Lumbar spinal disc protrusion has been diagnosed quite often recently. The provoking factors for the occurrence of pathology are different. Next, we learn what protrusion of the disc is. The treatment of what is happening, the stage of formation, causes - all this will also be considered in the article.
General information
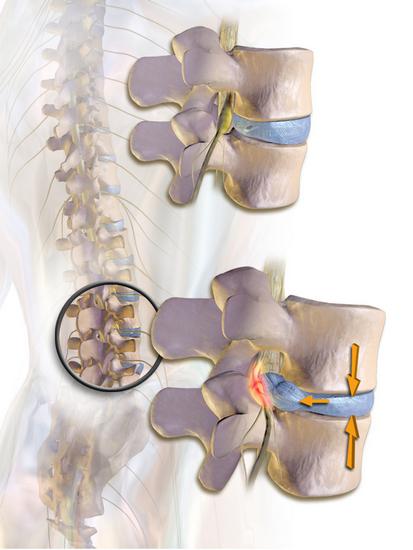
First you need to determine what protrusion is. This is a protrusion of the tissues of the spinal disc without tearing the fibrous ring. It should be noted that pathology has significantly rejuvenated over the past ten years. Daily stress most affects the condition of the lumbar vertebrae . Many people probably had to feel leg pain and fatigue at the end of the day. When you take a horizontal position, you can quite clearly feel the discomfort in the spine, diverging throughout the body. Very often, these phenomena are the first signals of the development of a pathological condition. Today, protrusion of the lumbar spine is not considered an independent pathology. Experts define it as one of the stages in the development of osteochondrosis. In addition, protrusion of the lumbar spine discs is recognized by many as the onset of hernia formation. The sooner the patient consults a specialist, the more chances there are to do without radical methods in therapy.

Protrusion of the lumbar spine: stages of the disease, causes
As mentioned above, more pressure is exerted on this area than on others. Excessive loads provoke changes in the structure of elements. Under daily pressure, disks break down: they lose elasticity and flexibility. This leads to their bulging. As one of the main reasons for the appearance of pathology, experts call physical inactivity. Due to a sedentary lifestyle, dystrophic processes begin to develop, fraught with very serious consequences. Also, protrusion of the disc of the spine of the lumbar can be triggered by trauma. As a result of mechanical damage there is a violation of the structure of structural elements. In the absence of timely and adequate treatment, osteochondrosis can take a neglected form, which is manifested by protrusion of the intervertebral discs. Quite often, pathology is detected in the elderly. This indicates a change in the structure of the spine over the years. A provoking factor here, again, is a decrease in activity.
Of particular importance are pathologies that have left, to one degree or another, an imprint on the condition of the spine. Also contribute to the appearance of a pathological condition:
- Weakened muscle corset.
- Improper posture.
- Infectious lesions.
- Failures in metabolic processes.
- Continuous physical activity.
- Heredity.
Stages of development
Protrusion of the lumbar spine disks goes into the hernia very imperceptibly. The first stage is characterized by violations in the functioning of the nucleus. In this case, the fibers of the fibrous ring are gradually destroyed, cracks appear. The pulpous nucleus then begins to change position. The next stage is characterized by protrusion of the nucleus beyond the ring by 3 mm. At the last stage, the bulging can be up to 4 mm. Subsequent bulging of the nucleus is accompanied by compression of the vessels and nerve roots located nearby. Soreness begins to develop, lumbago appears. With a protrusion of 5 or more millimeters, they speak of a hernia. At this stage, the fibrous ring is often broken.
The consequences of pathology
Why is it important to detect protrusion of the lumbar spine in a timely manner? Why are they dangerous? The main problem is that before the bulging reaches a certain size, the pathology does not manifest itself. Only with the beginning of the pinched nerve roots, the appearance of soreness, people go to the doctor. As a rule, the patient gets to the specialist when the second, and sometimes the third stage takes place. This, in turn, entails prolonged therapy, and in some cases radical measures. If you do nothing at all or self-medicate, then the risk of disability is high.
Clinical picture
How is protrusion of the lumbar spine manifested? Symptoms (treatment will depend on their intensity) come down to discomfort and pain. They differ in their distribution depending on the stage of development of the pathology. Pain appears in the damaged segment and constantly torments the patient. In the course of the development of pathology, they spread to the limbs. After physical exertion, severe but temporary pain occurs in the area of the affected segment. In addition, it is noted:
- Tingling and cramps in legs and feet.
