Shingles is known to us as an extremely unpleasant disease that violates the usual way of life due to itching and pain. Almost no one is safe from the manifestation of its symptoms, since the causative agent is a virus that spreads extremely rapidly among people. However, at the present stage of development of medicine, a person not only collected a lot of information about what herpes zoster is, but also developed methods for successful treatment.
The disease itself was known for a long time, the first mention of its symptoms was found back in antiquity, however, due to the lack of technological ability to conduct differential diagnostics, shingles and chicken pox belonged to different ailments: lichen was considered a separate skin disease, while chicken pox could be mixed with other types smallpox. Later discoveries in the field of medicine helped to describe both diseases more specifically and revealed a common pathogen.
General information about the disease
Herpes zoster (according to ICD-10 it is assigned the code B02) can also be called herpes zoster, since it is provoked by the herpes zoster virus - the same that causes chickenpox. Therefore, those who already had contact with viruses and had chickenpox are susceptible to the disease. However, in some cases, the virus can immediately appear in the form of shingles. This is extremely rare and, as a rule, among people with immunodeficiency.
As a rule, the elderly are at particular risk for the appearance of symptoms of shingles in adults. Among children, usually those whose immune system is weakened fall ill. There is also an extremely high risk of contracting shingles in a child with HIV-positive status. The period that is the most dangerous is autumn-winter. At the same time, many people have seriously weakened immunity, so the symptoms of shingles in adults and the treatment of this disease should be under special control in the fall and winter. Particular attention should be given to older people and those who have recently undergone severe treatment. The age from which it is necessary to closely monitor possible human contacts with carriers of chickenpox is from sixty years.
Shingles in a child can occur almost at any time of the year, however, in the fall and winter, you should closely monitor the baby's health, especially if he is often inclined to get colds.
Frequency of occurrence
The frequency of the disease - up to fifteen people per hundred thousand people in the age range from sixty years. Those whose immunity is weakened significantly can suffer the disease again. In this case, the patient already knows what shingles is, and independently limits his contacts with chickenpox. However, the contact of a child who has not had chickenpox with a person suffering from this type of lichen does not pose special risks, as it is manifested by the symptoms of chickenpox.
Virus spreading process
What is shingles? The virus itself is extremely contagious. It spreads both in direct contact with the bubbles on the epidermis, and by airborne droplets. This means that you can, without even contacting the rashes, become infected with an unpleasant disease.
In some cases, transmission of the virus through the placenta may occur. Analyzes of infected babies are subsequently tested for virus activity, after which the babies undergo therapy.
If there is a danger of infection, you need to carefully protect yourself from contact with possible carriers, but remember that most of the pathogenic particles entering the body successfully inactivate the immune system. Therefore, the spread of the virus can be limited by improving the overall health of people, including the promotion of strengthening immunity.
