Man is a rather fragile creature. But nature, caring for the survival of the species, gave people a very significant gift - immunity. It is thanks to him that our body exists, evolves and prevents aggressive infectious agents.
Is inflammation harming or protecting the body?
The Latin word inflammo in translation means "to burn", and its other interpretation is inflammation. The stages of inflammation, its types and forms will be described in detail in this material. First you need to understand the essence of the process and find out its significance for the human body.
Such changes under the influence of certain circumstances (diseases, injuries, the presence of parasites, allergic reactions) did not appear by chance - this is an immune reaction to the invasion of infection, the destruction of cellular structures or allergens. This process is aimed at localizing the damaged area, isolating it from healthy tissues. Such actions of the body are due to the need to fix the pathogenic factor in the area of inflammation, to utilize the products of its decay and to heal the invasion site. As a result, the compulsory development of immunity occurs.
It is important to consider that inflammation is not synonymous with infection. This is a typical immune response to any pathogenic penetration into the body, while infection is an aggressive agent that provokes such a reaction.
History reference
Inflammation, stages of inflammation, its characteristic signs were known at the beginning of our era. In particular, ancient scholars Claudius Galen and the Roman writer Cornelius Celsus were interested in these issues.
It was the latter that identified four main components of any inflammation:
- erythema (appearance of redness);
- edema;
- hyperthermia;
- pain.
There was a fifth sign - a violation of the functions of the affected area or organ (the last paragraph was supplemented much later by Galen).
Subsequently, many scientists dealt with this topic. He was studied by the world famous biologist Ilya Ilyich Mechnikov. He considered the inflammatory reaction to be a healing, true natural gift, but still in need of further evolutionary development, since not all such processes lead to the recovery of the body. Not to mention the fact that especially severe inflammations end in fatal cases.
Terminology
If this process occurs in the body (stages of development of inflammation in this case they are not taken into account), then the characteristic ending “-it” is necessarily added to the name of the disease, as a rule, in Latin. For example, inflammation of the larynx, kidneys, heart, peritoneum, pancreas are called, respectively, laryngitis, nephritis, myocarditis, peritonitis, pancreatitis. If a disease of the connective or fatty tissue adjacent to it is attached to the general inflammation of the organ, then the prefix “para-” is added to the name: paranephritis, parametritis (inflammation of the uterus) , etc. But in this matter, as in any rule, there is exceptions, for example, specific definitions such as tonsillitis or pneumonia.
Why does inflammation appear?
So what are the main causes of inflammation? There are three types of them:
- Physical. This means that the inflammatory process in the body starts as a result of various mechanical injuries, burns, including radiation injuries, frostbite, the presence of foreign bodies, exposure to electric current.
- Biological. In this case, we mean a pathological process caused by microbes, parasitic agents and viruses. Pathogens of certain diseases, such as Koch's bacillus (tuberculosis), pale spirochete (syphilis), mycobacterium leprosy (leprosy), and others, also belong to this category of signs.
- Chemical. This group of reasons is based on the effects of various substances of a chemical nature (medicines, poisons, salts, alkalis, acids, as well as toxins formed in the body itself).
Serious psychological trauma, persistent stress and alcohol abuse can also cause inflammation.
Such processes are either acute, or take a chronic form. When a reaction to an irritant occurs immediately, that is, white blood cells and plasma come into motion and behave very actively in the affected areas, this is what characterizes the acute process. If changes at the cellular level occur gradually, then inflammation is called chronic. More on types and forms will be discussed later.
Symptomatology
All stages of inflammation are characterized by similar underlying symptoms. They are divided into local and general. The first group of signs includes:
- Hyperemia (redness) of the affected area. This symptom occurs due to an intense blood flow.
- Hyperthermia is an increase in local temperature, as the metabolism accelerates.
- Swelling, if there is an impregnation of tissue exudate.
- Acidosis is an increase in acidity. This symptom often occurs due to fever.
- Hyperalgia (intense pain). Appears in response to effects on receptors and nerve endings.
- Loss or malfunction of the affected area. Occurs as a result of all the above symptoms.
By the way, inflammation of the internal organs is not always manifested by painful sensations, but if the process proceeds on the surface, then almost all of the above symptoms are present.
Common signs can be detected using laboratory tests, in particular, a detailed blood test. For example, characteristic changes in the blood formula in its leukocyte part, as well as a significant increase in ESR. Thus, by carefully studying this complex of symptoms, you can diagnose inflammation. The stages of inflammation are the next question that interests people studying this topic.
Stages and types of development of the inflammatory process
Like any process, this one also develops in steps. There are 3 stages of inflammation. They can be developed to varying degrees, but are always present. If you describe them in simple words, then this is damage, the yield of exudate and tissue proliferation. The first stage of inflammation - alteration. This is followed by exudation, and after it - proliferation.
