The most common form of spinal disease is osteochondrosis. This disease is relatively easy to treat if you notice it in the early stages. In the future, severe (sometimes even irreversible consequences) arise. The most common causes are adverse heredity and age-related changes in bone structure. Pathology can be provoked by infections, injuries, curvature of the spine, carrying weights and just a long stay in an uncomfortable position.
Symptoms of osteochondrosis
In medical practice, thoracic, sacrococcygeal, cervical and lumbar osteochondrosis are distinguished. Typical signs of the latter are frequent dizziness, paresis, tension in the muscles of the neck and upper limbs, cervical lumbago. Lumbago is an intense pain that is felt during head movements. A person cannot move his neck normally and occupies the least painful position. Overvoltage, prolonged stay in an uncomfortable position can provoke a symptom. Symptoms and consequences of osteochondrosis, by the way, are often related. So, with a pathology of such a localization, vision may deteriorate, fainting and various signs of impaired brain activity due to insufficient blood supply are also characteristic.
A rare form of the disease is thoracic osteochondrosis. The disease is difficult to diagnose because there is no pain in this part of the spine. Most often, discomfort is felt under the shoulder blades, which is why it is perceived as a symptom of diseases of the heart, respiratory system or kidneys. Therefore, patients do not turn to the specialist who can actually help. The consequences of breast osteochondrosis are a violation of the gastrointestinal tract, respiratory and cardiac functions, because in this part of the body some centers are concentrated that are responsible for the normal functioning of the internal organs. Symptoms are chest lumbago.
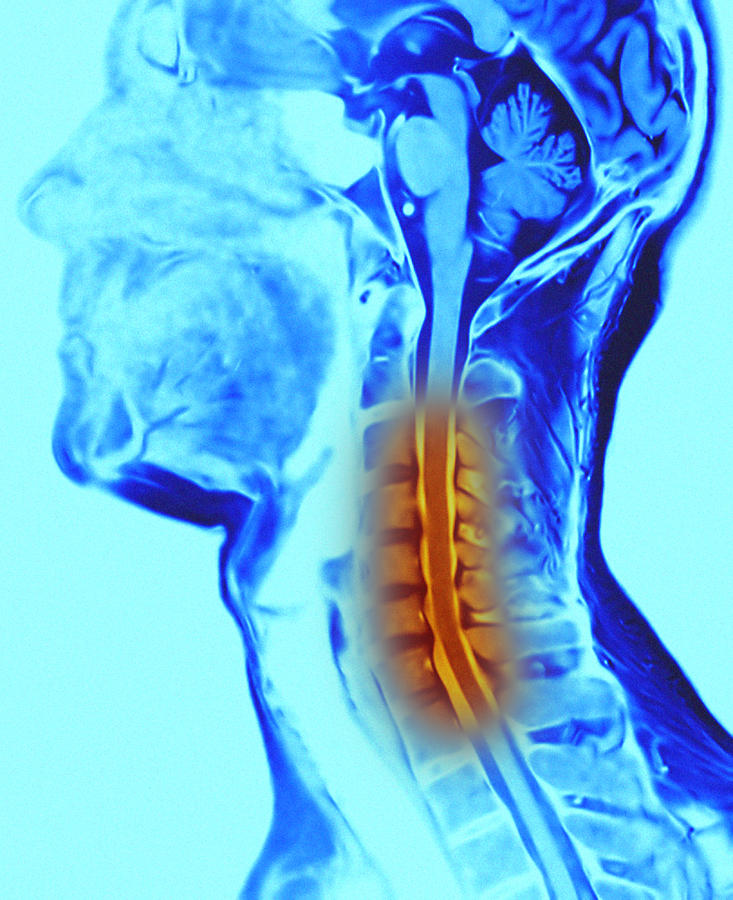
The lumbar region is most at risk of developing osteochondrosis. This area is very mobile, it is affected by significant loads. The onset of the disease is often not accompanied by any symptoms. Osteochondrosis begins with a feeling of fatigue and slight discomfort, but over time, the discomfort intensifies. Often symptoms of cervical osteochondrosis often appear. The consequences are the most unfavorable.
The sacrococcygeal form of the disease rarely manifests itself. Very often, pathology is accompanied by lumbar osteochondrosis. Symptoms are very similar. Often with sacrococcygeal osteochondrosis, the lower limbs become numb, painful sensations appear in the corresponding section, paresis of the leg muscles.
The consequences of osteochondrosis
With osteochondrosis, a person always complains of pain, which is accompanied by many other unpleasant symptoms and concomitant diseases. A serious complication is a violation of the functioning of blood vessels, compression of the sciatic nerve, sciatica, intervertebral hernia and other complex pathologies. Ignoring the symptoms of the disease and inadequate treatment (refusal of traditional therapy, late treatment to the doctor, non-compliance with individual recommendations of a specialist, incorrect diagnosis) can lead to the addition of a number of minor, but no less dangerous health pathologies to the main diagnosis.
