
Laboratory tests may show that bilirubin is elevated. What means? An increase in its level may be associated with any disease, therefore, an early diagnostic examination is required. A physiological increase in bilirubin levels is observed in newborns.
Clinical picture
Despite the fact that an increase in bilirubin is characteristic of newborns, clinical manifestations are not fixed in all. Symptom of this condition is the appearance of icteric color. It is detected not only on the skin, but also on the mucous membranes. Conjugation physiological jaundice passes without a trace, however, if this does not occur, pathology should be suspected.
Diagnostics
Jaundice can be not only a physiological state, but also a symptom of a disease. If a child has a specific coloration of the skin and mucous membranes, he needs constant monitoring by a pediatrician. Also in such cases, control of the bilirubin level is necessary. As a rule, in the first days of life, its amount reaches 60 μmol / l, but no more. Further, this level rises (by 3-7 days).
Usually, an increase in bilirubin is safe and does not have a toxic effect on the baby's body, but this level should not exceed the so-called boundary value - 205 μmol / l. Increased bilirubin - what does such a change mean? Jaundice is pathological and requires urgent treatment. If this indicator is within normal limits, but jaundice does not pass for a long time, it is considered conjugation, that is, the cause of the immaturity of the liver enzyme systems.
Conjugation Jaundice Treatment
After the examination, it is determined whether jaundice is physiological or pathological. The first does not require any treatment and ends independently and without a trace. Prolonged jaundice (conjugation) also passes by itself when the enzyme systems of the liver finally mature. However, if the amount of bilirubin exceeds a critical level, pathology should be detected. It can be viral hepatitis, obstruction of the bile duct or hemolytic jaundice.
Viral hepatitis
Such a pathology can be transmitted to the child from an infected mother. As a result, the baby is born with hepatitis of a viral nature. The action of the virus in the early stages of fetal development can additionally cause physical abnormalities. A feature of the disease, in contrast to hepatitis in adults, is the most severe course. Pathology can manifest itself even before the onset of jaundice. Often there is an increase in temperature, a deterioration in appetite and small catarrhal phenomena. In some cases, the preicteric period in infants is asymptomatic.
Hepatitis can be suspected by detecting discoloration of urine and feces. A clinical blood test is characterized by a decrease in white blood cell count and erythrocyte sedimentation rate. Monocytes are slightly increased. With the icteric form, a significant increase in bilirubin and thymol test is noted. For early diagnosis of the disease, a study of the activity of liver enzymes is carried out. The severity of the process is indicated by a sharp decrease in prothrombin and an increase in ammonia.
Treatment of children is carried out, as a rule, in a hospital. Therapy combines antiviral drugs, hepatoprotectors, vitamins, as well as choleretic drugs. Detoxification therapy is recommended . Among the non-drug methods that complement pharmacotherapy, bed rest and rest are necessary.
Hemolytic jaundice
This pathology associated with erythrocyte hemolysis is very dangerous. The reason is the mismatch of the Rhesus factor of the mother and child, that is, the Rhesus conflict. Pathology often leads to death - mortality is 60-80%. In addition, the presence of a Rhesus conflict can lead to spontaneous miscarriage.
Prevention
Prevention of jaundice helps to maintain pregnancy and breastfeeding, regular pediatric examinations are also required. If premature jaundice still develops, regular monitoring of bilirubin levels in the blood is necessary.
Patients with jaundice are characterized by a characteristic color of the skin and mucous membranes. This symptom may indicate the presence of a disease or reflect physiological changes in the body (transient jaundice of the newborn).
Conclusion
If jaundice is detected, an immediate determination of the bilirubin level and further diagnosis are made. Conjugation jaundice in newborns lasts longer than transient, but is also safe. The specialist should reassure parents and schedule an examination. As a rule, no complications are observed.