Scleroderma is very common among autoimmune diseases. What is it and how to treat such an ailment? Pathology affects the skin, connective tissue, musculoskeletal system, and in some cases internal organs. The etiology of the disease is associated with impaired immunity. Protective cells that normally fight microbes begin to destroy their own tissues. There is a severe damage to the skin and connective tissue. Often the patient gets disability with scleroderma. ICD-10 refers this pathology to systemic sclerosis, the disease code is M34.
What is scleroderma?
Among autoimmune processes, scleroderma is the second most common after lupus erythematosus. The disease is chronic and progressive. Skin and connective tissue undergo scarring, which leads to a violation of tissue metabolism and blood circulation in small vessels. Collagen is formed in excess, scleroses and hardens. With the systemic form of the disease, serious damage to the internal organs occurs.
Most often, women suffer from scleroderma. The disease is usually diagnosed at middle age, but skin lesions are often detected in children or adolescents. There are 2 forms of scleroderma: focal and systemic. In the first case, the ailment proceeds more easily.
Focal scleroderma
With focal scleroderma, individual areas of the skin are affected. Sometimes changes occur in the bones and muscles. Internal organs are not affected by the pathological process. There is no vasospasm, which is accompanied by numbness of the fingers (Raynaud's syndrome). The disease is often detected in childhood. More often this ailment affects girls. Doctors give a relatively good prognosis for this type of scleroderma. The focal form of the disease is divided into several varieties:
- Ring-shaped. Plaque-like spots appear on the skin. They have a brown color.
- Linear White stripes of scar tissue appear on the face. They have the appearance of a line.
- Plaque. It manifests itself in the form of redness of the skin due to the expansion of small blood vessels, as well as seals on the body, arms and legs. In the affected foci, the secretion of the sebaceous glands ceases, the skin pattern disappears and the hair falls out.
- Idiopathic atrophoderma Pasini-Pierini. This rare form of the disease is observed in young women. Purple spots form on the back, rashes on the face are not typical for this type of scleroderma. Over time, education on the body progresses.
- Hemiatrophy of Parry-Romberg face. The disease begins in childhood or adolescence. On one half of the face, yellow or bluish spots form, which creates a strong cosmetic defect. The pathological process can affect not only the skin, but also the musculoskeletal tissue.
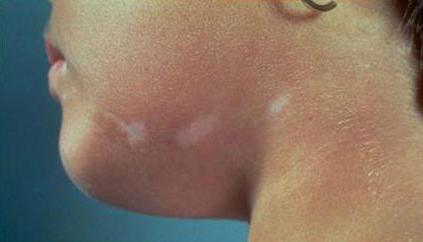
- Scleroderma Bushke. Puffiness forms on the skin of the face, neck and shoulders. They are dense and painful on palpation.
- Teardrop-shaped ("white spot disease"). White spots appear on the face of a child or adult. The rash is convex, with a pearly shade. The size of the formations is from 0.5 to 1.5 cm. Often this type of disease is combined with a plaque form of scleroderma. Photo spots can be seen in the photo.
Systemic scleroderma
Systemic scleroderma is characterized by damage not only to the skin, but also to internal organs. Raynaud's syndrome is expressed. This form of the disease is divided into the following types:
- Diffuse scleroderma. First, the skin of the whole body is affected, and then the pathological process passes to the internal organs.
- Scleroderma. There are no skin manifestations, painful changes occur only inside the body.
- Juvenile scleroderma. The disease begins in children and adolescents, pathology affects the skin, bones and internal organs.
- Eosinophilic fasciitis (Schulman syndrome). In the place of the passage of veins, an “orange peel” forms on the skin, as with cellulite. This phenomenon is accompanied by severe swelling of the limbs.
- Limited scleroderma. Small lesions are formed on the skin of the legs and arms. With timely treatment, they disappear. In the absence of therapy, the pathology goes to the internal organs.
- Cross shape. Scleroderma is combined with other autoimmune processes - systemic lupus erythematosus or rheumatoid arthritis.
