Acute intestinal obstruction (ONC) is one of the rapidly developing pathologies that, without timely medical attention, leads to death. Everyone should know the symptoms and signs of this disease, so that if it occurs, urgently consult a doctor.
What is acute bowel obstruction?
With ONC, regardless of its variation, overcooked food and feces are not able to pass through the intestines. The disease can occur at any age, neither children nor the elderly are protected from it. However, according to statistics, most often it affects people over 40 years old and patients who have a history of gastrointestinal surgery.
There are several types of acute intestinal obstruction, they can be divided into two main groups.
Mechanical obstruction
Acute mechanical obstruction of the intestine is manifested in the fact that food cannot move along the gastrointestinal tract due to some kind of obstruction. Depending on what caused the blockage, it happens:
- Obstructive CN. With this pathology, some physical objects are an obstacle to the passage of feces. For example, hair lumps, large gallstones or accidentally swallowed foreign bodies. These objects stand inside the hollow intestine and prevent the digested food from moving on. Also, the intestine can squeeze the tumor if it formed in a nearby organ. With obstructive obstruction, blood supply to the intestine does not stop.
- Strangulation KN. In this case, the obstruction of the body leads to obstruction. Intestinal loops are wrapped in the form of impassable nodes, most often the loop of the small intestine is intertwined with the cecum. In this case, the blood supply to the vessels in the mesentery is disrupted. With untimely help, necrosis begins, i.e., necrosis of sections of intestinal tissue.
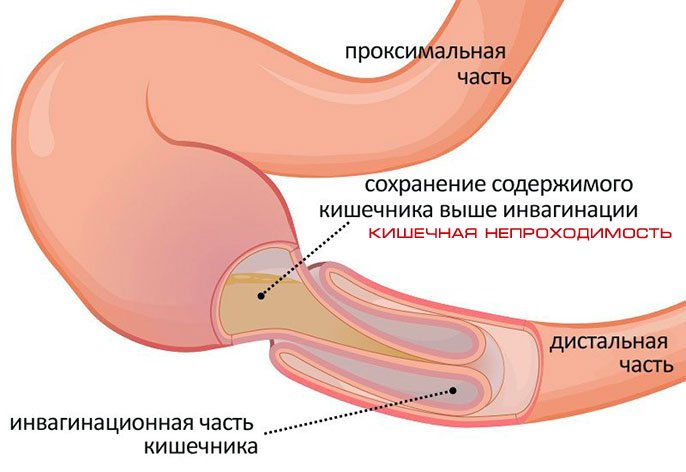
- Intestinal invagination. In order to understand this mechanism, it is enough to imagine how the telescope is shortened. The principle of operation of this process is the same: one part of the intestine, after a strong contraction, is introduced into another. Most often, this type of acute intestinal obstruction of the intestine affects children up to the first year of life, which is facilitated by the special anatomical structure of the intestine. Improper feeding plays a large role, for example, if parents decide to diversify the baby’s diet before a certain time. However, adults are also completely immune from intussusception.
Dynamic obstruction
Pathology occurs due to the fact that the intestine partially or completely ceases to function. Various factors can lead to this condition:
- Chronic or acute diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, for example, appendicitis, pancreatitis, etc.
- Abdominal surgery.
- Eating large amounts of food after prolonged fasting.
- Intestinal colic, which can also be caused by a number of diseases of various etiologies.
Regardless of the cause of acute bowel obstruction, one of two forms of organ motility disorder develops.
With spastic blockage, spasm occurs only in a certain area of the intestine, without affecting other departments. With a more severe, paralytic form, the intestine ceases to function fully.
Symptoms of occurrence
If the patient is not provided with medical care on time, then many serious complications, including death, cannot be avoided. It is necessary to be able to recognize OKN, if it is delayed by going to the doctor, death can occur within 2-3 days after the onset of the disease.
The development of acute intestinal obstruction can be divided into three stages.
Early stage
This is the first 12 hours after the onset of pathology. Body temperature is still normal or slightly lower. A person has paroxysmal pains in the abdomen, which can vary in strength and location. It all depends on what type of intestinal obstruction has arisen.
