Diabetes is known to many as a complex disease that you have to live with. But in some cases, the fact of this problem is complicated by additional destructive processes. One striking example is Charcot's foot. This diagnosis is quite serious and dangerous.
Features of the disease
Charcot's foot in medicine is also defined as diabetic osteoarthropathy. It is a serious complication of diabetes, which is characterized by various bone changes:
- Hyperostosis The cortical bone layer grows.
- Osteoporosis. It is about weakening and thinning of bones.
- Osteliosis. Bone tissue is completely absorbed.
As you can see, Charcot's foot with diabetes is fraught with serious negative consequences. In the framework of the usual way of life, such a disease can lead to frequent fractures of bones, as well as their improper fusion. The latter fact sometimes causes the deformation of the foot.
Expect a similar development of events is for those who are diagnosed with a decompensated form of diabetes. Moreover, this is true both for insulin-dependent patients and those who do not fall into this group. After a certain period of time, neuropathic complications are often fixed in such patients, which cause fractures in the foot area, and frequent ones.
The problem described above may also be accompanied by ulcerative lesions of the skin, which makes the already difficult situation difficult. The bottom line is that when ulcers appear on the foot with neuropathy, they cause a noticeable flow of blood, leaching calcium from the bones. Naturally, after such a process, the bones lose their strength and can break under moderate loads.
It is worth noting the fact that Charcot's foot appears mainly in patients who have been struggling with the disease for more than 10 years.
Forms of the disease
There are several background diseases that cause the appearance of a diabetic foot. Given this fact, several forms of the disease itself can be distinguished:
- Neuroischemic. Its development occurs against the background of diabetic angiopathy, which is expressed through the deterioration of blood flow in the lower extremities. In this state, the foot does not change its shape and its sensitivity is maintained. In this case, puffiness occurs, the surface of the skin becomes cold, and the pulse is weak.
- Charcot's foot is a neuropathic form. In this case, the disease develops against the background of diabetic polyneuropathy and leads to damage to the nerve endings in the feet. Symptoms of this condition are reduced to a significant decrease in the sensitivity of the foot, while there is no pain. Due to the fact that the innervation is disturbed, the patient incorrectly distributes the load on the joints of the legs, which creates a risk of foot deformation.
- Mixed. In this case, the signs of both of the above forms are manifested simultaneously.
Charcot's foot in diabetes: stages of development
If we take into account the assessment of the disease by Dr. Wagner, then it will be possible to distinguish 5 stages that the patient undergoes with a diagnosis of diabetic foot. Here is a brief description of them:
- First stage. An ulcer of a superficial type, in which only the upper layers of the skin are affected. As a treatment, the technique of removing corns is used. If necessary, antibiotics are used.
- The second one. It is a deep ulcer that does not affect the bone. At the same time, the effect of infection can be determined by the following signs: high fever, pus and redness of the skin around the affected part of the foot. Actual is antibiotic treatment and surgery to remove dead tissue.
- The third. At this stage, a deep ulcer forms and bone damage occurs (osteomyelitis develops). Destructive processes also affect the soft tissues in the foot area. This condition is often accompanied by suppuration. Treatment is prescribed the same as in the case of the second stage. With a particularly severe course of the disease, amputation is possible, but such cases are rare - the condition of patients can often be improved by medication.
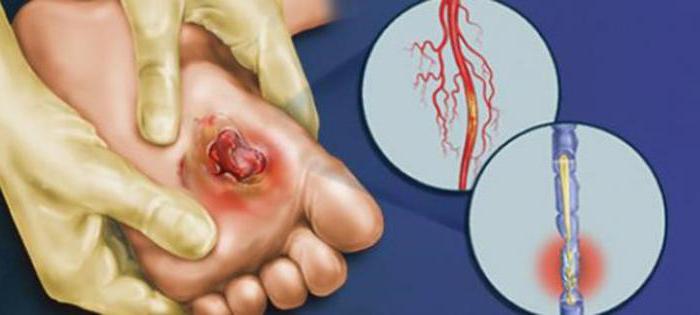
- Fourth. Charcot's foot at this level is characterized by gangrene, which affects a certain area, such as a finger. With this diagnosis, amputation of the dead parts is carried out and in especially severe cases - legs below the knee.
- Fifth stage. At this stage, the lesions are maximum: extensive gangrene of the foot develops, which can lead to a fatal outcome. The only effective measure is amputation, and immediate.
Understanding what constitutes Charcot's foot, it is worth mentioning the zero stage, which precedes everything described above. In fact, we are talking about people at risk. In this condition, there are no ulcers yet, but deformity of the foot is already becoming noticeable, corns or corns appear, and hyperkeratosis also makes itself felt.
Diagnostics
Charcot's foot with diabetes, the photo of which confirms the seriousness of this disease, needs timely treatment, otherwise serious complications may develop.
Therefore, diagnosis at the first signs of the disease must be carried out with the participation of qualified specialists. At the first suspicion of diabetic osteoarthropathy, you should pay a visit to the endocrinologist. If possible, it is better to go to a specialized medical center.
In order to make an accurate diagnosis, a careful study of the clinical picture and radiological signs, which will indicate a specific stage, will be required. The complexity of the process of determining the disease boils down to the fact that the symptoms may resemble the manifestation of foot phlegmon, thrombophlebitis, lymphostasis and other diseases.
The most difficult is the differential diagnosis in the case when Charcot's foot (diabetic) is in the acute stage. In this case, untimely treatment may cost the patient loss of limb.
How is a differential diagnosis made in the acute phase?