Causes of the disease
The causes of this disease are not fully understood. It is assumed that the development of pathology is influenced by genetic factors. There is a hereditary predisposition to autoimmune diseases. This does not mean that the disease will manifest itself immediately after birth, pathology can develop at any age.
In people with a tendency to scleroderma, the following factors can provoke the onset of the disease:
- previous infections;
- hormonal disorders;
- hypothermia (especially frostbite of hands and feet);
- molecular mimicry of microorganisms, due to which there is an increased activity of lymphocytes;
- hormonal disorders;
- intoxication with drugs or chemicals;
- poor ecology of the place of residence;
- work related to harmful effects (for example, in chemical production).
The environment and human health are closely interlinked. Very often, the development of scleroderma provokes living in a region with a large number of industrial enterprises. this is especially true of the juvenile form of the disease, which manifests itself at an early age. Silicon dioxide, white spirit, welding gases, ketones, solvents, trichlorethylene can have a harmful effect. Not every person whose work is related to these substances will necessarily develop a disease. But with a hereditary predisposition, the risk of scleroderma due to constant contact with chemical compounds is very high.
Skin symptoms
Symptoms of the disease depend on its variety. Skin changes go through several stages of development. First, a dense swelling appears, usually it is located on the hands and face. Then the skin thickens, and in the later stages of the pathology atrophic processes are observed.
The following external signs of the disease can be distinguished:
- Raynaud's Syndrome. Numbness, burning and tingling of fingers and toes. Such phenomena are observed with even slight freezing. The skin of the limbs becomes pale and cyanotic. This symptom is associated with spasm of the vessels of the arms and legs.
- The skin on the fingers becomes rough. Scar tissue appears. Lesions of the skin of the hands are accompanied by thickening and deformation of the fingers. Because of this, the disease is often mistaken for rheumatoid arthritis.
- Around the mouth can be seen purses.
- Skin pigmentation.
- Feeling of constant chilliness, the patient often freezes quickly.
- With a drop-shaped form, white spots on the face of a child or adult become the first sign of a disease.
- Facial expression disappears. The face becomes smooth and masky, the nasolabial fold is almost invisible.
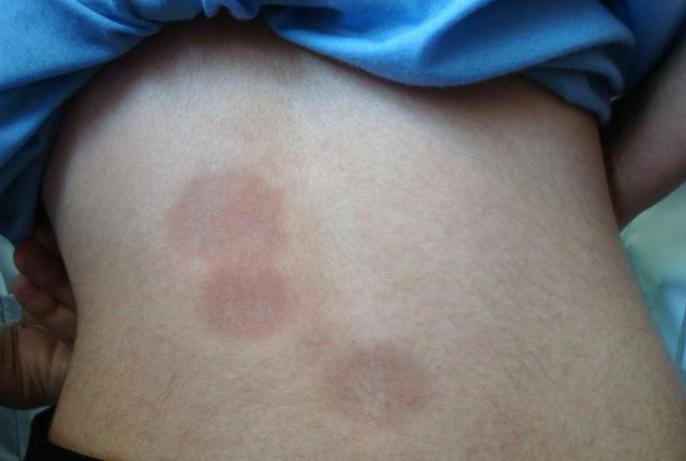
In addition, a person loses weight, gets tired quickly and complains of a headache. Rashes appear on the body. Their color can vary from brown to red. The nature of the rash depends on the form of scleroderma. Photo spots can be seen in the photo above.
Manifestations of the internal organs
The systemic form of scleroderma affects the entire body. The patient may complain of negative manifestations from different systems. Most often, changes are observed in the kidneys, lungs, and heart. Often there are changes in the digestive organs, which is manifested by the following symptoms:
- heartburn;
- flatulence;
- diarrhea;
- ulceration on the walls of the stomach;
- difficulty swallowing;
- peristalsis disorders;
- deterioration in food processing.
If the pathological process has affected the kidneys, then the following symptoms may be observed:
- rare urination;
- protein and red blood cells in the analysis of urine;
- arterial hypertension;
- renal failure;
- disorders of consciousness.