With obstruction, seizures most often occur in waves, severe pain gives way to several minutes of rest. With strangulation obstruction, on the contrary, pain is constantly present, from slight to unbearable, sometimes a person experiences severe pain shock.
In the early period, nausea and vomiting are most often not observed. However, if blockage occurred at the beginning of the small intestine, then they do occur.
Intermediate
It starts after the first 12 hours and lasts up to a day. During this period, the clinical picture of the disease is most pronounced. No matter what form of intestinal obstruction occurs, the pain no longer subsides even for a short period of time. The stomach is inflated and takes an unnatural form, noises and boiling in the intestine are clearly audible. Sometimes bloody diarrhea is possible if internal hemorrhage has begun.
If intestinal obstruction occurs in the small intestine, then the patient often vomits abundantly, but vomitus undergoes visible changes. At first they look like semi-digested food, but the smell of feces and a characteristic yellowish color gradually appear. The body tries to push the intestinal masses through the stomach, the so-called emergency exit.
If a blockage occurs in the large intestine, only nausea is more often present. Vomiting, even if it is, does not bring any relief. In this case, the body cannot get rid of stuck feces, since the distance to the stomach is too far.
Late or terminal stage
It starts after the first day after the start of the PMC. The body every minute more and more reacts to severe poisoning by toxins. Acute intestinal obstruction is manifested by the fact that a person has a fever, respiratory rate and pulse increase; urine ceases to be produced and peristaltic activity of the intestine completely disappears.
Often at this stage, peritonitis or sepsis begins. If a person is slow, does not cause emergency medical care, then a fatal outcome is inevitable.
Etiology of acute intestinal necessity
Obstruction can occur due to many reasons. For example, if in the intestine or mesentery, with which the organ is held in the peritoneum, there are some abnormalities: adhesions (this type is called acute commissural obstruction of the intestine), scars, etc. They can form in any part of the intestine, if previously in history the person had some kind of inflammatory disease, injury or surgery on the gastrointestinal tract. In this case, these factors are considered to be predisposing.
There are also producing factors. They, on the basis of predisposing factors or without them, also cause acute intestinal obstruction. The second group includes spontaneous violation of intestinal motility, the proper functioning of which depends on various circumstances.
Intestinal motility may stop working due to too high a food load or a change in the usual type of food. Very often, acute obstruction begins in the summer, when people massively begin to consume a large number of vegetables and fruits, which in their composition have a large amount of fiber.
The pressure inside the abdominal cavity can also increase sharply due to a lot of physical stress. In young children under the age of one year, obstruction most often occurs during the period when they are transferred from breast milk to artificial feeding.
Pathogenesis of the disease
With intestinal obstruction in adults and children, pathological changes begin in the departments of the organ and abdominal cavity. If the intestinal loops are intertwined into a knot, then it is in this place that blood circulation is first of all disturbed.
With mechanical obstruction, if an object has stood in the way of feces, the intestinal walls are excessively stretched under pressure and a secondary blood flow disturbance occurs. Further, the pressure only increases, the organ swells greatly. Walls that initially increase in thickness due to edema, on the contrary, become thinned.
A day after the start of this process, if the pressure in the gut reaches the level of 20 mm Hg, irreversible changes occur in the walls of the intestine.
In addition to changes in the abdominal cavity, severe dehydration is observed. If no measures to eliminate intestinal obstruction are used, then a person can lose about 4 liters of fluid contained in the body per day.
One of the important processes in ONC is endotoxemia. In this process, the body experiences severe intoxication, as toxic molecules from the rotting intestinal contents and digestive juices enter the bloodstream.
Diagnostics
Depending on what kind of acute intestinal obstruction occurred, the symptoms can be expressed more or less clearly.
Pain can occur without visible precursors at any time of the day or night. They can be either cramping in nature, alternating with moments of calm, or last constantly.
There may be a lack of stool and gas. However, with obstruction in the small intestine, initially the stool, which managed to drop below the place of blockage, comes out. In this case, you can not start only from this symptom, since there is a high probability of making the wrong diagnosis.