Severe headaches
Osteochondrosis of the cervical spine results in severe headaches. It is there that the artery is located, which provides a sufficient supply of blood and oxygen to the brain. As the disease develops, the vertebral discs lose their cushioning functions, so that even minor loads provoke their displacement. As a result, bone formations grow pathologically, discs are displaced and exert significant pressure on the artery. This consequence of osteochondrosis of the cervical spine (3 degrees or even earlier) is felt by most patients.
Migraines in diseases of the spine are associated with compression of nerves and arteries, hypertensive syndrome (a set of symptoms caused by increased intracranial pressure), pinching of nerve endings and muscle spasm. Usually attacks of pain occur during movements and turns of the head, vomiting, nausea, high blood pressure, irritability, and a feeling of weakness in the body are possible. Sometimes pain in the shoulders and shoulder blades can be observed, the functions of the heart and blood vessels are disturbed (as a complication of cervical osteochondrosis).
With spinal deformity, the pains are one-sided, bursting in nature. For stopping, ointments with a warming effect ("Finalgon", "Capsicum") can be used to increase blood circulation in the muscles of the neck, relieving pain cramps. With severe pain you need to go to bed and completely relax the muscles of the spine. Massage during an attack is undesirable. This accelerates blood flow, but does not affect the focus of pain. As a result, the patient's well-being may worsen. Cold compresses are acceptable.
Visual impairment
What are the consequences of cervical osteochondrosis? The list is quite extensive. A consequence of cervical osteochondrosis (if the disease is not treated for a long time) is visual impairment, because in this section there are arteries that provide blood supply to the central visual structures. Compression causes a disruption in the functioning of many parts of the brain, including reduced visual acuity. The oxygen level in the brain tissue decreases, the conductivity of nerve impulses worsens. This indicates a complicated course of pathology and needs early treatment.
Also a consequence of osteochondrosis of the cervical spine is vertebral artery syndrome. This syndrome is characterized by a split vision, dizziness, nausea and vomiting, eye pain and tension, darkening in the eyes, fog, flickering of black dots and colorful spots in front of the eyes. Examination of such symptoms will show that the arterial vessels of the retina are narrowed, swelling of the optic nerve is possible, sometimes glaucoma develops in the background, which is accompanied by pain and a feeling of fullness due to increased intraocular pressure.
Hearing impairment
A consequence of osteochondrosis of the cervical spine is hearing loss of 25-30%, periodic dizziness and ringing in the ears. Such symptoms result from compression of the nerve roots. You can improve your hearing with the help of special exercises, such as listening to music or TV at low volume. A positive effect is given by the massage of the auricles. At the first sign of hearing impairment, you must go to the hospital, because partial deafness is a common complication of osteochondrosis.
Radiculitis (radiculopathy)
The disease affects about 10% of patients over the age of 40. The disease affects the nerves of the spinal cord, paresis, sensory disturbance and pain occur. The result of pathological changes in the spine is a compression of blood vessels, spinal roots and spinal cord, that is, blood circulation worsens. Due to poor blood flow, limb paralysis, neurological syndromes, and brain dysfunction can develop. Different forms of the disease that have different symptoms may develop. For treatment, painkillers, tranquilizers and analgesics are prescribed, as well as novocaine-hydrocortisone blockades. In complex cases, infusion therapy is indicated.
Bouts of pain (lumbago)
Lumbago is a consequence of osteochondrosis, if pathology is not treated. The condition is characterized by acute lower back pain caused by irritation of the nerves and compression of the spinal cord. The most severe pain is noted at the beginning of the attack. It lasts about 30 minutes, but sometimes it can last several hours. After the intensity of spasms goes into decline. The next attack usually occurs at night and passes only on the seventh day. With timely treatment, the unpleasant symptoms of lumbago disappear after 5-8 weeks.
The manifestation of lumbago can be spasms of the back muscles, acute lower back pain, decreased motor functions. The main symptom is pulsating, tingling or shooting pains that give to the thigh, buttock, and spinal muscles. The attack often complements Horse Tail Syndrome. In this case, weakness appears in one or two legs, numbness, the digestive and genitourinary systems are disturbed (urinary retention or involuntary urination, intestinal obstruction). Lumbago may be a consequence of osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine. The syndrome occurs with other localizations of the disease.
