The Ionian order is one of the three most ancient Greek orders. So, it differs from the Doric one, which arose earlier than the Ionic one, with a greater liberty in choosing proportions, as well as in the absence of parts that would not have been decorated. Architects of ancient Greece loved the ionic order and considered it “feminine” because of sophistication and a large number of jewelry.
The main distinguishing feature of the ionic architectural order is the specific design of the capital. The capital consists of two symmetrical volutes (volute is a spiral curl with a small circle in the center).
The exact time and place of occurrence of the ionic column construction is unknown, but it is assumed that this is the middle of the sixth century BC and the northern coast of Asia Minor, respectively. The very first large building that used ionic columns was the temple on the island of Samos, built by Roikos and dedicated to the goddess Hera. Unfortunately, after some time the temple was destroyed by an earthquake.
And the temple of Artemis of Ephesus, which also has an ionic order, as you know, was recognized as one of the wonders of the world. However, he did not survive to this day.
The Ionian order has two aspects: Attic and Asia Minor. The Asia Minor version, in which the frieze is not present, is considered to be the initial one, while the Attic one is sometimes considered not a separate option, but just a modification, a remake of Asia Minor.
The column, according to the principles of building an ionic order, is divided into three parts: the capital, the trunk and the base. The base, as a rule, rests on a square plate called a plinth. Half-shafts (half-shafts are called the convex element of the base) are decorated with ornaments and horizontal gutters. Concave scocia, as a rule, leave smooth.
As already mentioned, the main distinguishing feature of an ionic order is two volatos on capitals. From the front, volutes are curls, and from the sides, volutes are connected by so-called balustrades, which are very similar to scrolls. If at first the volutes were in only one plane, then they began to be made in all four, which, by the way, saved the ionic order from criticism, according to which the top of the column should look the same from all sides - this was originally from Doric, but did not immediately appear in ionic warrant.
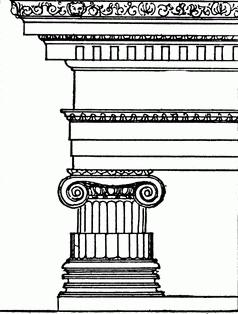
The cut was usually decorated with oats (from the Greek and Latin word meaning "egg"). These are egg-shaped decorative elements, and on the column they alternate with various arrows and leaves. The number of flutes (flute is a vertical groove on the column barrel) in the ionic order constantly changed, but eventually stopped at 24. This value was taken for a reason: this number of flutes made it easy to maintain the proportion of the diameter of the column and flute, even if the height of the column was for some reason overestimated.
If you see two columns, the ionic and the Doric, you will immediately notice that the ionic order looks more elegant. Its construction is based on the basic rule: the height of the column should be at least eight to nine of its diameters. That is why this type of order is so beautiful.