Reasons for the appearance
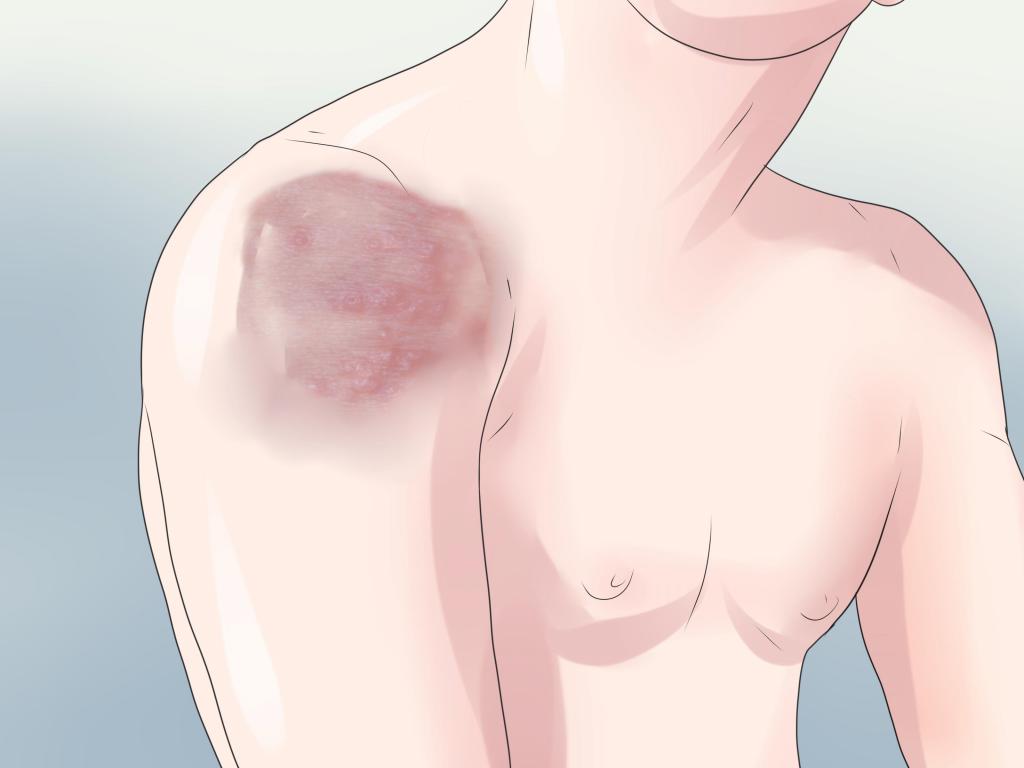
The causative agent of herpes zoster is the herpes zoster virus. The same virus causes symptoms of common chickenpox: blisters on the skin that contain fluid inside and are prone to itching. As a rule, after the disease goes away, a person retains specific immunity to the Zoster herpes virus, and he will not have chickenpox anymore. However, a particle of herpes itself remains in the body in a depressed form for life. And therefore, as soon as immunity begins to act a little less intensively on the virus, the particle wakes up and begins activity. In this case, the manifestation of symptoms of shingles in adults (the photo attached below shows the initial stages of the disease) will not take long.
However, not all people with impaired immunity will suffer specifically from this disease.
In addition to immunity problems, the following factors can influence the awakening of the virus:
- Treatment with drugs with immunosuppressive (immunosuppressive) effects.
- The effect of severe stress on the body, as well as overwork and excessive mental stress.
- Oncological diseases and therapy of these ailments (chemo- and radiation therapy).
- HIV infection in the absence of drugs that inhibit the virus.
With viral immunodeficiency, the manifestations of shingles in adults (in the photo) are practically impossible to treat and arise very quickly. Therefore, we can say that with serious violations of the immune system, herpes viruses are one of the very first to show themselves in the body.
Symptomatology
A photo of the symptoms of shingles in a person can be easily found, however, like most skin diseases, the usual image of the rash does not give a full picture of what the disease looks like in a particular patient. For a more successful diagnosis, a detailed description of each feature of the disease is necessary:
- The very initial stage is characterized by a condition resembling colds and flu: weakness, lethargy, in rare cases, fever. There is also a headache and a slight ache in the bones. The first stage of the disease can be taken for a cold and not take action. However, after the appearance of this symptom in a person, herpes zoster declares itself in the form of rashes.
- 1-2 days after the appearance of lethargy, rashes appear in the body in the form of bubbles. All bubbles are filled with a fluid containing millions of copies of the virus. It is extremely undesirable to independently destroy the vesicles, since they can be additionally seeded with bacteria, which on the damaged skin can cause rapid suppuration. Many people may wonder how tinea shingles. In fact, girdle, as such, does not occur. Bubbles are located either on one side of the body, or along the nerves, or in the intercostal part of the chest. Rashes are localized on one part of the body and, as a rule, do not appear in other places. In the latter case, herpes zoster is encircled as if by lines diverging along the chest. In almost all cases, the vesicles are painful and itchy. The strength of the pain and itching in this case depends on the particular patient, and some admit that they cannot fully perform their usual actions.
