Today, the diagnosis of syphilis is becoming an everyday activity in the practice of doctors of all specialties. Every year, the number of people who have secondary syphilis increases. According to numerous forecasts, an increase in the number of late forms of the disease that provoke a violation of the nervous system and internal organs is expected in the coming years. Secondary pathology begins to develop three months after infection of a person. It manifests itself in the form of a rash with a large number of vesicles, papules and pustules throughout the body. This is due to the fact that the infection begins to spread throughout the body with a blood stream, affecting the internal organs and systems of the body.
Description and characteristics of the disease
Syphilis is one of the STDs that has a chronic course. The causative agent of the disease is pale treponema. This disease goes through three stages of development: primary, secondary and tertiary. Secondary syphilis is the second stage of the development of pathology, which begins to manifest itself in the third month after infection of a person. During this period, the pathogen spreads rapidly throughout the body, affecting all organs and tissues, as well as the central nervous system. The main sign of pathology is the spread throughout the skin and mucous membranes of rashes in the form of papules, vesicles and other formations.
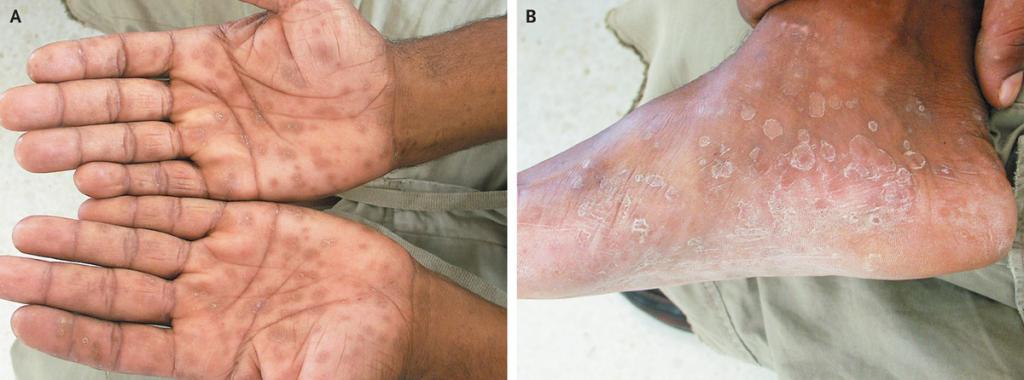
In the presence of healthy immunity, pale treponema forms cysts in which it is in a passive state, which characterizes the latent period of the development of pathology. In case of a violation of the immune system, the pathogen activates and acquires a pathogenic form, a person has secondary recurrent syphilis. This stage of syphilis can occur for several years, periods of remission alternate with relapses. In this case, skin rashes are observed in a person for several months, after which they disappear on their own for a while, and then reappear. Many doctors theoretically allow a spontaneous cure for a disease that depends on the functionality of the human immune system.
Causes of the disease
The causative agent of venereal disease is Treponema pallidum. Infection of a person occurs with the penetration of treponema through the skin (the integrity of which is impaired), during sexual intercourse or through a contact-everyday way. Some doctors talk about the possible penetration of pathogenic microorganisms through intact mucous membranes.
Secondary syphilis in men and women can occur in a latent form and can be accidentally detected only with a planned diagnosis. In some cases, the disease at the first stage does not show symptoms, therefore, a person is immediately diagnosed with a secondary pathology.
The causative agent of infection is able to survive only in the human body, outside it it is sensitive to the influence of environmental conditions, therefore, it dies when exposed to ultraviolet radiation and chemicals, high temperatures, but low temperatures do not have any effect on it.
Classification of Secondary Syphilis
The disease goes through three periods of development:
- Fresh disease (observed after primary syphilis) lasts about four months. It is characterized by the appearance of a small rash.
- A hidden ailment is caused by the disappearance of signs and lasts about three months.
- Recurrent secondary syphilis, in which the period of remission is replaced by a relapse. The rash appears again, but it is less pronounced and has a larger size. At this stage of the development of pathology, a person begins to lose hair. The number of relapses during the period of the disease of secondary syphilis reaches four.
Symptoms and signs of the disease
Typically, a secondary disease begins to show signs that are similar to symptoms of acute respiratory viral infections: an increase in body temperature, malaise, the development of myalgia. Seven days after this, benign rashes on the skin are observed, which have a round shape, clear boundaries, and sometimes itch. The disease contains a large number of pathogens, so a person is a danger to others, as it can easily infect them.
Skin lesion
Signs of secondary syphilis are manifested by a rash, which can be of several types:
- Roseola (spotted syphilis) - round pink spots up to ten millimeters in size. The formations are most often located on the limbs and trunk, they appear in groups of twelve pieces a day for one week. Sometimes roseola can peel off, become covered with scales or rise above the skin, resembling blisters. Small red nodules on the hair follicles, large erythematous spots due to the fusion of the elements of the rash can also be observed.
- Papules of pink or red hue, reaching sizes up to five millimeters. The central part of the papules begins to peel off after a certain time, then peeling spreads to its edges. After the disappearance of papules in their place appears hyperpigmentation.
- Pustules occur infrequently. Typically, such formations are observed in alcoholics and drug addicts, as well as patients with tuberculosis. Rashes are characterized by suppuration, which eventually dry out, forming a yellow crust.
