The transport of food from the mouth to the stomach passes through the esophagus. If peristalsis of smooth muscles is functioning normally, then the food lump easily and quickly gets to the stomach. In case of violation of its activity, a spasm occurs. Food moves with difficulty along the esophagus, causing pain. The individual is concerned about the severity and pressure in the throat, chest as a result of a spasm of the esophagus. How to remove it and how to alleviate the condition? This will be discussed in the article.
general information
Esophagospasm, or in another way an esophageal spasm, is a disease, as a result of which peristalsis malfunctions from time to time, i.e., an increase in pressure and spastic contractions of its walls occur in the lower esophageal sphincter. A diagnosis is made on the basis of diagnostic measures, which include: pH- and manometry of the esophagus, radiography, endoscopy. The disease is manifested by chest pains, belching, dysphagia, heartburn. The treatment is mainly conservative, aimed at reducing intra-abdominal pressure and esophageal myotonus, and dietary nutrition is also indicated.
Common types of esophagospasm
Often in practice there are two types of spasm of the esophagus:
- Diffuse, the symptoms of which are manifested by a malfunction of motor activity, and spastic uncoordinated contractions of the smooth muscles of the food tube occasionally occur. At the same time, muscle tone is preserved, as well as reflex opening during swallowing. In the sternum and stomach, severe pain occurs, which extends to the shoulder and even the jaw. Severe pain senses the individual at rest and at night, that is, they are not associated with eating. When the contraction stops, a regurgitation appears. Swallowing disorder is more pronounced when drinking liquid or eating a soft consistency. The attack lasts from several minutes to several hours.
- Segmental (“nutcracker” esophagus) - in this form, smooth muscle contraction occurs with greater intensity in certain areas of the esophagus and stomach. Spasm is manifested as follows. The appearance of pain when swallowing fluids. Dysphalgia, which appears when eating mashed food, porridge, cottage cheese. Difficulty swallowing when swallowing foods rich in fiber. The duration of the spasm is a few seconds. In some cases, its duration increases to three hours. Pain sensations are moderate and quickly pass. Attacks begin suddenly, gradually their intensity decreases.
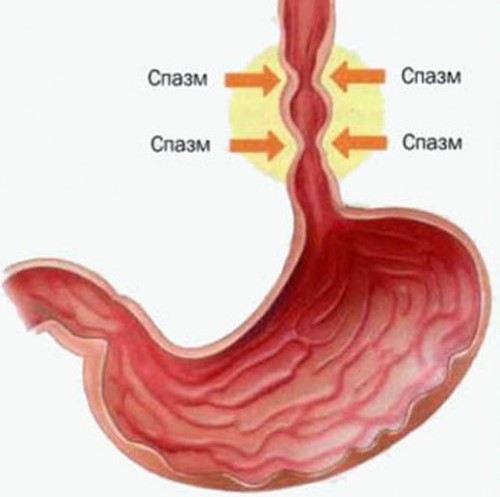
The following esophagospasm variants are known:
- Idiopathic, often called primary - organic changes in the nervous system.
- Reflex, or in another way secondary, is a companion of ulcerative lesions of the digestive system, hiatal hernia, gallstone disease, i.e., those pathologies in which the mucous membrane of the food tube is affected.
Other types of esophagospasm
In medical practice, there are other types of esophageal spasm:
- On nerve soil - it is characterized by febrile muscle contraction due to mental disorder (depression), sleep disturbance, stress, an increased tendency to anxiety, and fear. A time attack lasts only a few minutes.
- When swallowing - the following symptoms indicate such a spasm: a sensation of a lump in the throat accompanies a panic attack; with convulsions, a feeling of suffocation occurs; with sudden unexpected sounds, vomiting begins; with a neurosis-like state, spasm can prevent even saliva from being swallowed; frequent companions of neurosis are considered attacks of nausea and vomiting; pain in the chest area is similar to cardialgia, and their intensity is variable and varies from insignificant to sharp.
- Cardiospasm - is acute and chronic. For acute, pain behind the sternum and in the epigastric region are characteristic; the feeling that the food lump lingers over the stomach. At the same time, drinking water does not bring relief. At the end of the attack, regurgitation or burping occurs. With slight excitement, the pain intensifies. Late-started therapy is dangerous with sudden weight loss, esophageal vomiting. The development of pneumonia is not excluded. One of the main causes of esophageal spasm, the symptoms of which are described above, is considered a long-term ulcerative lesion. The main provocateurs are tobacco smoking, inhalation of toxic fumes, the use of strong alcohol.