- After a week, the bubbles begin to dry out. At first they are drawn in, becoming covered with a crust, but later they form scars, on the side looking like plaques above the skin. Many of the plaques have a lighter color than the skin around. As a rule, complete elimination of the symptoms of shingles in a person with treatment and normal immunity takes from 2 weeks to a month. However, if the patient has a pronounced deficiency of immunity, then the treatment may be delayed for a long time, and the disease itself will be much more difficult.
- However, even if the underlying symptoms of the disease have already disappeared, pain problems can persist for up to several years. This is called postherpetic neuralgia and, unlike the shingles in adults, does not require treatment. But you can apply symptomatic therapy in the form of ointments containing substances from the NSAID group: "Ketoprofen", "Diclofenac", "Nimesulide" and others.
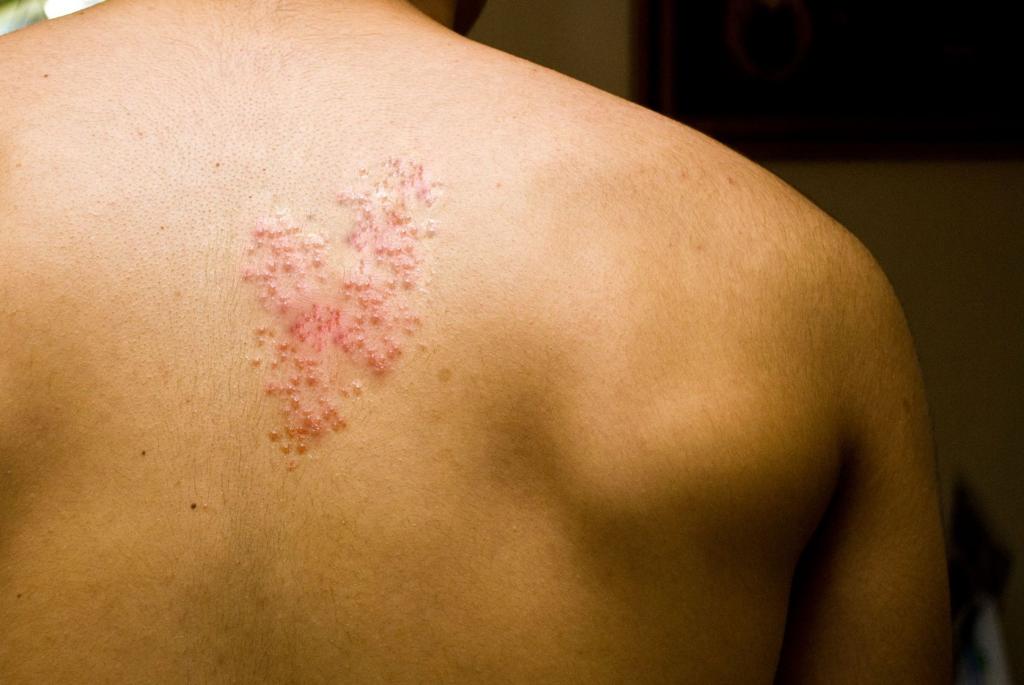
There are also so-called atypical forms of shingles. Atypical is the variation in the development of a disease when its clinical picture is significantly different from that observed most often. In case of shingles, these are the following forms of the disease:
- A form in which rashes and pain are completely absent, however, viral particles are present in the body in an activated state in large quantities.
- The bullous form is characterized by large blisters having irregular edges.
- Bubbles are filled with contents in which bloody spots are visible. As a rule, such vesicles have the ability to leave scars and heal for a long time.
- A necrotic form in which vesicles can contribute to the formation of necrosis of adjacent tissues. It is especially dangerous because healing takes place extremely slowly, and patients at risk of developing this form of the disease are mainly elderly people who have a history of diabetes mellitus.
