Sinusitis often develops as a complication of a cold, a viral or bacterial infection. Conservative therapy is usually used to treat the disease. Antibiotics for sinusitis in adults are shown only if the pathology is of bacterial origin. This can be determined by characteristic symptoms.
Description of the disease
Sinusitis is a pathological process in which the mucous membrane of the paranasal (paranasal) sinuses becomes inflamed. The latter perform a number of important functions - they warm the air inhaled through the nose, participate in the pronunciation of sounds, and reduce the mass of cranial bones. Maxillary (maxillary), frontal (frontal) and ethmoid - three paired sinuses. The sphenoid, located in the body of the main bone of the skull, is unpaired. Depending on the localization of the inflammatory process, the following forms of the disease are distinguished: frontitis, sinusitis, sphenoiditis, ethmoiditis.
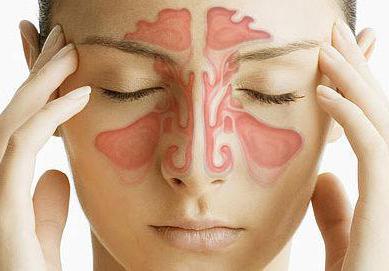
Both pathogenic microorganisms (bacteria, fungi, viruses) and allergens can provoke the development of sinusitis. Most often, the ailment develops against a background of a viral infection, to which, with improper treatment, a bacterial infection also joins. If the outflow of mucous secretion from the sinuses is impaired, conditions are created for the multiplication of pathogens. Antibiotics will help to cope with their activity. With sinusitis in adults (and in children too), it is important to start treatment in a timely manner.
Symptoms
The intensity of the symptoms of sinusitis depends on the form in which the inflammation proceeds. An acute inflammatory process is characterized by pressing pain in the sinus area. Unpleasant sensations are concentrated in the forehead or nose, under the eyes or on both sides of the nose, in the upper jaw or teeth. The manifestation of the syndrome is usually enhanced by tilting the head.
Another characteristic sign is discharge from the nose. If they have a yellow-green tint, they talk about the development of a bacterial infection. In this case, you will need to take antibiotics.
With sinusitis and sinusitis in adults, the sense of smell and breathing through the nose significantly worsen, severe headaches appear. There are signs of intoxication - the temperature rises, weakness and malaise appear, and the ability to work is reduced. Having found such symptoms, you should immediately consult a specialist.
Adult sinusitis treatment
Antibiotic drugs are almost always used to treat the inflammatory process in the sinuses. They are usually prescribed in the acute phase of the pathology, when the patient's body temperature rises and a purulent secretion is released from the nose. This condition can quickly go into the chronic stage, which is practically not amenable to drug exposure and worsens with every cold. To avoid this, it is important to start antibiotic therapy.
Treatment of sinusitis is aimed at the complete destruction of the pathogen pathology, relief of symptoms and the prevention of complications. In addition to antibiotics, the composition of the therapy should include drugs with anesthetic and antipyretic effect, vasoconstrictor drops (sprays) for the nose.
Should I use antibiotics?
Only a doctor can prescribe the “right” antibiotics to treat adult sinusitis. Previously, a laboratory study should be performed to determine the type of pathogen of the inflammatory process. After diagnosis, the optimal means are selected to suppress the vital activity of microbes.
The duration of treatment will depend on the form of pathology. In acute sinusitis, treatment should last at least 10 days. The chronic form requires a longer drug exposure.
To combat various types of sinusitis, several types of antibiotics are used:
- Penicillins - antibacterial agents of this category have selective therapeutic activity and do not affect the whole organism.
- Macrolides are considered the safest of all antibacterial agents and have a wide spectrum of action.
- Cephalosporins - according to the mechanism and spectrum of action are similar to penicillins. With sinusitis, first and second generation drugs are used.
- Tetracyclines - are similar to macrolides, but often cause side effects and have a number of contraindications.
- Aminoglycosides - have a wide range of therapeutic effects and efficacy, but at the same time have high toxicity.
Prescribe antibiotics for sinusitis in adults, depending on the stage and form of the disease. Macrolides and cephalosporins will help to cope with a mild form of the inflammatory process. If the disease proceeds with complications and threatens to go into a chronic form, doctors recommend taking protected penicillins. In some cases, taking local antibacterial drugs is acceptable.
