Many young mothers are worried about the skin color of the newborn, and when the pediatrician in the hospital diagnoses that the baby has jaundice, they all panic. In fact, this symptom is a physiological condition that occurs in the majority (from 40 to 70%) of healthy full-term children. In some cases, however, it can be pathological. How exactly does physiological jaundice of a newborn occur, when it passes, does it require treatment - we will understand.
Description of the physiological symptom
Jaundice staining of the skin, sclera of the eyes and mucous membranes of the child that occurs in the first two to four days of life, in medical practice is called physiological jaundice of the newborn. The causes of this condition, as indicated by the word "physiological", are natural, but some cases still require treatment.
Jaundice occurs due to immaturity of the liver enzyme systems. In this case, other symptoms, which are usually characterized by a protein deficiency that ensures the transfer of bilirubin through liver cells, are not observed. Such symptoms include anemia, an increase in the size of the liver and spleen, and hemolysis.
Physiological jaundice occurs in newborns in the norm in almost 60-70% of cases. But in premature infants, the condition is more common, the symptom is more pronounced, jaundice lasts longer. If the child’s skin and mucous membranes are very colored, the doctor may recommend appropriate treatment.
Brief classification of jaundice
There are several types of symptom:
- jaundice of full-term newborns;
- premature babies;
- hereditary, arising from endocrine pathology;
- jaundice in children with birth injuries and asphyxia;
- medication, which is due to the appointment of large doses of vitamin K, chloramphenicol, quinine and other things.
There is also pregnan jaundice, which occurs in children who are breast-fed, in the first week of life or on 7-14 days after birth.
Diagnosis of a physiological symptom
The physiological state of the baby is diagnosed during a stay in the hospital by a neonatologist, the first examining baby after birth, or a pediatrician. A visual assessment of the condition of the child uses the Cramer scale. So, the first degree is characterized by yellowness of the face and neck, the second - the spread of a yellow tint to the navel, the third - to the level of the knees. With the fourth degree, jaundice covers the entire body of the baby, but excluding the palms and soles of the feet, with the fifth newborn, all is painted in "autumn" colors.
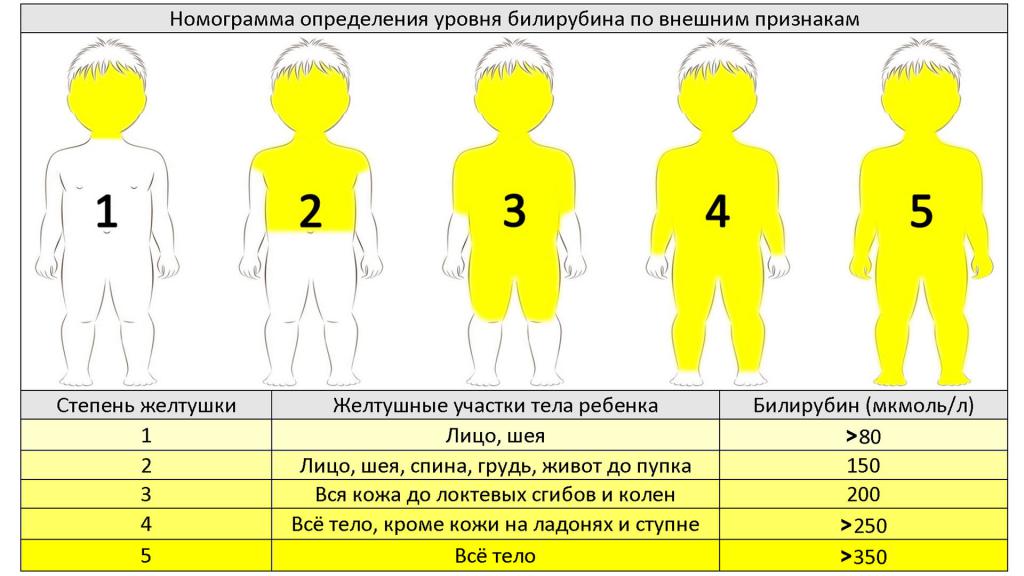
The bilirubin norm is determined as part of the diagnosis of physiological jaundice in newborns. In the first degree, its content does not exceed 80 μmol per liter, in the second - 150 μmol / L, the third - 200 μmol / L, the fourth - 300 μmol / L, the fifth - 400 μmol / L. A mother and baby blood test, liver tests, and urinalysis are also taken. Ultrasound diagnostics of the liver, bile ducts, abdominal x-ray can be performed.
Mechanism of occurrence
The physiological jaundice of the newborn develops as a result of the immaturity of the enzyme systems of the liver, as mentioned above. This is not a disease, but a marker of certain physiological processes that occur in the baby’s body, adapting to new conditions of life after the mother’s womb. But in order to accurately understand the causes of physiological jaundice in newborns, it makes sense to recall a few paragraphs of the school biology course.