- Generalized. As the name implies, this form of the disease manifests itself in the fact that rashes do not appear on one part of the body. Bubbles in the generalized form of shingles cover the patient's body as a whole and are visible on both sides of the body.
- A particularly rare, but most dangerous form is encephalitic. It is manifested by rashes in the region of the cervical spine, and the virus can affect the nerves leading to the spinal cord. In especially severe cases, after some time, symptoms of encephalitis begin, which can lead to coma. This is the only form of shingles that can really threaten the patient's life: about 60% of patients with it die. In this case, the principle of timely diagnosis of the disease and the earliest possible start of its treatment is more important than ever.
Symptoms of shingles in the photo can make an extremely depressing impression, which in itself does not contribute to a speedy recovery. Therefore, when the first signs of the disease appear, it is necessary to give the patient information that at the modern level of development of medicine it is successfully treated in a few weeks in the absence of severe immunodeficiencies in the patient.
Complications after an illness
Despite all the treatment for shingles, in adults the symptoms (photo below) may not go away for a sufficiently long time, and in especially severe cases, complications can occur, including significantly undermining the patient's health. These complications affect mainly the nervous tissue, which makes their consequences much more dangerous. But since the virus in the active stage damages the entire body, then all organs and organ systems can suffer from it. In particular, when a herpes acts on the motor branches of nerves, the symptoms of herpes zoster in a person (pictured) may not be treated with treatment, and the pain may persist for up to a year. In particularly difficult situations, the patient may begin to suffer from paralysis.
Also, with damage to the facial nerves, the patient's face may become skewed. Parts of it, such as ears or eyes, may also suffer. In the case of an ear form, the likelihood of disorders of the facial nerves increases significantly. Eyes can be especially badly affected by the disease, a person can even partially lose their vision.
Also, if bacteria are present in the body, then suppuration can form at the site of the formation of vesicles, which will significantly slow down their drying out and, as a result, will delay the final healing for a few more weeks.
In order for the symptoms of herpes zoster after treatment (the photo in the article shows the initial stages of the rash) to disappear faster, it is necessary to start therapy as soon as possible. Ideally, the start of medication should coincide with the symptoms of a cold. However, there are a sufficient number of treatment features that depend not only on the level of immunity, but also on the age of the patient.
In some cases, shingles can be the cause of the development of other diseases:
- Ramsey Hunt Syndrome. This disease affects the peripheral facial muscles, and also manifests itself with abundant rashes in the ear canal.
- Motor and ophthalmic herpes zoster, affecting the nerves associated with muscle tissue and the eye.
Both the listed diseases and individual milder complications can cause serious harm to health. Therefore, it is necessary to protect yourself as much as possible from the possible development of complications, first of all, observing the hospital regimen.
Treatment of herpes zoster (an adult photo attached)
Priority areas of therapy cover several aspects of the disease:
- To accelerate the healing of already existing rashes.
- Perform analgesic therapy to improve the quality of life of the patient during the illness.
- Reduce the likelihood of complications and the development of a severe form of the disease.
- To reduce the likelihood of pain persisting after recovery, since postherpetic neuralgia is extremely difficult to stop.
Before embarking on the therapy itself, it is necessary to tackle the stress that may occur after identifying signs of the disease. Rashes of shingles in adults and children can cause excessive fright, affecting the psychological state of the patient, especially in old age. The first thing to do in this case is to assure the person that modern medicine can treat this disease well enough and there is nothing to worry about. In some cases, mild sedatives may be indicated to help prepare psychologically for therapy. Then you can proceed to treatment. In adults, shingles is not so difficult to cure.