Now it’s worth a little more discussion of the types of inflammation directly associated with the stages. As already mentioned, when a process develops rapidly, it is called acute. Usually, in order to qualify it as such, in addition to the temporary factor, such stages of acute inflammation as exudation and proliferation should prevail.
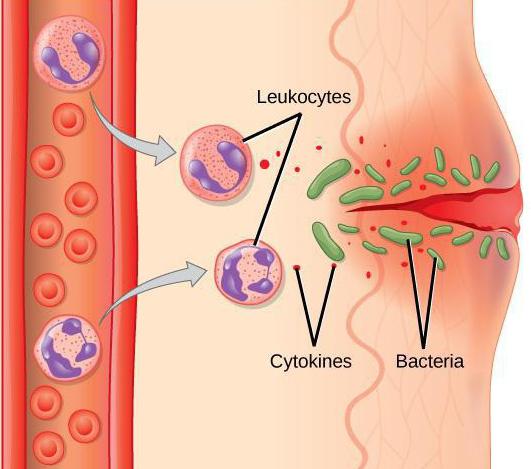
There is one more division: banal (usual) and immune inflammatory process. In the second case, this is a direct reaction of the immune system. Studying the stages and mechanisms of inflammation of this type, we can say with confidence that the stepping depends on whether it is slowed down or immediate. This statement is explained quite simply: first of all, it is worth noting that the mechanism for this inflammation is the antigen-antibody tandem. If the reaction to a certain intervention in the body develops immediately, then this mechanism is first activated, and later, due to the processes of phagocytosis, mixing of the indicated tandem with leukocytes and damage to this complex of vascular walls, tissue edema and multiple hemorrhages rapidly increase. An example of such an acute condition is anaphylactic shock, Quincke's edema (or angioedema) and other processes that require the application of resuscitation measures.
With a delayed reaction to the antigen, the process is not so fast (for example, the Mantoux reaction). In this case, the lymphocytes first find and destroy the foreign agent along with the tissues. Then there is a slow increase in granuloma. This process is characterized by a rather protracted course.
Thus, the following types of inflammatory processes are distinguished:
- Acute. Its duration is estimated at several hours. There are times that it takes about a week.
- Subacute. It usually ends after a few weeks.
- Chronic. It can last for years or even for life, flowing in waves: from exacerbation to remission.
Damage: Stage One
So, we pass to the direct description of stepwise changes in the body. Any inflammation starts that way. As already mentioned, stage 1 inflammation is called alteration (from the word alteratio - "damage").
It is rupture of tissues and, accordingly, violation of the integrity of cells and blood vessels that lead to necrotic changes and the release of
inflammatory mediators. These active substances change vascular tone, causing sharp pain and swelling.
Exudation
Vascular disorders in the inflamed area cause exudation (exudatio). This is the 2nd stage of inflammation. The process is to exit blood fluid in the tissue. It is called exudate, which gave reason to call this process that way. When this stage occurs, it is the activation of mediators and the disruption of blood vessels that causes inflammation.
Due to the spasm that occurs in the arterioles, the blood flow in the damaged area is significantly increased, which leads to hyperemia. Further, the metabolism increases, and hyperemia from arterial to venous. Vascular pressure rises rapidly, and the liquid blood part leaves their borders. Exudate can be of various filling, the inflammatory form caused by it will depend on this.
Productive process
The third stage of inflammation is called proliferative. This inflammatory step is final. Regenerative processes occurring in the tissues allow either to restore the areas damaged by inflammation, or a scar forms in this place. But in this established and stable scheme there are nuances: 3 stages of inflammation can be of varying degrees of intensity. Therefore, there are also different forms these processes.
Main forms
Types, forms and stages of inflammation - this is what you need to pay attention to first. As we have already found out, the duration of a process is determined by such a concept as type. But these are not all characteristics with which to evaluate inflammation.
The stages of inflammation are the basis of his qualifications and assessments. But it so happens that the components of the process are expressed to varying degrees. Three forms of specific changes are distinguished depending on the basis of the inflammatory reaction:
- Alterative. This form is characterized by the predominance of necrotic processes in the inflamed organ. While the remaining symptoms are much weaker. Usually, this form of inflammation is observed in parenchymal organs: heart, kidneys, and liver. In this case, the death and decay of muscle fibers and tissues is characteristic. This term is somewhat outdated, but in some areas of medicine it is still relevant.