- Lower sections - with such a spasm, the organ tube expands along the entire length.
- Non-sphincter - simultaneously affects several of its departments throughout. Individuals complain of regurgitation of mucus, pain behind the sternum, episodes of dysphagia, the duration of which is from several seconds to several weeks.
Esophageal spasm occurs with other abnormalities. For example, as a symptom, it is observed with tuberculosis, syphilis, scarlet fever, inflammation of the pleura or aorta.
Esophagospasm during pregnancy
During the period of expectation of the baby, the appearance of cramping in the esophagus, the causes of which will be discussed below, is quite common. Despite the fact that carrying a crumb is a natural process, in some cases pathological conditions may appear. Changing the position of the diaphragm and hormonal imbalance contribute to food retention in the esophagus and provoke vomiting. The occurrence of GERD is affected by a malfunction in the muscles of the stomach and motility of the esophageal contractions. In addition, as a result of the increase in the acidity of the digestive juice, which is characteristic of this period, acidic contents are thrown into the esophagus, causing it to burn. In practice, esophagitis occurs in every fifth pregnant woman. The clinical picture:
- burning sensation in the cheeks and tongue;
- cough, sensation of severe lack of air;
- hoarseness, voice disturbances;
- belching, heartburn, pain in the chest area and some other phenomena associated with damage to the esophagus;
- flatulence, a feeling of fullness in the stomach.
Causes
Often spasms occur at the exit or entrance of the esophagus, as in these places there are many nerve endings, and they are the first to respond to a malfunction.
The main causes of esophageal spasm, the symptoms and treatment of which are discussed in this article, are as follows:
- violation of swallowing;
- chemical poisoning;
- the presence of a foreign body;
- ulcerative lesions of the stomach or duodenum;
- very cold, hot, dry or hard foods;
- exposure to concentrated organic or mineral acids;
- exacerbation of gastroesophageal disease;
- minor injuries of the walls of the esophagus resulting from swallowing a foreign body or eating hard food;
- inflammatory processes in the internal organs located next to the esophagus;
- infectious ailments, for example, scarlet fever, rubella, and others;
- nervous diseases;
- improperly selected denture;
- pathology of the intercostal nerves;
- the use of strong alcohol-containing drinks;
- excessive emotional stress, overwork.
Before acquiring a stable form, esophagus spasm occurs periodically and is associated with overwork, fear, nervous excitement, fever or lack of sleep. The disease becomes chronic, when the vagus nerve is inflamed, nerve endings located near the esophagus are affected, there are CNS disorders, that is, there is constant pressure on the muscles of the esophagus tube.
Signs of esophageal spasm
“A lump in the throat” - usually with such a phrase the individual describes his feelings with such a problem. The clinic depends on the shape and location of the pathological process. Typical symptoms of any form of illness are a violation of swallowing, chest pains that occur when swallowing saliva and food, but can also be spontaneous. Stressful situations exacerbate discomfort. In addition, the pain gives back, shoulders, lower jaw, shoulder blades. The duration of the attack is about sixty minutes. In some cases, its duration is longer. After taking antispasmodics, the pain subsides.
When using both solid and liquid foods, dysphagia occurs. She appears immediately with pain and is irregular in nature. Heartburn occurs in every fifth individual. Severe cramps and a large volume of food coma in the esophagus provoke regurgitation.
Mostly, there is a spasm of the upper narrowing of the esophagus in individuals predisposed to sudden changes in mood, neurosis-like conditions or tantrums, i.e., a nasal spasm of the esophagus. It manifests itself as nausea, cough, pain behind the sternum of a pressing nature, excitement, a sense of fear, redness of the face. Spasmodic phenomena are formed sharply or gradually increase. The intermittent nature of the disease contributes to the following: the individual becomes restless, fearing the return of symptoms, eats irregularly and thereby worsens the situation.
Chronic spasm of the upper narrowing of the esophagus is characteristic of age-related individuals with mastication disorders, tooth defects. In such patients, the passage of solid food is difficult, unpleasant sensations are noted behind the sternum, there is a need to drink liquid every swallowing of food. Constant obstruction of the esophagus leads to the formation of its compensatory expansion in the spasmodic area.
Therapeutic measures
After confirming the diagnosis of individuals, the question of how to relieve stomach cramps and esophagus is of interest. If the exact cause of the disease is not identified, then doctors do not recommend conducting treatment on their own. Therapy involves the use of:
- medicines;
- physiotherapeutic procedures;
- dieting;
- lifestyle changes;
- medicinal herbs.