- Radiculitis in the lumbosacral area.
- Sensory skin disorder on the outside of the leg.
- Muscle weakness (especially felt in the lower extremities).
- Lumbar stiffness.
In severe cases, dysfunction of urination may be noted. This is a fairly serious complication of the pathology, and you need to see a doctor. Disc protrusion in the cervical region is manifested by soreness in the neck and neck area, extending to the forearm, shoulder, fingers and hand in general. Darkening in the eyes, dizziness, numbness in the upper extremities are also noted. Against the background of pathology, stiffness of the neck, weakness in the hands are observed.
Diagnostic measures
The main stages of identifying a pathology are:
- Inspection of the patient, during which the degree of sensitivity of the areas of the back and limbs is checked. Motor and neurological tests are also performed.
- Collection of medical history, including family.
- X-ray of the spine.
- CT or MRI. These procedures are performed to assess the state of the vasculature and determine the degree of muscle atrophy.
- Myelography It is necessary to exclude stenosis in the spinal canal.
- Electromyography. The procedure is performed to detect compression in the nerve roots.
- In some cases, spinal fluid puncture may be prescribed.
During the examination, differential diagnostics are carried out to exclude bone tuberculosis, oncology, ankylosing spondylitis, circulatory disorders in some arteries.
How to treat protrusion of the spinal disc?
Adequate therapy can only be prescribed by a specialist. The selection of the treatment regimen is carried out in accordance with the neglect of the condition (bulging of the disk). At 3-4 mm, bed rest and therapy in a hospital are recommended. Conservative methods are aimed at eliminating soreness and inflammation, relieving swelling and improving blood supply, reducing vascular spasm and restoring the functions of the spine and muscles. For these purposes, the following medications are recommended:
- NSAIDs. This category of drugs includes such drugs as Xefocam, Ortofen, Ketoprofen, Movalis, Indomethacin.
- Muscle relaxants. Among these drugs should be noted Midokalm, Orfenadrin, Diazepam, Metaxalon. In most cases, when taking these drugs against the background of elimination of muscle spasm, the intensity of pain is significantly reduced.
- Glucocorticosteroids. This group includes medications such as Methyl Prednisone, Phlosterone, and Diprospan. These funds are prescribed in the absence of the effect of NSAIDs and muscle relaxants. The most effective method of eliminating soreness is injection into soft tissues in the area of nerve compression.
- Chondroprotectors. This group includes funds such as Aflutop, Arthra, Structum. These medications can be given as injections into the intervertebral zone or orally for an extended period.
- Blood circulation enhancers. These drugs include drugs such as Actovegin or Trental.
Additional funds
More recently, enzyme therapy has begun to be used. In this case, apply such drugs as "Karipain", "Chymotrypsin". This method involves the course of the introduction of drugs using electrophoresis. Due to this, the tissue of the pulpous nucleus splits, and the disk assumes a normal position. During therapy, the patient is recommended B-group vitamins as injections into the muscle. External agents are also used: plasters, creams, lotions and compresses with bischofite and dimexide.
Physiotherapy and other methods
Additionally, a specialist can prescribe procedures such as:
- Manual or vacuum massage.
- Manual therapy.
- Exposure to dry heat.
- Reflexotherapy
- UHF
- Hydromassage treatments.
- Laser Therapy
- Swimming, exercise therapy, gymnastics. These procedures are prescribed after the main treatment course. Dates and intensity of classes are indicated by the doctor.
- Magnetotherapy.
Folk methods
They are used as an additional effect and allow to consolidate the results of conservative treatment. Among the most popular folk recipes, the following should be noted:
- To speed up blood circulation and relieve inflammation, tincture of 300 g finely chopped garlic per 150 ml of vodka is used. Stand the mixture for ten days. After this, the pulp should be applied to the affected area, fixed with cellophane and a towel. After half an hour, the compress is removed. If burning sensation is felt earlier, then the slurry should be removed from the body and wash your back.
- For any pathology of the spine, turpentine baths are considered effective. Course - at least 10 procedures. Baths help relax muscles, relieve spasm in blood vessels, increase blood flow to segments of the spine.
- Kalanchoe reduces swelling and inflammation. The sheet needs to be slightly beaten off with a knife and tied to the back in the form of a compress for the night.