- Exudative. The essence of the definition is that with such an inflammatory form, exudate is required. Depending on how it will be, there are several subtypes of such inflammations: purulent, hemorrhagic, serous, fibrinous, catarrhal. Let us briefly dwell on each of them. For example, serous inflammation is characterized by the formation of protein fluid. It can fill any cavity (pleural or articular bag, and others). It is also possible to impregnate fibers and tissues with it, resulting in edematous configurations. You can cure this form by pumping out the exudate. The fibrinous form of inflammation is divided into croupous and diphtheria. In this case, the secreted protein forms characteristic films of a white tint. The danger of this form is that it can form commissures. Purulent inflammation is characterized by the formation of protein-leukocyte exudate. Discussing the forms, stages, types of inflammation, it is worth noting that this is a very severe form that can literally melt the tissues that affect. The penultimate form is hemorrhagic. Exudate in this case includes many red blood cells. That is, as a result, discharge with an admixture of blood may occur. Such inflammation is inherent in serious infectious diseases: anthrax, hemorrhagic meningitis, plague, smallpox and others. Its outcome will depend on the causative agent of the disease. But this type of inflammation is in any case very unsafe. The catarrhal inflammatory form is the mildest of all. It is characterized by the release of a large amount of mucus (runny nose, tracheitis).
- Proliferative. This form is characterized by rapid proliferation of tissues and the formation of granulomas. It provokes cirrhosis (wrinkling) of various organs, develops around foreign bodies and parasitic inclusions.
Based on the foregoing, it is necessary to dwell in more detail on what stages of purulent inflammation are distinguished by specialists:
- Serous infiltrate.
- Necrotic process (phlegm, gangrenous, abscessed)
The main pustular formations are divided into the following types:
- Focal inflammation (ulcer). Otherwise, such a process is called an abscess. With such inflammation, the following occurs: a festering cavity forms in the focus of infection with a constant influx of leukocytes into it. If an abscess breaks out, then it is called a fistula. Boils and carbuncles are also included here.
- Empyema is the formation of purulent exudate in natural cavities (appendix, pleura, parenchyma) due to the impossibility of outflow of contents.
- Infiltrate. In another way, this stage is called phlegmon. In this case, pus completely impregnates the organ. The process is widespread throughout the structure of the affected area.
Purulent exudate can completely dissolve, forming a scar. But there is the possibility of an adverse outcome. This happens if pus enters the bloodstream. As a result, sepsis inevitably develops, and the process becomes dangerous, generalized, the infection spreads throughout the body.
Case study: pneumonia
This is one of the most serious and rather unpredictable diseases, the cause of which are various pathogens that cause pneumonia. It is the presence of exudate in the alveoli that makes the patient’s breathing difficult and provokes a change in the quality of life for the worse. The incidence depends on various factors, primarily on human immunity. But in any case, track all three stages of the inflammatory process on the example of this ailment is possible.
Pneumonia also proceeds in steps. From the point of view of pathogenesis, 4 stages of pneumonia are distinguished: tide, red guardianship, gray guardianship, resolution. The first of them just characterizes the invasion of an infectious agent into the body, damage to the integrity of cells (alteration). As a result of this there is hyperemia, skin allergic reactions, shortness of breath, rapid pulse, signs of severe intoxication.
In the stages of hepatization (red and gray hepatitis), exudate is actively formed in the lung tissues. It is this process that causes obvious wheezing, manifestations of intoxication, neurological disorders. The formation of sputum is very plentiful - exudate literally fills the entire affected area. How serious pneumonia is, says the factor of the extent of the lesion (focus, segment, lung lobe, or total inflammation). There are cases of merging foci into one.
During the course of the resolution stage, separation of the resulting exudate occurs, restoration (proliferation) of the affected areas of the lung, and a gradual recovery. Of course, the stages of pneumonia illustrate the processes characteristic of the described state of the body. In addition to pneumonia, an example of the most characteristic diseases directly related to the development of inflammation can be:
- Atherosclerosis.
- Cancerous tumors.
- Asthmatic changes.
- Prostatitis: both acute and chronic.
- Diseases of the cardiovascular system (e.g., coronary artery disease).
- Glomerulonephritis.
- Intestinal inflammation.
- Ailments of organs located in the pelvic area.
- Rheumatoid arthritis.
- A group of autoimmune diseases.
- Vasculitis.
- Cystitis.
- Graft rejection.
- Sarcoidosis
Finally, a commonplace acne also appears due to inflammatory processes on the surface of the skin and in the deeper layers of the epidermis.
It is noteworthy that immunity often makes a cruel joke with the body, provoking the development of inflammation. If we briefly describe this process, we can say that immune bodies attack their own body. They can perceive whole organ systems as a threat to the life of the whole structure. Why this happens, unfortunately, is not fully understood.
Brief conclusion
Of course, none of the living is immune from inflammatory changes of varying severity. Moreover, this process was presented to mankind by nature and is designed to develop immunity and help the body more successfully follow the path of evolution. Therefore, an understanding of the mechanisms that occur during inflammatory metamorphoses is necessary for every conscious inhabitant of the planet.