Vomiting is one of the earliest signs of OKS. If at first it occurs at the level of the reflex, then it continues due to the fact that the gastrointestinal tract is full.
The main signs of acute bowel obstruction are:
- The abdomen is asymmetric, this is often seen with the naked eye.
- Palpation can be felt swelling of the intestinal loop and severe peristalsis.
- With percussion (a research method by tapping), high tympanitis is heard.
The history should be supplemented with rectal examination. Using this method, the doctor carefully inserts a finger through the anus into the rectum, in order to determine the place of obstruction of feces or intestinal nodes.
At the final, third stage of development of acute obstruction, intestinal paralysis occurs. In this case, all the noise in the abdominal cavity disappears, and complete silence ensues.
There are several ways to diagnose acute intestinal obstruction in a hospital, such as radiography, colonoscopy, or abdominal ultrasound.
In order to make a correct diagnosis, it is necessary to exclude diseases with a similar clinical picture. For example, acute appendicitis, gastric ulcer, pancreatitis, ectopic pregnancy have the same symptoms at some stages.
Treatment
In acute bowel obstruction, symptoms and treatment, as in the case of any other pathologies, are interrelated. If there is even the slightest suspicion of a disease, the patient must be urgently taken to the surgical department of the hospital. Until the moment the doctor examines the person, you can not independently carry out any manipulations. It is forbidden to make enemas and gastric lavage, take any pain medication, or use drugs with a laxative or diuretic effect.
If it is precisely determined that peritonitis has not yet begun, then the method of decompression of the gastrointestinal tract using aspiration of the contents through the probe is used. Then a siphon enema is placed. This type of the latter can only be performed in a medical institution, with the help of it, toxins and poisons are removed from the intestines, as well as the chyme that has begun to rot.
If acute bowel obstruction is manifested by cramping pains, then antispasmodics are introduced (Drotaverin, Atropine, etc.). They help to reduce increased intestinal motility.
There is an opposite condition called paresis. With it, gradually developing paralysis of the intestinal muscles is observed. In this case, drugs that stimulate motility are used (for example, "Neostigmine").
In order to reduce dehydration and minimize the resulting water-electrolyte balance in the body, various saline solutions are administered.
If after all the measures taken the condition does not improve, non-surgical treatment of bowel obstruction is ineffective, then emergency surgical intervention is required. The essence of the operation is that doctors eliminate mechanical obstruction or remove a non-viable area.
Surgeons can also eliminate inversion of intestinal loops, nodules, or dissect adhesions, if any.
If the patient has already begun peritonitis, then the transversostomy procedure is performed, which is necessary for the urgent and safe removal of feces.
After the operation, the volume of circulating blood is compensated; various types of therapies are also prescribed. It is necessary to remove the remains of toxins and poisons from the body, to prevent the development of bacterial infections. Particular attention is paid to controlling intestinal motility.
Prevention and Predictions
To make any accurate predictions, it is necessary to consider each case separately. Much depends on what type of pathology met, how timely and complete the treatment of bowel obstruction was.
If the patient seeks medical help too late, an adverse outcome is possible. At risk are older people, as well as those who have an inoperable tumor in the intestine.
The occurrence of this acute disease cannot be completely prevented, however, to reduce the likelihood of its development, several rules must be observed:
- You must adhere to a clear nutrition schedule. It is strongly recommended that you do not categorically switch to another volume or type of food.
- An untrained person should not take on huge physical exertion, since the body can respond with an inversion of the intestines.
- You need to carefully monitor your health, for the prevention of gastrointestinal diseases or the formation of stones in time to undergo an ultrasound of the abdominal cavity. From time to time, it is necessary to take tests for the presence of helminths, as they can also provoke acute intestinal obstruction.
Conclusion
This disease should be able to recognize not only a doctor, but also an ordinary person. According to statistics, approximately 100 deaths per 100 cases. If you seek help during the first hours after the onset of symptoms, then almost all patients receive surgical care and recover.
If you experience any abdominal pain, sudden problems with the stool, as well as bloating, you should immediately consult a doctor, because in this case the count goes to the clock. Only timely treatment of acute bowel obstruction will give a positive result.