Red blood cells - red blood cells that are contained in human blood, carry oxygen and carbon dioxide throughout the body. Every day, a small part of the red blood cells dies (the life of each cell is no more than 4 months), and when they are destroyed, bilirubin is released - the yellow pigment involved in the exchange of hemoglobin.
Bilirubin is a dangerous substance that is toxic to internal organs. As soon as it enters the liver, enzymes neutralize it. The process of destruction of the decay product of red blood cells in medical practice is called conjugation of bilirubin. After this, the substance is excreted from the body using the excretory system.
Violations in this chain of formation and excretion of bilirubin lead to the accumulation of this substance, as a result of which the yellow pigment penetrates the skin. This is the pathogenesis of physiological jaundice in newborns.
If it was not about babies, but about older people, then the symptom should be considered as a pathology, a sign of serious liver disease, intoxication or acute hepatitis, poisoning, inflammation of the gallbladder. In the case of children, this is due to the immaturity of the liver systems.
Causes of jaundice in newborns
Many reasons can lead to an increase in the level of bilirubin, but the main one is considered to be the increased number of red blood cells that are necessary for the normal functioning of the fetus in utero (they quickly collapse after birth, which is accompanied by excessive release of yellow pigment), as well as immaturity of the baby’s liver, which is why deficiency of protein excreting bilirubin.
Among the causes of physiological jaundice in newborns can be called the late departure of meconium, hypothermia, starvation. A good prevention of jaundice is early attachment to the chest, frequent feeding. Colostrum acts as a laxative, so it helps meconium get out of the baby’s body as soon as possible and remove bilirubin.
Causes of pathological jaundice
In addition to physiological, there is also pathological jaundice. This condition occurs in 50-70 children per 1000 newborns. The main reasons for the development of this type of jaundice are:
- Congenital infectious diseases requiring long-term therapy.
- Premature birth.
- Hemolytic disease, that is, the incompatibility of the mother and child by blood group or Rh factor.
- Birth from a mother with diabetes, including gestational.
- Various small hemorrhages in the baby that appeared during childbirth.
- Swallowing blood, for example, from cracks in the nipples of a nursing mother.
- The introduction to the woman during childbirth of certain drugs, the baby - antibiotics.
- Congenital biliary tract disease. In this case, the stool is also discolored and the urine is stained.
Within normal limits or pathology
The physiological jaundice of a newborn is usually the norm. A high level of hemoglobin at birth sharply begins to decline under new conditions, so that the baby’s body does not have time to adapt and cope with the breakdown of red blood cells. At least 60% of healthy and full-term children on the second or third day turn yellow. The percentage of premature infants who develop jaundice is even higher - 80-90. The risk group also includes twins, triplets, babies whose mothers are sick with diabetes.
When does physiological jaundice of a newborn pass? Normally, the condition should pass in 14-21 days. If the baby's skin color after 21 days has not become natural pink again, it is imperative to consult a pediatrician. With the help of tests and analyzes, he will accurately determine at what stage of the formation and excretion of bilirubin failures occur and for what reason. The reasons that can provoke pathology are:
- Violation of the liver. This can be due to diseases, including hereditary ones. Such jaundice is called hepatic.
- Too intense, permanent destruction of red blood cells. This condition is characteristic of a hemolytic disease that occurs as a result of a conflict between a blood group or rhesus blood of a mother and a child.
- Disorders of the biliary tract. Bilirubin is excreted through the bile ducts, so if the baby has obstruction of these paths, the substance can accumulate in the body, coughing up the skin and mucous membranes in yellow.
For more than three weeks, jaundice in a newborn can also be normal. All children are individual. It is impossible to accurately predict the date when, for example, he learns to walk. Also, no pediatric doctor is able to say when the baby’s liver “learns” how to properly process bilirubin.
It must be understood that the newborn himself is an indicator of his condition. If his skin remains yellow for more than three weeks, but at the same time the baby does not show signs of anxiety, is not capricious and does not cry, eats and gains weight well with appetite, then there is most likely no reason to worry. It is only necessary with the help of a pediatrician to begin tracking bilirubin in the blood of the child.
If jaundice does not go away after three weeks
In case of pathology, it is necessary to visit a pediatric doctor who will recommend adequate treatment. With the help of tests and analyzes, he will determine the causes of this condition, and then prescribe therapy that will treat the disease, and not the symptom. The main method for treating the manifestation of pathology is phototherapy, that is, light treatment. It is best to combine this method and natural feeding, which will help remove an excess of bilirubin from the baby's body as soon as possible. In some severe cases, infusion therapy or replacement blood transfusion is required.
