Benign or malignant neoplasms in the spinal cord are quite rare - in only 10% of all organ pathologies. They can be primary or secondary (metastases of cancer of neighboring organs). Symptoms of a spinal cord tumor may not appear for a long time, especially if it is benign. The growth of the neoplasm worsens the situation. In men and women, the disease develops with the same frequency. Rarely, the tumor appears in the elderly and children.
Reasons for the appearance
Before considering the symptoms of a spinal cord tumor, you need to find out why it appears. There are two types of reasons.
Internal reasons:
- Genetic changes at the stage of fetal development.
- Metastases of neoplasms of other organs.
- Previously transferred oncological diseases.
- Frequent stressful situations, emotional outbursts.
- Neurofibromatosis
- Impaired functional immunity.
- Inflammatory pathology.
- Cerebrotinal angiomatosis.
- Vertebral column injury.
External reasons:
- Difficult environmental conditions.
- Accommodation in the immediate vicinity with high voltage lines.
- The effect of radiation.
- Exposure to chemicals, toxic agents.
A benign tumor of the spinal cord, if it does not grow, may not appear for a long time and is detected completely by accident.
Disease classification
The classification of spinal cord tumors is as follows:
- By origin: primary, secondary.
- By benign level: histological (cell cancer: angioma, lipoma, sarcoma), topographic.
Also, the ailment is classified by location:
- Intramedullary spinal cord tumor. It grows inside the spine and is able to infect the substance of the brain. The main danger of such formations is trauma to the spinal column. The formation of such tumors is associated with a violation in the structure of the cerebrospinal fluid in the case of jugular vein pressure. In humans, mobility is impaired, and sensitivity is also deteriorating.
- Extramedullary spinal cord tumor. These types of neoplasms are considered the most insidious. They begin to grow on the outer shell of the spinal cord or brain. Their danger lies in the fact that they give metastases. Such formations are characterized by clear neurological symptoms. Minimally invasive methods are used to remove them to avoid damage to the spinal cord.
- Intradural tumors. They grow in the lining of the spinal cord and put pressure on it, causing various severe symptoms. Such formations can also be found on nerve processes. Most often they are primary, but have a favorable outcome. Surgical intervention is necessary only in case of a rapid increase in the size of the tumor.
- Extradural. Such tumors develop least often. They are true and false. In the first case, the neoplasm is formed inside the spinal canal. The tumor includes nerve roots, the outer layer of the hard shell, fat cells and blood vessels.
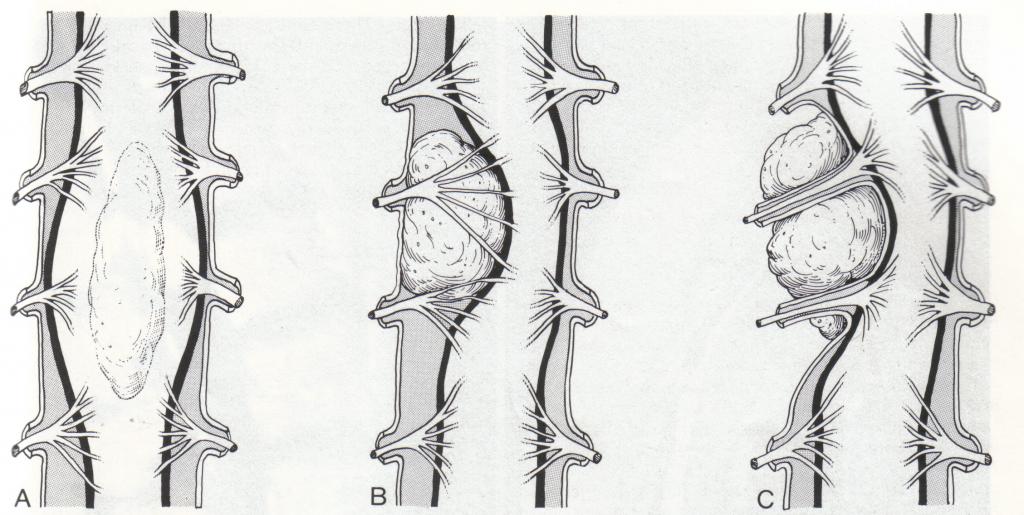
You can also highlight the following classification of neoplasms:
- Neurinoma. Most often, it develops in place of highly differentiated cells. In most cases, it is benign and does not pose a threat to life.
