Farah disease was first described in the 30s of the twentieth century. This is a hereditary disease (calcification of cerebral vessels). Most often, this is the name of a group of pathologies in which areas of the brain and its vessels are affected. Calcium salts are deposited in the walls of small arteries, capillaries. Farah syndrome is observed at the age of about 40-50 years, but cases of its earlier manifestation are also known.
Neurodegenerative disease group
This group of diseases is characterized by damage to the central nervous system. A certain number of neurons die, and this leads to neurological pathologies. Neurodegenerative diseases can have different causes and different clinical manifestations. It is characteristic that all diseases of this category are incurable. All therapy that is used is symptomatic. That is, it facilitates the manifestation of the disease, but does not contribute to the regeneration of damaged areas. Nerve transplantation would be most effective, but the method has both technical and moral obstacles. Such diseases include Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, Farah. As a rule, the diagnosis of such diseases in the early stages is difficult. Most often, when making a diagnosis, specialists rely on patient complaints and results of observations of their behavior. But the main tool is tomography (computed, magnetic resonance).
Symptoms of the disease
Since this disease is a rather rare phenomenon, it is difficult for specialists to provide the correct clinical picture of the syndrome. Symptoms may occur if the patient is over 40 years old. In younger people, Farah disease symptoms may be blurry and fuzzy. Patients have impaired coordination of movement, parkinsonism. Also, signs of tremor, dystonia, fast and irregular movements of the limbs (chorea), involuntary contractions of the hands, feet can testify to the development of the disease. Since the disease affects areas of the brain, it decreases working capacity, mental capabilities. Human memory also suffers. Often speech is disturbed. Other neurological signs include pain, mental disorders. There are juvenile forms of the disease, which is manifested in children and adolescents. The main symptoms are: dystonia, chorea, seizures of epilepsy. The senile form is characteristic of people of middle and older age. In this case, Parkinsonism, speech disorders, other problems in the functioning of the nervous system are observed. Urinary incontinence may also occur.
Possible causes of Fahr syndrome
The reasons for the development of the disease are not precisely established. However, it is known that the thyroid and parathyroid glands have a huge impact on its occurrence . In this case, interruptions in the metabolic processes of calcium and phosphorus occur. Similar neurodegenerative diseases can also occur with violations of the acid-base balance in the body. Alkalosis leads to a significant loss of acids. But alkaline compounds are present in excess. There is also an opinion that Farah syndrome manifests itself in genetic disorders. That is, a gene mutates, which is responsible for the exchange of such an element as calcium. However, this version has many contradictions. Isolated cases are known when the symptoms of the disease appeared after irradiation of the head region, poisoning with poisons, lead, in children with Down syndrome. Also, calcification was diagnosed in people who have had rubella (rarely). Another possible cause of calcification of the basal ganglia is birth trauma.
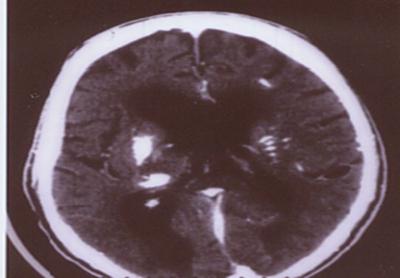
Research Methods for Diagnosis
Before the appearance of computed tomography, patients underwent x-ray studies of the brain. Thanks to the advent of modern research methods, specialists received more informative pictures from the affected area. However, it is worth noting that computed rather than magnetic resonance imaging has greater sensitivity in this clinical picture. In the analysis of most images, the affected areas are limited to a pale ball. They are small in size. Most often, the basal ganglia, thalamus, cerebellum suffer changes. The level of calcination is approximately the same in young people and in elderly people. Also, no differences were found between groups in which Fahr’s disease is asymptomatic and those where the syndrome is accompanied by pronounced signs.
Histological examination
When conducting a post-mortem examination in the brain, the following picture is observed: the vessels have a whitish appearance (some branched areas). When they touch the knife, they make a sound similar to a crunch. For histological analysis, a material is taken: sections of the cerebral cortex, basal ganglia, cerebellum. It is in the field of the latter that calcification occurs most often. Calcium salts are present on the samples. Also, most often they are detected on the arteries (small, medium), capillaries. Less commonly (isolated cases), Farah disease affects the veins. Along the entire length of the vessels, as well as in adjacent tissues, calcium conglomerates of small sizes are found. Traces of arsenic, aluminum, cobalt, and mucopolysaccharides are also distinguished in tissues.
Establishing diagnosis
Depending on whether the Farah disease has symptoms, the diagnosis may be somewhat difficult. Often, she is diagnosed by accident, performing a tomography scan to confirm a completely different disease. First of all, the specialist eliminates the violation of calcium metabolism, other malformations. Then computed tomography (or X-ray studies) is prescribed. Doctors say that one of the problems in making the correct diagnosis is hypoparathyroidism. This is a disease that occurs with parathyroid hormone deficiency. As a result, the level of calcium in the blood decreases, and the level of phosphorus increases. If calcification of striopallidotooth structures is observed with computed tomography, then additional tests are needed to distinguish hypoparathyroidism from a condition such as Phar's disease. First of all, it is important to determine the level of parathyroid hormone and calcium. Also, when diagnosing, a parasitic lesion of the nervous system is used. Specific reactions occur in the blood, cerebrospinal fluid. Infrequently, Farah's disease differentiates with a condition such as Bourneville sclerosis.
Treatment
Removing accumulations of calcium that have formed in the brain and its vessels is not possible. As a rule, the treatment of such a disease is symptomatic. First of all, it is aimed at improving the metabolism of calcium and phosphorus in the body. If symptoms of Parkinson's disease are observed , then the specialist prescribes special drugs (levodopa). Also, Farah’s disease, the treatment of its manifestations, involves the use of antioxidants, drugs to improve metabolism. Therapy with calcium channel blockers is ineffective. It is worth considering the fact that the disease is quite rare and poorly understood. In most cases, therapy alleviates the symptoms of the disease, but does not affect the degree of calcification.
Predictions for the disease Headlamp
Since this condition disrupts the metabolism in the brain, as well as calcium salts have an irritating effect on its tissue, Farah's disease forecasts are very mixed. The disease progresses slowly, with age, calcium deposits increase. Of course, all this does not happen in one year. As a rule, neurodegenerative diseases progress for several decades. The main problem is the lack of information on this condition, as well as the lack of specific treatment. Therefore, therapy is aimed at improving the quality of life of the patient. Another negative point - the disease is poorly diagnosed in the early stages.