Damage to the heart can be manifested by the following symptoms:
- dysfunction of the left ventricle;
- myocardial compaction;
- inflammation of the serous and muscle membranes of the heart;
- dyspnea;
- tachycardia;
- heartache;
- heart failure (rare).
If the lungs are involved in the pathological process, then the following manifestations are observed:
- cough without sputum;
- shortness of breath during physical exertion;
- inflammation of the pleura and lungs with the formation of scars and seals;
- increased risk of developing lung cancer.
In addition, peripheral nerve damage may occur. There are pains in the limbs and on the face along the trigeminal nerve. The patient complains of numbness or a violation of the sensitivity of the arms and legs. In severe cases, paresis (paralysis) is possible. On the part of the endocrine glands, a decrease in thyroid function (hypothyroidism) is possible.
Disease prognosis
Patients are often confused upon hearing a diagnosis of scleroderma. What is it and how to treat this ailment? This question worries patients. We can say that today this disease is not completely cured. It is impossible to stop the increased formation of collagen. Modern therapy can only slow down the development of pathology.
The prognosis for the focal form of scleroderma is more favorable than for the systemic one. The average survival rate for this disease is about 68% over 5 years. The effectiveness of treatment depends on the following factors:
- Gender of the patient. The disease in men has a more poor prognosis.
- The age of the patient. Scleroderma is worse for therapy in people over 45 years of age.
- The degree of damage to internal organs. If in the first 3 years of the disease the lungs and kidneys were involved in the pathological process, then the prognosis of the course of the disease worsens.
- A decrease in hemoglobin in the blood, an increase in ESR and the presence of protein in the urine indicates a severe form of the disease.
- An unfavorable factor is the early onset of the disease before the age of 20 years.
Is scleroderma dangerous? Without treatment that inhibits the development of the disease, this pathology can lead to very serious consequences. Autoimmune disease can cause life-threatening complications, such as kidney and heart failure, pulmonary hypertension, finger necrosis due to circulatory disorders.
Diagnosis of the disease
Which specialist should I contact if the patient has noticed manifestations similar to symptoms of scleroderma? A rheumatologist treats diseases of the connective tissue of autoimmune origin. After collecting an anamnesis, external examination of the patient, listening to the heart and lungs using a phonendoscope, the following examinations will be prescribed:
- clinical analysis of blood and urine;
- blood test for antibodies to scleroderma;
- capillaroscopy;
- biopsy of affected tissue;
- X-ray of limbs and internal organs;
- echocardiography;
- Respiratory function tests
- CT scan to detect tissue changes.
A rheumatologist will give the patient answers to all questions about scleroderma. What is it and how to treat the disease, it will become known after the diagnosis, when the form and nature of the pathology is revealed. You may need additional consultation of specialists: urologist, cardiologist, pulmonologist, dermatologist.
Scleroderma treatment
In the treatment of scleroderma, drugs are used to reduce collagen production, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, as well as drugs to suppress the immune system.
Of the antifibrotic agents, Kuprenil is most often prescribed. The drug helps to remove copper from the body. The use of the drug leads to a decrease in the activity of scleroderma. Copper reduces the production of an enzyme that processes collagen. Therefore, the removal of this substance from the body improves the condition of patients and slows down the pathological process in the connective tissue.
Another popular antifibrotic agent is Lidase. This is an enzyme that is obtained from the seminal glands of cattle. The drug has the ability to break down hyaluronic acid, which is involved in the formation of collagen. The drug "Longidase" has the same properties.
Often, antibiotics of the penicillin group are prescribed with Lidase. The exact mechanism of action of these drugs in scleroderma is unknown. However, their use leads to the necessary therapeutic effect. Penicillins are thought to have antifibrotic and anti-inflammatory effects.
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed for low disease activity and complaints of joint pain. These are the drugs Ortofen, Indomethacin, Nise, Ibuprofen, Diclofenac, Piroxicam. In addition to tablets, local anesthetic ointments can be prescribed for application to the affected areas.