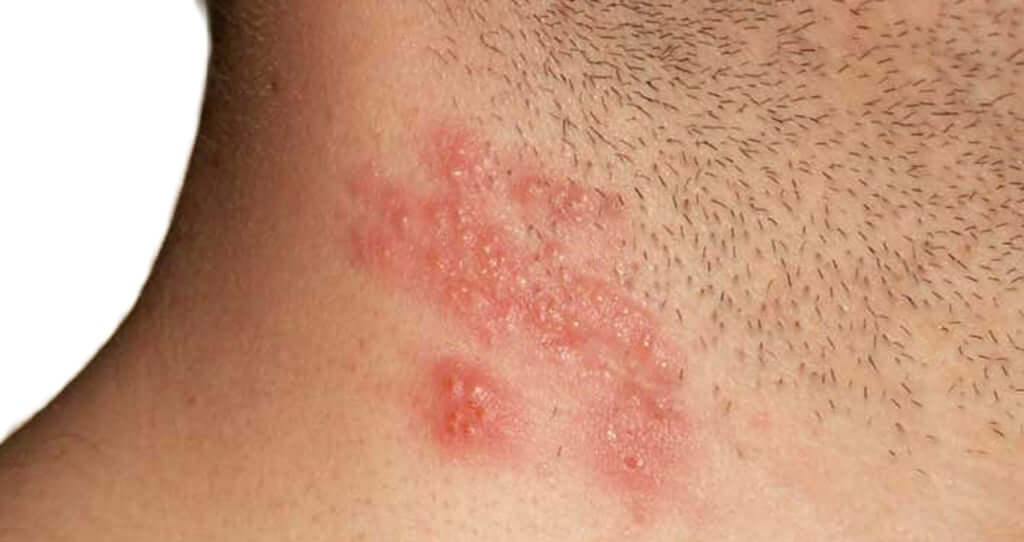
Of course, the primary need is to visit a doctor. It is the specialist who must carry out all the procedures and establish the final diagnosis. Typically, the diagnosis does not take much time, and the doctor can almost immediately determine if the patient has a disease. After this, the treatment itself begins, requiring the use of not only specialized antiviral drugs for herpes zoster, but maintenance therapy in the form of vitamins and painkillers to relieve severe pain. Antiviral drugs and antibiotics should be distinguished: the former are the drugs of choice for viral skin diseases, and the latter are only required if bacterial seeding appears in the rash and there is a risk of suppuration.
Remember that the virus is successfully carried by the wind, and the discharge from the vesicles on the skin contains many copies of the virus particles. Therefore, it is highly advisable to observe the hospital regimen during treatment and not to visit crowds of people unless absolutely necessary. This will help not only protect others from infection, but will also help stabilize the patient’s immune system. It is necessary to explain to the patient that, in addition to the aesthetic factor, there is also a risk of transmitting the virus to other people.
Painkillers are symptomatic therapy that helps the patient return to normal. It is competent anesthesia that helps to get rid of pain at the rash site, which can interfere not only with comfort, but also with breathing or movement. As painkillers, drugs from the NSAID group are used: Diclofenac, Ketoprofen and others. However, in some countries, such as the United States, the use of narcotic analgesics for the relief of very strong pain, as well as in the treatment of patients with severe forms of shingles, is allowed.
The main medication used to treat shingles is antiviral drugs. The drugs of choice, in this case - “Acyclovir”, “Valacyclovir”, “Famciclovir” and their analogues from the same drug group. Their action is based on the incorporation of the drug molecule into the DNA of the viral particle and the complete stop of its reproduction. All drugs from this group act similarly, the difference between them is the speed of suppression of viral particles. At the moment, antiviral drugs are the most well-known and effective medicines in the fight against diseases caused by the herpes virus.
, . , . , . , ( ), . .
. , , . . .
, , . .
, , , . , , . , , , .
In humans, shingles can only occur if the virus itself is already present in the body. This means that the child had previously had chickenpox, and re-infection with reduced immunity occurred. The second factor that can cause this disease in a young organism is the presence of immunodeficiencies that contribute to the activation of viral particles, which should normally be suppressed by the immune system.