The consequences of physiological jaundice
For several weeks, during which the baby's bilirubin level was elevated, nothing really dangerous could happen to his health. Bilirubin is toxic, but its quantity in physiological jaundice of newborns is not enough to cause any noticeable harm.
In the event that the condition lasts (that is, it lasts more than 21 days), you need to contact the pediatrician and begin to monitor the level of the substance in the child’s blood. Even in this case, it’s not worth worrying too much. Under the systematic supervision of a qualified doctor, there will be no serious consequences of physiological jaundice in the newborn.
Nuclear jaundice in a newborn
Problems can appear only if the level of bilirubin is exceeded ten times the norm or more. In addition, there is a danger if the upward trend continues. In this case, complications can occur that are usually associated with the toxic effect of the substance on the nervous system and liver. This condition is called nuclear jaundice.
With nuclear jaundice, symptoms such as lethargy, apathy, poor appetite, indifference, moodiness and tearfulness are also observed. The kid can scream for no reason, stretch his limbs and throw his head back.
What level of bilirubin is critical for the conversion of physiological jaundice to nuclear? Doctors do not know this, but there is a concentration threshold at which the risk of central nervous system damage increases. For example, after the third day of life, an indicator of 380 μmol of bilirubin per liter of blood is dangerous, and measures must already be taken at the level of 250. At a level of 290, hospitalization is indicated.
Therapies
Treatment of physiological jaundice in newborns involves almost the only method - this is phototherapy, or phototherapy. Assign it depending on the duration of labor and the weight of the baby. For example, for a baby of the third day of life, an indication for phototherapy is a substance level of 260 μmol / L.
A device for treating light is a box and a lamp with ultraviolet radiation. Under the influence of ultraviolet light, bilirubin loses toxicity and is excreted from the body within the next 12 hours with feces and urine. For a visible effect, continuous therapy is recommended. This method is also used for premature babies in cases where the concentration of the substance is at a dangerous level.
In the process of phototherapy for newborns, they close the eyes of the child and the genitals of the boys. The baby's body temperature is constantly monitored and additional fluid is introduced, that is, frequent feeding is indicated. Under these conditions, treatment with light will not lead to complications, that is, to overheating, dehydration of the child. But loose stools, drowsiness and peeling of the skin are possible. These manifestations will disappear after the end of therapy.
The duration of treatment is 96 hours. As a rule, significant results can be achieved already in the hospital, but sometimes you have to visit the clinic for additional procedures.
Drug use
Clinical recommendations for physiological jaundice in newborns exclude the appointment of medicines to the baby. Medical practice has shown that some drugs only increase symptoms and increase the risk of central nervous system damage. Choleretic drugs and B vitamins are useless; the effectiveness of Smecta and activated carbon has not been proven.
General recommendations for jaundice
The early departure of meconium (delay can be a provoking factor for jaundice) is facilitated by the attachment of the baby to the mother’s chest immediately after childbirth. Even during a cesarean section, doctors try to put the baby on the mother’s chest as early as possible. Physiological jaundice passes faster with breastfeeding. During light treatment, the number of applications should be increased by approximately 20%.
With physiological jaundice of the newborn, sunbathing is recommended for 30 minutes daily. Frequent walks, breastfeeding are also recommended (it can be expressed and given from a bottle). Regular monitoring by a pediatrician is necessary. These methods will allow the baby's body to quickly adapt to new conditions and cope with the production of bilirubin.
Natural Jaundice
Safe jaundice, which can last longer than three weeks, can occur as a result of the natural feeding of the baby with breast milk of the mother. The fact is that milk contains a substance that blocks the liver enzymes of the child. Doctors have not yet been able to find out why nature blocks this mechanism.
If the mother wants to make sure that the baby has jaundice of breastfeeding, it is worth switching to the mixture for several days. As a rule, the yellow tint of the skin and mucous membranes noticeably brightens. If so, then you can calm down and calmly return to natural breastfeeding.
Mom's diet for newborn jaundice
As a rule, there are no special recommendations on the nutrition of a nursing mother with physiological jaundice of the newborn. It is enough to adhere to the usual diet for a woman who is breastfeeding. It is less to eat fresh vegetables and fruits. It is often recommended to put the baby to the chest, in addition, you can drink decoctions of rose hips and fennel, lay out the baby without diapers (sun and air baths).
Finally
So, young mothers should remember that jaundice in a newborn is a physiological condition in 60-70% of cases, due to the fact that his body has not yet had time to reorganize to a new mode of work, in some moments to adapt to life outside the mother’s body. The doctor will determine if this condition is pathological, and if necessary, prescribe therapy.