The sacroiliac joint is a fairly strong connection. The joint is paired. It connects the somewhat prominent iliac surface and the lateral sacrum. In accordance with the classification, it is referred to as tight joints. Next, consider the sacroiliac joint in more detail.
Anatomy
The sacroiliac joint is a ligamentous apparatus, the elements of which are arranged in the form of short bundles. These ligaments are considered the most durable in the human body. They act as axes of rotation for the probable movements that the sacroiliac joint carries out. An additional strengthening in the joint are ligaments: ventral (anterior), dorsal (posterior). Another - additional, iliac-lumbar - runs from the transverse process of the fifth vertebra of the lumbar to the iliac crest. The joint capsule is attached along the edge of the surfaces. It is tight enough enough. The joint has a slit-like cavity. The auricular flat surfaces of the sacrum and ilium are covered with fibrous cartilage. Blood supply is carried out through the branches of the lumbar, external sacral and iliac-lumbar arteries. Outflow occurs through the veins of the same name. Lymphatic drainage is carried out in deep vessels. They fit the iliac and lumbar nodes. The innervation of the joint capsule is due to the branches of the sacral and lumbar plexus.
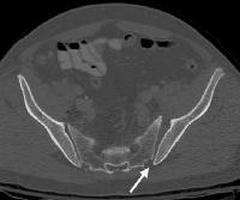
Structural features
Both the shape and size of the surfaces of the joints in different people can be completely different. In children, for example, they are smoother, and in adults with bends. The sacroiliac joint in structure is a real joint. It contains the synovial membrane and a small amount of fluid. Fibrous fibrous cartilage is lined on articulated surfaces. Moreover, on the sacrum, it has a greater thickness. In depth there is a layer of hyaline cartilage. In some cases, the articular surface may be covered with connective tissue. This area (gap) with all the elements is found already in childhood and is present in any adult. This allows us to conclude that, as in other areas, inflammation of the sacroiliac joints, trauma and other injuries can occur. Due to the peculiar structure in the joint, movements are performed in very limited volumes. Compounds of this type are intended not so much for mobility as for stability. In addition to anatomical interactions, the joint is given stability by durable ligaments that strengthen the capsules.
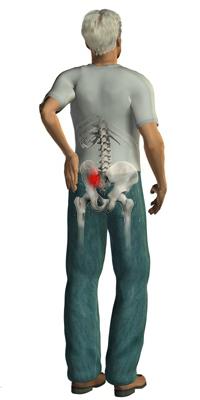
Arthrosis of the sacroiliac joint
This is a chronic disease characterized by the presence of dystrophic type processes. They occur due to mobility disorders and prolonged inflammation in the joint cavity. This pathology can pass on its own, without any additional impact. However, due to hypothermia or under the influence of excessive loads, the sacroiliac joint may again begin to disturb. Treatment includes conservative methods.
Clinical picture
The signs that accompany the pathology are almost identical to the manifestations of other types of arthrosis. The main symptoms should, in particular, include dull, aching, and sometimes severe severe pain localized in the lower back. A characteristic feature is stiffness in movements.
Diagnostics
First of all, the patient is examined. The nature of biochemical changes is also evaluated. In particular, sensitivity is determined during palpation, during movement, muscle tone and so on. Additionally, the specialist may prescribe:
- Laboratory blood test. Typically, with sacroiliac arthrosis, a high level of ESR is detected.
- For women, a gynecological examination, as a number of pathologies in the organs in the pelvis can be accompanied by pain that spreads to the sacral region.
- Roentgenography. This research method will confirm or exclude traumatic injuries in the pelvic bones and spine.
- Computed tomography or MRI of the sacroiliac joints. These methods make it possible to exclude the presence of tumor formations on the vertebral bodies or pelvic bones.
It should be noted that palpation and examination are available only in the posterior articular regions and only in case of mild severity of subcutaneous tissue. If there is pain in the process of feeling, the specialist can conclude that there is damage or inflammation. If a deformation complicated by pain is detected during palpation, a subluxation or dislocation of the joint is assumed. Some patients have a swaying gait. This manifestation, accompanied by pain in the pubic and sacroiliac joints, indicates pelvic post-traumatic instability. The most informative research method by many experts is considered to be radiography. Joint surfaces are projected in the form of oval elongated shadows. At the edges of their visible strips of enlightenment in the form of arcs corresponding to the cracks of the joint.
Arthrosis of the sacroiliac joint: treatment
As mentioned above, therapeutic measures include conservative methods. First of all, it is necessary to reduce physical activity. Doctors recommend not to be upright or sitting for a long time. To unload the joint, a special bandage should be worn (especially for pregnant women). Given the stage of pathology, the severity of the course, and clinical manifestations, the complex effect may include measures such as:
- Taking medications. The list of recommended medications includes analgesics, vitamins, hormonal and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
- Performing blockades using drugs such as Lidocaine, Hydrocortisone, and others.
- Physiotherapy.
- Manual therapy. This technique is aimed at improving blood circulation and restoring lost joint functions.
- UHF, infrared radiation and other physiotherapeutic procedures.
- Acupuncture.
Prevention
To prevent the development of arthrosis in the sacroiliac joint, it is necessary to adhere to an active lifestyle. An important condition is the exclusion of stressful situations, emotional overstrain. Of particular importance is the diet. You should not overeat, because with excess body weight an additional load is created on the spinal column.