Lumbargia may be a consequence of osteochondrosis of the lumbar region. At the same time, the onset of an attack is preceded by lower back injuries, hypothermia or severe stress on the spine. The pathological condition lasts from a month to several years. The main goal in treating pain is to alleviate symptoms and prevent new attacks. Therefore, at the first signs of pathology, you need to go to the doctor. Treatment of lumbago is carried out with anti-inflammatory ointments and suppositories ("Ibuprofen", "Diclofenac", "Fastum gel"), drugs against muscle spasms ("Spazgan", "Papaverine") and injections. During the entire course of therapy (one week), bed rest should be observed.
Sciatica: symptoms and treatment
What consequences of osteochondrosis may appear? Patients are often diagnosed with sciatica, that is, compression of the sciatic nerve in the sacral region, which is accompanied by a complex of symptoms. When pinching, severe pain occurs, which is given to the thigh or buttock, as well as the lower part of the leg. Symptoms are muscle stiffness, aching pain in different parts of the body, cramping and tension of the lower back muscles, aggravation of pain during movement, sneezing or coughing, as well as a change in body position, shooting pains, the intensity of which can increase to such an extent that the patient cannot walk or even to sleep. Sensitivity in the lower extremities and in the pelvis also decreases, muscle atrophy can occur (usually, one leg is losing weight).

Sciatica is associated with osteochondrosis of the lower back or sacrum, a hernia of the intervertebral discs (another consequence of osteochondrosis). The disease can occur due to large loads on the back, destruction of the tissues of the spinal column, damage to the sciatic nerve due to trauma, various infectious diseases, high blood sugar, cancer, and so on. Typically, sciatica causes a feeling of "goosebumps", loss of sensation in the toes and lower legs, problems with raising the torso, difficulties with prolonged stay on the legs, complete or partial paralysis of the lower extremities, weakness in the muscles. Treatment should be aimed at the causes of the pathological condition.
Vegetative-vascular dystonia
Such a diagnosis is made by 90% of patients. Vegetative-vascular dystonia is a syndrome that is characterized by a violation of the autonomic functions of internal organs due to malfunctioning of the central nervous system. This can also be a consequence of osteochondrosis of the spine. VVD may be accompanied by neurosis, depression, and other disorders. The appearance of dystonia in many cases is preceded by improper treatment of cervical osteochondrosis. These two diseases increase the risk of other pathologies.
VVD for cervical osteochondrosis is manifested by pain in the muscles and spine, general weakness, sudden changes in body temperature, impaired sexual function, frequent jumps in blood pressure, cramps and numbness of the extremities, pain in the back of the head that are shooting in nature, and impaired heat transfer.
The main goal of treatment is to stop the destructive processes in the bone and cartilage tissues of the spine. Physiotherapy exercises, pool visits and massages are recommended on an ongoing basis. Manual therapy relieves the main symptoms of VVD. Medication includes the use of anti-inflammatory drugs (Ibuprofen, Diclofenac), chondroprotectors (Teraflex, Structum, Artra) and analgesics (Nise, Etodin Fort, Ketanov). Soothing, antioxidants are indicated to eliminate the symptoms. For panic attacks or nervous disorders, antidepressants (Grandaxinum, Paxilum, Noofen) and tranquilizers are used.
Urogenital diseases
A consequence of osteochondrosis of the 3rd degree can be various pathologies of the genitourinary system. Patients often experience pain in the bladder, groin, lower abdomen, urinary disorders (incomplete emptying of the bladder, urinary retention or involuntary urination, burning, too frequent urination), bladder dysfunction, decreased potency in men, weak sexual desire in women, an irregular menstrual cycle. In most patients, these symptoms completely disappeared only after the complex treatment of osteochondrosis.
The relationship between diseases of the spine and the genitourinary tract is diagnosed with good reason. Confirmation is expressed clinical signs of degenerative processes in the tissues of the spine, the simultaneous manifestation of symptoms. If you suspect osteochondrosis or diseases of the genitourinary sphere, self-medication is not recommended. It is important to remember that only a doctor can conduct a complete diagnosis, identify the relationship between pathologies and prescribe a comprehensive treatment.
Intervertebral hernia
Symptoms of an intervertebral hernia depend on the location of the problem. This consequence of osteochondrosis is characterized by muscle weakness in the arms and shoulders, shooting pains in the upper limbs, numbness of the chest wall and shoulders, if the roots of the spinal cord in the thoracic or cervical spine are compressed. With a lumbar hernia, pains are felt in one leg, they bother constantly or only periodically, have a paroxysmal character, and often appear with prolonged sitting. Unpleasant sensations disappear or decrease as the spine relaxes, but intensifies with careless movement, coughing or sneezing.