- Pigments (leukoderma) develop on the neck in the form of round white spots. They are formed as a result of the action of the pathogen of infection on the nerve plexuses in the neck, which are responsible for the production of melanin.
Often with this disease, the structure of the nail plates is disturbed. Papules or pustules form in their bed, which cause pain and inflammation. In this case, the nails fade, thicken and crack.
Symptoms of secondary syphilis are also manifested in an increase in lymph nodes, which do not cause pain, hair loss, damage to the epithelium of the oral cavity and larynx. On the part of internal organs, an increase in the liver occurs, gastritis develops, the activity of the digestive tract is disrupted. The patient develops nephrosis, meningitis, periostitis, sleep disturbance. Sometimes a person develops otitis media, retinitis, pleurisy. When there is a suspicion of syphilis, it is urgent to contact a medical institution, as a person is a carrier of infection.
Syphilis baldness
Hair loss with this pathology can be of several types:
- Small focal alopecia appears as a result of exposure to toxins on hair follicles. In this case, the hair falls out on the head and eyebrows in small bundles. Eyelashes also often fall out.
- Diffuse alopecia appears due to the influence of the pathogen on the hypothalamus, endocrine and autonomic nervous systems, which are responsible for the nutrition of hair. In this case, a person completely falls out all the hair throughout the body.
With effective treatment, the hairline is completely restored within two months.
Damage to the epithelium and internal organs
Rashes on the mucous membrane of the oral cavity often cause transmission of the infection with a kiss, the use of hygiene products and cutlery. The causative agent of the infection affects the tonsils, palate, larynx, tongue and surface of the cheeks. Because of this, a person often has hoarseness, swelling of the tonsils without the development of pain when swallowing.
The defeat of the internal organs occurs without symptoms, therefore, their pathology is detected only during the diagnosis. Secondary syphilis affects all internal organs, causing the development of many other diseases.
Survey
The disease has a variety of symptoms. In medicine, it is recommended that all people who have a diffuse rash in combination with multiple lesions of the body’s glands receive an analysis for syphilis. For this, a detachable mass on the skin is examined and an RPR test is performed. It is also possible to conduct a biopsy of the lymph nodes, puncture of cerebrospinal fluid during the relapse. These diagnostic methods can identify the causative agent of infection.
With symptoms of damage to internal organs, additional consultation with a urologist, neurologist, otolaryngologist, gastroenterologist and others is required. As an additional diagnosis, ultrasound, radiography, gastroscopy, pharyngoscopy, CT are prescribed.
Pathogen test
The doctor also prescribes a test for syphilis, which shows serological reactions, such as RPHA or RIF. You can take it both in specialized clinics and in state medical institutions. In the latter case, the analysis is free, but the time it takes to get the results can be long, and not all hospitals have the appropriate equipment. If you need a quick result, it is recommended to contact a private laboratory.
Such a study is mandatory for pregnant women, as well as for employees of certain professions, for example, medical cooks or military personnel. Also, the test is performed before surgery. To test for the presence of infection, venous blood is taken.
Differential diagnosis
Since rashes with syphilis are similar to a rash characteristic of other skin pathologies, differential diagnosis is necessary to make an accurate diagnosis. The doctor differentiates secondary syphilis with diseases such as typhoid, smallpox, toxicoderma, psoriasis, tuberculosis, lichen planus, ecthyma, impetigo, genital warts, HPV, stomatitis, glossitis, as well as tonsillitis, thrush, leukoplakia and others. Based on the results of a comprehensive diagnosis, a tactics for treating pathology is being developed.
Therapy
Treatment of secondary syphilis involves the use of the same medications as with the primary disease. Most often, this is a penicillin antibiotic, which is prescribed as an injection. Treatment is carried out in a hospital, drugs are administered within 24 days. With penicillin intolerance, tetracyclines can be used. Therapy of secondary syphilis also includes the use of the following medicines:
- Immunomodulators.
- Antihistamines.
- Vitamin complexes.
- Probiotics.
Rashes on the skin are treated with antiseptic solutions or iodine. With damage to the internal organs, symptomatic treatment is used. Failure to comply with the doctor's prescriptions or premature termination of drug use causes the pathology to go to the next stage, in this case tertiary syphilis develops.
Forecast
Secondary syphilis is well treated, so therapy gives positive predictions and results. In the absence of treatment, complications begin to appear, and after them the third stage of the pathology, which leads to death. Modern medicine has enough funds for the successful treatment of the disease.
Prevention
Prevention of secondary syphilis should be carried out in the following areas:
- preventive drug therapy;
- use of contraceptives;
- emergency treatment of primary syphilis.
For the purpose of prevention, it is necessary to monitor personal hygiene, use your own cutlery. It is also recommended to periodically take tests for the presence of infection and undergo a medical examination once every six months.
For the purpose of prevention, doctors recommend:
- have one sexual partner;
- Do not enter into casual intimate relationships;
- do not contact the carrier of infection;
- Do not use other people's hygiene products, household and cutlery;
- do not use drugs;
- periodically undergo examination by a doctor;
- Do not pierce, tattoo without the use of antiseptics.
When symptoms of the disease appear, it is strictly forbidden to engage in self-medication. In specialized medical institutions, preventive measures are taken to prevent transmission of the infection by domestic means. For this, the genitals must be treated with special disinfectants, then a special solution is injected into the urethra.