When the patient is in this condition, doctors try to get an answer to two key questions:
- If there are appropriate radiographic signs of bone destruction, what kind of nature do they have - infectious (osteomyelitis) or non-infectious (OAP)?
- Is it possible to identify inflammatory changes as a result of destruction of bone structures, or are they signs of another disease (rheumatic joint damage, acute thrombophlebitis, foot phlegmon, gouty arthritis, etc.)?
To get the answer to the second question, additional equipment will be needed, since without it it will be difficult to say that the patient has exactly Charcot's foot. X-ray in the framework of such an examination is the most relevant.
In addition to radiography, you will have to use magnetic resonance imaging. Scintigraphy of the skeleton of the foot will not be superfluous. All these diagnostic measures will help to identify inflammatory changes, increased blood flow in the affected area and micro fractures.
If necessary, biochemical markers of bone decay can be evaluated. Markers for tissue remodeling can also be taken into account, since they reflect the activity of the bone isoenzyme.
As for the first question, it is most relevant for obvious signs of trophic foot ulcers. This information may also be relevant during the postoperative period following amputation, or surgery related to the foot. To determine the nature of bone destruction, a blood test is taken for osteomyelitis.
Charcot's foot: treatment
First of all, you need to understand that the treatment process will give the greatest result if the patient promptly consults a doctor. But for this to happen, people with a diagnosis such as diabetes must be able to independently assess the condition of their feet.
A competent examination can and should be learned, consultations of qualified doctors will help in this. As a result, the patient must cultivate the habit of constantly examining the legs, and in particular the feet. As soon as any changes in the structure are recorded, even minor ones, you need to plan a visit to the doctor.
It is also important to consider the following fact that accompanies Charcot -Marie disease : foot pain in this condition is reduced due to atrophy of nerve endings, and it may seem to the patient that the injuries received are minor, while the damage is actually serious.
If ulcers appear on the foot, then they need to be examined with the establishment of depth. As for the therapeutic effect, with certain ulcers, recovery with orthopedic insoles is possible, since they significantly reduce the pressure when walking. If this measure is not sufficient, then immobilization is used, which prevents a strong effect on the skin.
Surgical treatment is prescribed when the ulcer spreads to the level of the dermis. If an infection has been recorded, the doctor prescribes antibiotics.
Sometimes plantar ulcers can spread even to bony protrusions. In this case, there is a need for surgical removal of the latter. An example is the metatarsal bone, which can be removed with an ulcer located in the forefoot.
More about conservative and surgical treatment
It is possible to fight with a diabetic foot operatively and by means of classical techniques.
Conservative treatment is focused on activities that can be divided into two types:
- Basic treatment. At this level, attention is paid to compensating for diabetes, controlling blood pressure, and normalizing blood sugar. Patients are taught the necessary knowledge and skills. If necessary, the doctor may require you to stop smoking, since it has a negative effect on the blood vessels.
- Additional therapeutic measures. If Charcot's foot is diagnosed with diabetes, treatment may include antimicrobial therapy using antibiotics. To relieve the pain syndrome, such painkillers as Ibuprofen, Analgin, etc. are used. The patient also undergoes a series of therapeutic measures aimed at restoring nerve conduction and improving blood flow in the foot area. Not without local exposure with antiseptic drugs.
As for surgical intervention, it is used when there is a need to remove abscesses and ulcers. Surgical treatment may be an urgent measure to improve blood flow. If the patient was admitted to a medical facility at the last stages of the development of the disease, then the likelihood of amputation of the feet and lower limbs is increased.
Restoration of the skeleton of the foot
When Charcot's diabetic foot appears, treatment is primarily focused on the removal of abscesses and ulcers, but surgery can also be used as a restorative measure. This is a correction of the deformation of the foot.
In fact, the resection of bone structures and arthrodesis is neutralized, which cause an increase in pressure on the plantar surface, which leads to the formation of a non-healing ulcer. In order to apply such techniques, it is necessary first to ensure that the verse is an inflammatory process, and completely, and there is no osteolysis. If these conditions are not met, then there is a risk that surgical intervention will lead to the appearance of new foci of destruction.
It is also advisable to strengthen the bones with appropriate preparations before surgery.
The surgical repair of the foot described above is necessary with a strong deformation of the foot, which makes the use of special orthopedic shoes ineffective.
Preventative measures
Obvious is the importance of information on how to prevent a problem like Charcot's foot. Photos of patients provides an opportunity to understand how serious this destructive process is. And even if he made himself felt and a course of treatment was carried out, this does not mean that the ulcers will not appear again.
So, it is possible to prevent and prevent the reappearance of Charcot's foot by following proven principles as part of prevention. First of all, you need to permanently independently examine the feet and, at the first sign of skin damage or deformation, immediately go to the endocrinologist for an examination.
You will also have to refuse scissors for cutting nails and use a nail file. Narrow shoes should also be a thing of the past, since it is easy to rub your feet in it and get corns later on. In addition, it is important to protect the feet from exposure to high and low temperatures.
If a wound has been detected, it must be treated with a 3% solution of hydrogen peroxide, Chlorhexidine and Miramistin, followed by a sterile dressing. In this situation, those medicines that have a tanning effect are contraindicated. These include iodine, zelenka and potassium permanganate. It is important to take care that the skin does not remain dry. Moisturizers (Callusan, Balzamed, etc.) will help with this.
Summary
A diabetic foot is a disease that can lead to serious complications if you start it. Therefore, when diagnosing diabetes, you need to undergo appropriate training and carefully monitor the condition of your legs.