In most cases (approximately 80%), uncomplicated hernia therapy does not require surgical intervention. Within six to twelve months, it loses moisture and decreases in size. However, all the unpleasant symptoms of pathology disappear. It is impossible to shorten the drying time of a hernia. This is a completely natural process.
Spondylarthrosis
Chronic disease of the spine is characterized by degenerative-dystophic changes in various segments of the motor apparatus. Most often, the pathology affects the lumbar. With the development of spondylarthrosis, cracks appear in the body of the nucleus, the fibers of the fibrous ring are destroyed, and the structure of blood vessels changes. In the early stages, the pathology proceeds without an inflammatory process, but in the future, the disease can lead to the formation of bone spurs and tissue damage. Spondylarthrosis accompanies osteochondrosis, is an age-related disease (usually the disease manifests itself after thirty to forty years).
The main symptom is a feeling of discomfort in the affected area. Often the pain is aching or pulling in nature. At rest, discomfort disappears, but with the slightest movement, the intensity of the pain increases. At first, the pains are only local, but already in the second or third stage, discomfort is felt in different parts of the back. In addition, symptoms requiring complex treatment are observed. The therapy is based on the use of medications (Etodin Fort, Nalgesin, Nurofen), which provide pain relief. Measures are being taken to reduce the load on the spine.
Spondylosis (protrusion of the disc)
The causes of the development of pathology are the same as with spondylarthrosis. In the early stages, this consequence of osteochondrosis may not be manifested by any symptoms, but then dull or aching pain occurs in the lesion.As the pathological formations grow, severe back pain appears, and in case of complications, sciatic nerve damage, vertebral hernia, vertebral displacement are possible. Basically, the disease affects the tissues of the cervical spine, but sometimes it develops in other segments of the spine.
, , , , . , , , . . , , , , . , . .
( ) — , . () . . ( ), , , , , , , , .
With stenosis (narrowing of the canal) of the lumbar, lower back pain intensifies with the slightest movement, and with relaxation, the discomfort is moderate or not felt at all. Also characterized by a feeling of weakness and numbness in the legs, disorders of bowel movements and urination, pain of the type of radiculitis, which is relieved by sitting or leaning forward, lameness. The clinical picture may change over time, because the symptoms are fully dependent on the degree of compression of the discs.
As part of complex therapy, vascular ("Berlitonin", "Vinpocetin", "Actovegin"), anti-inflammatory and analgesic drugs are prescribed. Physiotherapy, massage procedures, and the use of steroid drugs along with anesthetics are necessarily indicated. Physical exercise is indicated to strengthen muscles. Severe attacks can be relieved by blockages. For this, local anesthetics are introduced, which relieve inflammation and swelling. In some cases, treatment is not complete without surgery. Surgical intervention is necessary in case of partial paralysis, severe exacerbation, prolonged absence of any therapy, pelvic dysfunction, or low efficiency of conservative treatment.
Tips for choosing treatment tactics
The treatment regimen is determined depending on which disease caused the symptoms and consequences. The doctor can recommend both conservative treatment and surgical. In any case, an integrated approach is needed. Most often, treatment includes manual and reflexotherapy, various types of water massages, exercise therapy, medical nutrition, drug therapy, classes with a psychologist, laser and ultrasound therapy, vibration stimulation, electrical stimulation, magnetostimulation and so on. A visit to a psychologist or psychotherapist is recommended if the patient alone cannot believe in the possibility of rehabilitation. As a rule, the situation improves after several sessions.
As part of drug therapy, local painkillers (Voltaren, Diclofenac, Ketonal), drugs to improve blood microcirculation (Heparin, Warfarin), and antispasmodics (Spazmalgon, No-Shpa) are most often prescribed "), antioxidants (" Antiox + "," Glutargin "), anti-inflammatory drugs (" Ibufen "," Nimesil "), correctors of psychosomatic disorders (" Persen "," Tenoten "). In the event that conservative therapy does not help, you need to resort to surgical intervention. Most often, during the operation, the resulting hernia is removed or some vertebrae are replaced. Many aftereffects of grade 3 osteochondrosis (cervical, sacrococcygeal, lumbar or thoracic) are also treated promptly.
Spinal problems are often recommended to be treated with alternative methods. Various healers claim that the effectiveness of traditional medicine is much higher, and it does not harm. In the case of osteochondrosis, the only alternative treatment options should concern a maximum of bathtubs, special applications or ointments. It is best to supplement traditional treatment with such methods, and not completely abandon the recommendations of the attending physician. This is due to the fact that such pathologies of the spine can subsequently lead to complete disability. Refusing traditional medicine will not lead to anything good. Such a patient will soon face serious consequences of cervical osteochondrosis of the 3rd degree, for example, or another form of the disease, some of which are extremely difficult to treat.