To suppress immunity, hormonal drugs and cytostatics are used. Glucocorticoids are usually prescribed for high disease activity. Their dosage is carefully calculated, since these drugs can cause side effects, such as Itsenko-Cushing's syndrome (obesity, red moon-shaped face, increased blood pressure, disruption of the gonads). Hormonal drugs include:
Cytostatic drugs reduce the production of immune cells: T and B lymphocytes, which are autoaggressive. These medicines include:
- "Azathioprine."
- "Plaquenil."
- "Methotrexate".
- Cyclophosphamide.
- Cyclosporin.
In scleroderma of a high degree of activity, pulse therapy is prescribed: intravenous drip of large doses of cytostatics and hormones. Symptomatic treatment of scleroderma is carried out. Prescribe drugs to improve blood microcirculation "Dipyridamole", "Pentoxifylline", "Iloprost", "Alprostadil", "Warfarin". Often prescribed vasodilator drugs: Amlodipine, Verapamil, Nifedipine.
In case of damage to the digestive tract, antibiotics are indicated: Erythromycin, Amoxicillin, Metronidazole and Prokinetics Metoclopramide. As additional methods of treatment, the doctor can prescribe hemosorption, plasmapheresis, physiotherapy, exercise therapy exercises.
It is important for all patients with scleroderma to remember that in this disease, exposure to direct sunlight is very harmful. It is better to refuse tanning and visiting a solarium. Excessive exposure to ultraviolet radiation can nullify the effect of therapy.
Alternative medicine
Often patients are interested in: is it possible to treat scleroderma with folk remedies? Of course, it is impossible to completely recover from such a complex disease with only home remedies. The use of folk remedies is permissible only after consultation with a doctor, as an addition to the main therapy. The following recipes are used:
- Aloe juice is applied in the form of compresses to the lesion sites. Ichthyol ointment can be used.
- Baked onions are crushed and mixed with one part of honey and two parts of kefir. This mixture is used for compresses.
- Make homemade ointment from melted pork fat and dry herbs of wormwood or celandine.
- To restore the connective tissue used inside decoction of horsetail, medunica, knotweed.
- With heart complications, a decoction of adonis and cyanosis will help, and with kidney damage, compositions with bearberry and a leaf of lingonberry are useful.
New developments in the treatment of scleroderma
Medical scientists have long been studying the nature of scleroderma: what it is and how to treat this complex and serious illness. After all, traditional methods of therapy do not lead to the complete elimination of the disease. The search for new methods of treatment is underway, drugs are being developed that can more effectively influence pathology.
A new genetically engineered drug, Tocilizumab (Actemra), has been created. This drug is an antibody to interleukin-6 receptors. It is this anti-inflammatory cytokine that is the provoking factor in the occurrence of scleroderma and rheumatoid arthritis. Clinical studies have shown the effectiveness of the drug.
A new complex method of therapy with the enzyme "Lidase" in combination with the vitamins Pantogam, Dexpanthenol and Picamilon has been proposed. This method is effective in the focal form of the disease. Biologically active substances help improve metabolism in the affected tissues.
Currently, studies are being conducted on drugs that could block the signaling pathway for scleroderma. Inhibitor molecules are studied that can affect the pathogenesis of the disease. This could help prevent fibrosis - the proliferation of connective tissue. New in the treatment of scleroderma is also associated with the use of stem cells. They are able to replace the diseased cells. This leads to a decrease in fibrosis and the formation of new blood vessels in place of those that were damaged by pathology.
Disease prevention
Due to the uncertainty of the exact causes of the disease, specific prophylaxis of scleroderma has not been developed. Compliance with the following rules will help people with a genetic tendency to autoimmune pathologies to reduce the likelihood of a disease:
- It is necessary to timely treat infectious diseases.
- Avoid hypothermia and exposure to harmful chemical factors.
- Lead an active lifestyle to maintain the tone of the musculoskeletal system and connective tissue.
Patients with scleroderma should be registered at the dispensary and regularly visit a rheumatologist. It is necessary to take prescribed medications continuously, in many cases, lifelong maintenance therapy is required.