- Lipoma. This formation consists of fat cells. It is not prone to degeneration, but it is able to grow and destroy the spine quickly, so its functionality is impaired.
- Ependymoma. It can be benign or malignant. It develops in nerve conducting tissues. It is dangerous because it is capable of producing metastases in the spinal cord. Affected cells spread through the cerebrospinal fluid.
- Angioma. Its feature is the presence of blood and lymph vessels. If doctors do not intervene on time, then there is a risk of internal bleeding.
- Sarcoma. This formation is malignant. It can develop from any connective tissue. A tumor is detected in patients older than 25 years.
Tumors of the brain and spinal cord are dangerous with complications, so at the slightest sign of organ damage you need to be examined.
Symptoms of pathology
In most cases, the symptoms of a spinal cord tumor are nonspecific, so it is not always possible to immediately suspect a pathology. Common manifestations of the disease are as follows:
- Pain in the back, which has the property of spreading to the entire spine.
- Atrophy of muscle tissue.
- Sensory impairment in the arms or legs (depending on the location of the tumor process) or complete paralysis.
- Gait problems: a person may stumble and fall.
- Decrease in tactile sensitivity.
- Paresis and paralysis.
- Violation of intestinal motility, the work of the excretory system.
- Drowsiness, fatigue, general weakness.
- Difficulty swallowing: difficulty talking.
- Pathology of the heart system.
- Vegetative dysfunctions. With a significant development of the tumor process, the excretory system is disrupted. At the last stages of the development of pathology, fecal incontinence, spontaneous excretion of urine are observed.
Also, some symptoms of a spinal cord tumor can be combined into syndromes: radicular, conductor.
Manifestations of the disease depending on localization
Symptoms of a spinal cord tumor (the prognosis of the disease depends on the degree of damage) are also determined by the location of the neoplasm. Moreover, the manifestations are slightly different:
- Tumors of the cervical spinal cord. The patient has pain in this area, and it spreads to other parts of the spine. Muscles gradually atrophy, sensitivity and mobility of the hands is limited. Pathology extends to the diaphragm, so a person often develops respiratory failure.
- A tumor in the chest. Here the pain syndrome has a girdle character. Sensitivity can disappear in the arms and legs. Motor functions are also violated.
- Tumor in the lumbar. Pain syndrome extends to the lower back and abdomen. There is a violation of the blood circulation of internal organs. The thigh muscles atrophy. If the mobility and sensitivity of the legs deteriorates, then the hands do not suffer.
- A tumor in the sacral part. The patient feels pain that spreads to the legs and lower back. It often intensifies at night and with movement.
Despite the localization of the neoplasm, it is necessary to try to determine the symptoms of a spinal cord tumor in the early stages of development. In this case, the chance of a favorable outcome increases.
Developmental stages
It must be remembered that any damage to the spinal cord is treacherous, because the symptoms are not always specific. There are several stages of the development of pathology:
- Neurological There is a slight loss of sensitivity. Pain is detected in the back, but its intensity is negligible. At this stage, the patient can stay for years without suspecting the problem. Such a course is often characterized by benign tumors with slow growth. For 10-15 years, a person does not go to the doctor, since he does not suspect the seriousness of the situation.
- Brown-Sakarovskaya. After the neoplasm grows, it begins to put pressure on the spinal cord and can displace it. Here the symptoms intensify.
- Paraparesis. At this stage, there is a violation of the functionality of the autonomic system, pelvic organs. Sensomotor disorders become more pronounced. A person develops paralysis of the limbs, and he can be both temporary and permanent. In the area above the neoplasm, the skin turns red. If the tumor is malignant, then paralysis occurs within 3-4 months. Life expectancy here is six months to a year.