In children, the symptomatology is characterized by a greater lubrication of manifestations than in adult patients, therefore, the doctor’s control is even more necessary than in case of detection of the disease in an adult.
As a rule, a child is treated on an outpatient basis, that is, without hospitalizing in a hospital. However, in the case of a severe course of the disease, hospital conditions may be required. This is especially important for children who are diagnosed with immunodeficiency. Any viral disease in this case can face serious consequences, and therefore such children are observed only inpatiently.
Treatment is carried out according to a scheme similar to that for an adult; only the dosages of the drugs used change. And yet, in children it is undesirable to use painkillers from the NSAID group, since they have negative side effects that can cause serious violations of the gastrointestinal tract in the child. Treatment of a child must be prescribed and supervised by a pediatrician.
Diagnostics
All diagnostic procedures, as well as treatment, for shingles are carried out by an infectious disease doctor. As a rule, the diagnosis of the disease is quite simple, since the symptoms are pronounced on the skin of the patient in the form of rashes. However, in some cases, laboratory diagnosis may be required. It is carried out mainly in infants or children with immunodeficiencies. If a herpetic infection occurs in an atypical form, then laboratory tests may be urgently needed.
Basically, in the diagnosis in the laboratory, methods for detecting antibodies to the zoster herpes virus are used. In the case of the appearance of vesicles on the skin, the PCR method is used, with which a sample of secretions taken from the vesicle can be analyzed. But the PCR method is used much less frequently, while the detection of antibodies in the body is used, including with suspected infection of the child with a virus in the womb. PCR is the most applicable in the presence of a disease that gives a rash on the internal organs and does not give external manifestations.
During diagnosis, shingles should be differentiated, that is, separated from other possible skin diseases, including the viral nature: herpes simplex, eczema and chickenpox. However, most doctors know what shingles are, and as a rule, there are no difficulties in determining the diagnosis.
Preventive measures and prognosis after illness
Currently, pharmaceutical companies are developing several vaccines designed to protect people from infection with the herpes zoster virus. However, they are rarely used, since the vaccine is live (that is, it contains weakened, but living virus particles of another virus similar in structure to herpes zoster in structure) and can adversely affect the health status of patients with weakened immunity. Also, some antiviral drugs taken by a person during treatment for other diseases can weaken the effect of the vaccine or completely inactivate it.
The main preventive measure for shingles now is to protect the patient at risk of infection from potentially ill people as much as possible. It is best not to let people with immunocompromised children suffer from chickenpox, in order to avoid infection.
It is also extremely important to comply with the doctor's recommendations during the treatment of diseases that can lead to immunodeficiency. If a patient is diagnosed with HIV, he needs to take drugs that suppress the virus on time and observe consistency in the implementation of the treatment regimen. At the moment, it is HIV patients that make up a rather significant part of the total number of cases of shingles.
You should also try to reduce the influence of all factors that can lower immunity, including stress loads. You need to eat right and have regular exercise. This helps to keep your body in good shape and helps strengthen the immune system, which, in turn, helps to keep most of the conditionally pathogenic viruses in the body suppressed.
If all of the above tips have been followed, then the likelihood of contracting shingles is reduced to a minimum. However, it should be understood that regular medical examinations help to detect the disease at an early stage, even if the virus manifests itself, despite the efforts. Early treatment helps to recover more quickly and minimize the possible consequences of the disease for the patient.
But even if the symptoms of the disease have manifested themselves, there is no need to worry: uncomplicated shingles usually go away in a few weeks and the reappearance of the disease is extremely unlikely if the patient does not suffer from severe immunodeficiency conditions.
A disease is nothing that a person should be afraid of without concomitant disturbances. However, in some cases, it can cause serious harm, and therefore, if dangerous signs appear on the body, it is necessary to immediately diagnose the general condition of the body and urgently begin treatment in case of identified problems.
For patients with HIV, shingles is a certain danger, however, if you go to the hospital on time and follow the doctor’s recommendations exactly, you can recover completely.