If there is a underlying gastrointestinal disease that provokes esophagospasm, then initially treatment should be started with it to prevent the appearance of new attacks. Next, we consider in more detail than to treat a reflex esophageal spasm. For this, drugs of different pharmacological groups are used:
- Antacids, or antacids, protect the mucosa of the digestive canal.
- Gastrointestinal motility stimulants - facilitate the passage of a lump of food due to improved peristalsis of the muscle tube.
- Antispasmodics - remove spasm.
- Alginates - envelop the mucous membrane, protecting it from aggressive hydrochloric acid.
- Sedatives - a calming effect on the central nervous system.
- Antidepressants, tranquilizers and sleep-normalizing medicines are prescribed if necessary.
- Analgesics and anesthetics - have a local analgesic effect.
- Vitamins of group B.
The above medicines, doses and treatment regimens are selected individually by the attending doctor.
Consider how to relieve stomach cramps and esophagus using physiotherapeutic treatment. It is aimed at normalizing the functions of the nervous system and includes:
- Electrophoresis with anesthetic - a constant electric current together with the drug acts on the affected organ, which helps to ease pain.
- Radon baths - thanks to them, the sensitivity of nerve endings decreases.
- Galvanization - current is supplied through the electrodes at a constant frequency, low power and low voltage. As a result, the sensitivity of nerve fibers weakens. This method is especially effective for spasm of the esophagus, which arose against the background of osteochondrosis.
- Warm baths with decoctions of medicinal herbs that have a sedative effect.
- Inductotherapy is the effect of a high-frequency electromagnetic field with a predominance of the magnetic component. The exclusivity of this manipulation is that heat is generated in the muscle layer, as a result, the tone decreases and the spasm of the esophagus is eliminated. How can I take it off yet? Physical activity is especially important, i.e., performing simple exercises aimed at strengthening the spinal column and normalizing the central nervous system.
Phytotherapeutic treatment involves the use of medicinal plant materials that have different effects:
- anti-inflammatory - elecampane;
- sedative - peony, valerian, motherwort;
- antispasmodic - chamomile, sage, mint.
Alternative treatments include:
- Acupuncture. The course of treatment is up to ten days, three times a year.
- Medical hypnotherapy.
- Psychotherapeutic methods - sand therapy, autogenous Schulz training, art therapy.
Massage of certain points that are located on the midline of the chest is another non-standard way to treat esophageal spasm. How to shoot it with this method? The locations of the points are as follows:
- under the cervical fossa;
- between the chest;
- between the first and second point (at an equal distance from each).
These zones are massaged with the bones of the fingers, making rotational movements clockwise for five minutes. It is noted that when performing this manipulation, the individual has strong pain. There is an opinion that this is a normal phenomenon, and after twenty minutes of intense exposure to these points, the pain will completely disappear.
All of the above methods give a good result.
Actions for spasm of the esophagus
How to shoot it? In case of chest pain, it is necessary to calm down and lie down. If the spasm does not pass within five minutes, then perform the following steps:
- If you experience pain while eating, drink a glass of plain water.
- Perform the following exercise four to six times - take a deep breath, hold your breath for just two seconds and exhale slowly.
- Take a sedative. In case of its absence, prepare a tea drink with mint or dissolve mint candy.
- If previous manipulations have not yielded results, then the injection of Atropine is indicated.
The main thing is to cope with the panic and remember that there is no threat to life.
Proper nutrition
Treatment of cramping in the esophagus, the causes of which are clarified, is impossible without a properly selected diet. The basic principles of diet include:
- Take food at room temperature no more than five to six times a day, its last meal - at least three hours before bedtime.
- You can’t overeat.
- Dishes are steamed, boiled and stewed.
- Food should not irritate the mucous membrane of the stomach and esophagus. It is preferable to use it in a puree state.
- Strong drinks, spices, marinades, canned food, hot, cold and spicy dishes are banned.
Methods of treating esophagospasm
Various methods are used to treat diffuse spasm of the esophagus:
- Fractional nutrition - up to six times a day in small portions. Chewing food thoroughly. Do not take a horizontal position for two hours after eating.
- Pharmacotherapy - it is auxiliary in nature and is aimed at eliminating the symptoms.