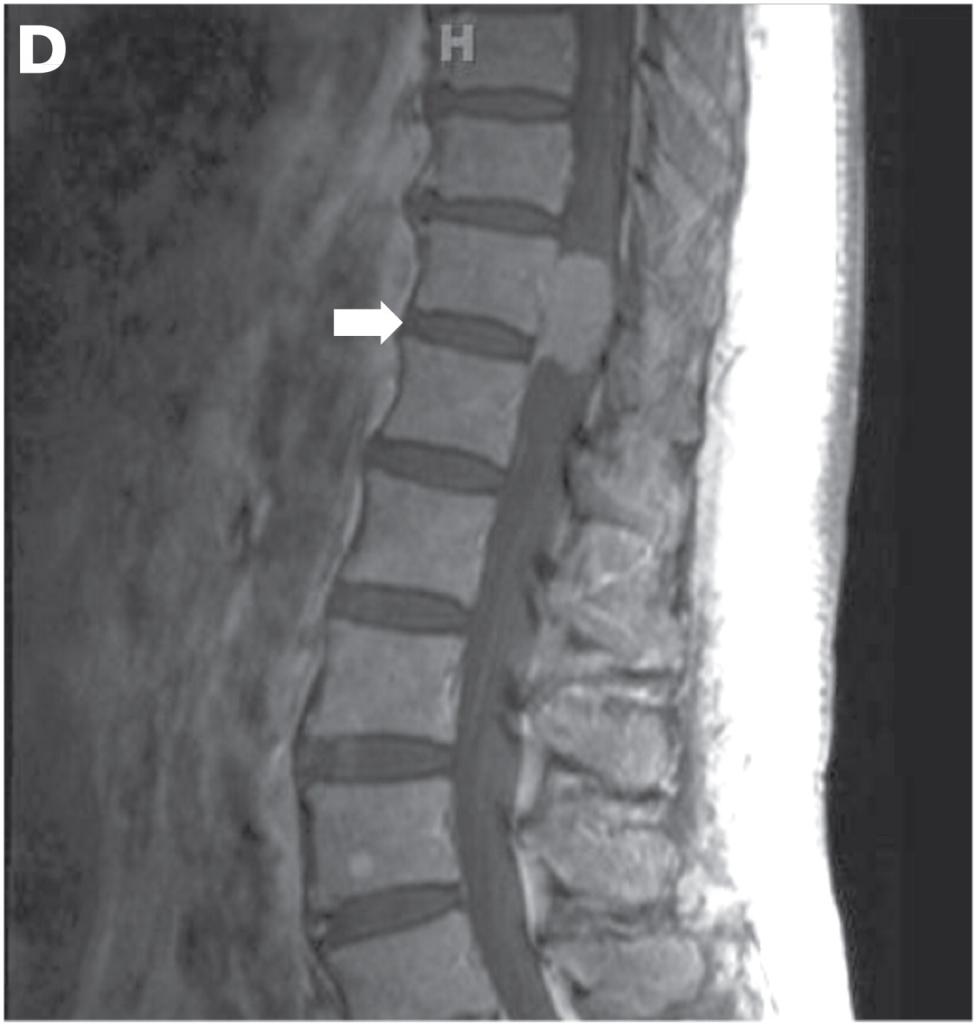
If symptoms of a spinal cord tumor appear, the prognosis is determined by the degree of development and malignancy of the pathological process, the effectiveness and timeliness of therapy.
Diagnosis of the disease
Symptoms of a tumor of the cervical spinal cord are in many ways similar to the defeat of its other parts, but treatment tactics are always selected individually. To do this, undergo an examination, which involves such studies:
- History taking. The specialist should find out when the first symptoms appeared, what is the characteristic of the clinical picture.
- Study of the structure of chromosomes. With oncological damage to cells, their DNA changes.
- Roentgenography. It is done in two projections. Thanks to this study, it is possible to detect the expansion of the vertebral arches, the destruction of bone tissue, its displacement.
- Myelography The study presented involves the use of water-soluble contrast.
- Blood test for tumor markers.
- Angiography is a contrast definition of the state of the blood vessels of the spinal cord.
- Neurological research. Here the sensitivity of parts of the body, reflexes, the level of muscle tone, sensory strength are checked.
- CT or MRI. These methods provide complete and accurate information regarding the type and location of education, the degree of damage to the spine and spinal cord.
- Spinal puncture. Too much protein may be present in the cerebrospinal fluid.
- Scintigraphy. It is used for suspected cancer. Research is able to detect it in the early stages of development.
Diagnostics must be differential. It is important to distinguish a tumor from an intervertebral hernia, congenital anomalies in the structure of the spine, atrophic sclerosis (an equally dangerous disease), and cerebrospinal stroke.