Effective antibiotics for sinusitis in adults
The names of some drugs have long been known in medical practice. For example, Amoxicillin refers to protected penicillins and is often used to treat diseases of the ENT organs of bacterial etiology. A significant advantage of the drug is its safety and the minimum number of side effects.
Another drug from the penicillin group - Amoxiclav - also belongs to the category of protected. The drug is resistant to the beta-lactamase enzyme, which is found in many bacteria and significantly reduces the therapeutic effect of antibiotics.
With sinusitis, the following drugs can be prescribed:
- Cephalexin.
- "Azithromycin."
- "Augmentin."
- "Cefazolin."
- "Flemoklav Solyutab".
- "Sumamed."
- Ceftriaxone.
- Clarithromycin.
Many drugs can eliminate the symptoms of inflammation in the sinuses. To understand what antibiotics to take with sinusitis in adults, you need to see a doctor. The dosage of the medicine and the treatment regimen are determined individually.
An effective local drug is Bioparox. Spray for the nasal cavity has a bacteriostatic effect and is often used to treat sinusitis. Another remedy from this group is Polydex. The medicine contains two antibacterial substances at once. Local antibiotics are used for purulent sinusitis in adults, not only to eliminate pathogens, but also to facilitate nasal breathing, relieve swelling of the mucosa.
Amoxiclav for sinusitis
Treatment for bacterial sinusitis should be comprehensive. The basis of therapy is usually antibacterial drugs. The advantage is given to the safest and most effective means. Such drugs include Amoxiclav, a synthetic broad-spectrum penicillin. The main components are amoxicillin and clavulanic acid. The medicine is released in the form of a lyophilisate for the preparation of an injection solution, suspension and tablets.
The drug is able to suppress the development of gram-positive, gram-negative, anaerobic and aerobic bacteria that cause sinusitis. At the same time, Amoxiclav does not have such a devastating effect on the intestinal microflora as other antibacterial drugs. It is worth considering that taking penicillins (antibiotics) for a long time with sinusitis in adults is highly not recommended due to the fact that bacteria get used to the drug and lose their sensitivity to it.
Dosage
Most often, for the treatment of sinusitis and other sinusitis, patients are prescribed Amoxiclav in the form of tablets. The manufacturer produces them in a dosage of 250, 500 and 850 mg. Dispersed tablets are also available (500 and 850 mg of amoxicillin). Clavulanic acid contains 125 mg in each type of tablet.
When treating with a medicine, the maximum daily dose of each substance should be taken into account. Amoxicillin in adults can be taken no more than 6 g, and clavulanic acid - up to 600 mg. Depending on the severity of sinusitis, a patient may be prescribed 250 or 500 mg of the drug three times a day. Another acceptable treatment regimen is 825 mg of amoxicillin every 12 hours. The duration of treatment is 5-14 days.
The drug "Cephalexin"
Sinusitis of mild to moderate severity respond well to antibiotics from the group of cephalosporins of the first and second generation. One of the effective remedies in this category is Cephalexin. The drug is active against many pathogenic microorganisms: Klebsiel, Escherichia, streptococcus, Proteus. The antibiotic is released in the form of tablets and granules for the preparation of a suspension.
The medicine is strong enough and therefore often causes side effects. In case of urticaria, abdominal pain, nausea, dry mouth, dizziness, headache, seizures, it is necessary to refuse further treatment with Cephalexin and choose a more gentle medicine.
Is Azithromycin suitable?
Macrolides have a fairly wide spectrum of antimicrobial activity and are well tolerated by the body. These antibiotics are often used for otitis media and sinusitis in adults and children. Macrolides are active against pyogenic staphylococci and hemophilic bacillus. One of the drugs in this category is Azithromycin. It can be used to treat sinusitis, frontal sinusitis and other inflammatory processes in the sinuses.
The tool has low toxicity and bacteriostatic effect. Take tablets or suspension only once a day before meals or 2 hours after a meal. With sinusitis, the daily dose of Azithromycin is 500 mg. The duration of treatment is usually 3 days, but in some cases, therapy may be extended.
Side effects and contraindications
Antibiotics for sinusitis should be taken with extreme caution. In adult patients, there may be some contraindications to treatment, which you should definitely familiarize yourself with. "Azithromycin", according to the instructions, is not prescribed for hypersensitivity to this category of antibiotics, liver and kidney diseases.
Side effects from the digestive tract (dyspepsia, nausea, diarrhea) and the immune system (urticaria, rash on the body) are extremely rare.