- Cardia expansion with special dilators - use pneumatic or mechanical medical products. A probe is inserted into the stomach, at the end of which there is a special balloon. When it enters the zone of the lower sphincter, they begin to pump air, and then they are removed. As a result, the necessary section of the digestive canal is expanded.
- Surgery - it is indicated in case of inefficiency of the previous method.
- The use of herbal recipes - the use of infusions, the adoption of herbal baths.
For the treatment of symptoms of diffuse esophageal spasm, conservative therapy is indicated:
- "Omeprazole", "Pancreatin" - to reduce acidity.
- "Tserukal" - suppression of attacks of nausea and vomiting.
- "Rennie", "Almagel" - protection of the mucous membranes from the aggressive effects of acid.
- "Nifedipine" - to normalize muscle tone and relieve spasms.
- "Anestezin", "Novocain" - for pain relief.
- "Atropine" - for intravenous or intramuscular administration for emergency care.
In addition, physiotherapeutic procedures are recommended for individuals: electrophoresis, radon baths, induction and microwave treatment. Any motor activity is required.
Duspatalin: mechanism of action, benefits
Under the influence of the drug, only the sphincter of Oddi and the smooth muscles of the digestive tract fall, which distinguishes it from other antispasmodics. Duspatalin relieves the esophageal spasm, which makes it difficult to move the food coma, and also normalizes the natural function of the digestive tract, that is, the medication does not adversely affect intestinal function, since it does not completely suppress contractions and does not violate normal peristalsis.
The main advantages are:
- slow release;
- a constant concentration of the drug in the blood for 15-18 hours;
- selective action;
- the absence of undesirable reactions inherent in other antispasmodics;
- does not accumulate in the body and can be used for a long period;
- in old age does not require dose adjustment.
Thus, the drug "Duspatalin" relieves esophageal spasm due to the sequential launch of the following processes:
- Reduces the permeability of intestinal muscle cells.
- Closes the channel of entry of sodium ions into the cell.
- Prevents reuptake of norepinephrine.
- It has an analgesic effect.
- Relaxes the smooth muscles of the intestines.
- Promotes better absorption of liquids.
- Improves the intestinal tract.
- Eliminates colic, cramping and pain.
Taking this medication allows you to stop the symptoms and at the same time preserve the natural gastrointestinal motility. It is indicated for all types of digestive disorders, which are accompanied by spastic pain.
Alternative medicine
How to relieve esophageal spasm at home? Such a question is often asked to the doctor. It turns out that if the cause of this condition is known, then it is quite possible to deal with this problem yourself using the following effective methods:
- Infusions of flax seeds and anise or mint and plantain. To prepare a drink, take 10 grams of each medicinal plant material and pour 500 ml of water. Before use, filter and add honey.
- If the spasm is caused by stressful situations, it is recommended to drink no more than fifteen drops of tincture of motherwort, peony or valerian before eating.
- They calm and cure spasms of the bath with the addition of an herbal mixture, which includes lemon balm, motherwort, linden, valerian and one of the oils (tea tree, orange or ylang-ylang). The duration of the procedure is no more than twenty minutes.
- Breathing exercises that perform slowly. They help prevent the further development of muscle contraction.
Now you know how to relieve esophageal spasm at home.
Recommendations to patients
If esophagospasm occurs, it is advisable to visit a gastroenterologist. He will prescribe the necessary examinations to exclude his secondary nature. When confirmed, all efforts are directed to the healing of the disease, which provokes a spastic condition. If the reason lies in the malfunction of the nervous system, then measures are taken to normalize it. Most often, personality-oriented therapy is indicated. In addition, a good effect is obtained by spa treatment in the Crimea and on the Black Sea coast.
How to relieve spasm of the esophagus at home? The following tips will be useful for both segmental and diffuse spasm:
- Give the individual warm water. This simple method helps in most cases. The attack goes away, the pain stops.
- If the cause of the spasm is a stressful situation, then the patient is shown sedatives based on herbs.
Self-medication is not recommended, since all of them have contraindications, side effects.
Forecast and Prevention
A spasm of the esophagus, with the symptoms and causes of the development of which you became acquainted with after reading the article, reduces the quality of life of the individual, including in the absence of serious consequences. The prognosis is influenced by such factors as the severity of the disease, the age of the patient, the duration of the symptoms until they seek medical help.
Prevention is an annual examination, which is carried out by a special optical device with an endoscope, as well as the treatment of concomitant gastrointestinal ailments. All patients are shown medical rehabilitation to prevent relapse.