Disease treatment
According to the ICD of the spinal cord tumor, the following codes are assigned: C.72 (malignant neoplasm), D.33.3 (benign neoplasm). In any case, the disease must be treated so that there are no complications. There are various therapies.
Treatment methods| Method name | Features |
| Therapeutic | It is used at any stage of treatment, but it will be most effective only in the early stages of the development of pathology, when the immune system can still fight the tumor on its own. Medications help with a small amount of affected tissue and the absence of metastases, if the neoplasm does not grow too quickly |
| Surgical | Removal of a spinal cord tumor is the main treatment method, which in some cases helps to completely get rid of the problem. The success of the intervention depends on the general condition of the patient, the degree of spread of the pathological process and damage to the spinal cord, and its level of malignancy. An intramedullary tumor of the spinal cord is difficult to treat, as it develops inside the spine and can damage it |
| Ultrasonic suction | This is a minimally invasive way to combat the disease, which consists in removing the formation by means of an ultrasound beam. It is aimed directly at the tumor, and with high accuracy. Such an operation practically does not cause side effects |
| Radiation therapy | With a spinal tumor, surgery is the only way to fix the problem. But it requires additional treatment and rehabilitation. Radiation therapy is used if a small part of the damaged cells could not be removed. It is used if the tumor is inoperable or metastases are present. A significant drawback of this method of therapy is the huge number of side effects, because healthy tissues are damaged. It takes a long time to recover from such treatment. |
| Chemotherapy | Its purpose depends on the prevalence of the pathological process. It is very important to choose the right drugs. They are mainly administered intravenously, although in rare cases, injections are made into the muscle |
| Radiotherapy | Specialists influence the tumor with a gamma-ray stream. It is able to completely destroy the DNA of affected cells. Such treatment is prescribed more often with large neoplasms |
As for the use of folk remedies, they must be authorized by a doctor. At the same time, it is worth remembering that decoctions are not a panacea and can not save from a neoplasm. But to reduce its size, to suspend growth, to strengthen immunity, folk recipes can.
Features of the therapeutic regimen
The general principles of treatment in this case are as follows:
- Such decoctions of herbs should be taken that restore immunity, normalize the functionality of internal organs, and cleanse the body of toxins.
- Try to take the prescribed courses of therapy to exclude the development of metastases.
- Follow a diet.
- Try to maintain an emotional, psychological balance. Instability of the nervous system will only aggravate the situation.
After surgery, the patient needs a long rehabilitation period. It provides for the use of massage, therapeutic exercises, as well as physiotherapeutic procedures. Their goal is the rapid restoration of damaged tissues and mobility of the spine, improving the sensitivity of the limbs. Regular exercise to prevent muscle atrophy, improve blood circulation and microcirculation, normalize tissue nutrition.
The prognosis and complications of the disease
It all depends on the size of the tumor, the degree of damage to the spinal cord, destruction of the spine. Timely removal of extramedullary tumor gives a chance for a full recovery. Internal neoplasms have a more unfavorable prognosis. Even surgery may not always help, as the spinal cord may be too badly damaged.
Primary tumors cause disability. With early diagnosis and correct therapy, the prognosis is favorable. If the treatment is incorrect or belated, then such complications arise:
- Systematic pain in the back, which can not be removed even with strong drugs.
- Mobility impairment and, as a consequence, disability.
- Incontinence of feces, urine.
- Sensitivity problems for certain parts of the body.
Timely therapy will help to avoid such problems. However, the patient must consult an experienced specialist. Self-medication in this case is deadly.
Pathology Prevention
There are no specific tips that could 100% help to avoid pathology. However, it is necessary to follow the general recommendations of specialists:
- Lead an active lifestyle, abandon bad habits and foods, eat rationally.
- In a timely manner, consult a doctor if you see strange symptoms, as well as periodically undergo preventive medical examinations.
- Strengthen the immune system. Here it is necessary to use multivitamins, to temper the body.
- Avoid viral and infectious pathologies. Do not contact infected people during epidemics.
- Avoid emotional outbursts, stressful situations.
- Avoid spinal injuries.
A careful attitude to your own health will help to avoid the appearance of pathology or to detect it in the early stages, when it will be easier to overcome it. Tumors of the spinal cord can leave a person disabled or even kill, so when the first symptoms appear, you need to be examined.