High intracranial pressure is a diagnosis that many people are familiar with. It is quite common. Moreover, it is often put unreasonably, without conducting relevant studies. But pathology is based on serious diseases. One of them is hydrocephalus. Symptoms of the disease are recognizable enough and can result in serious consequences.
A bit of anatomy
During normal human activity, the brain is constantly washed by a clear fluid. She nourishes him and protects. The fluid circulates in the space between the soft and choroid membranes of the hemispheres and the cerebellum. In the body there are special places - tanks, in which it accumulates. They are located at the base of the skull. These tanks are connected between themselves and the spinal cord. In gray matter, fluid is located in four ventricles. This is the norm.
Cerebrospinal fluid is produced from the blood. The norm of the total volume is 150 ml. The process of fluid production and absorption are in equilibrium. The disharmony of this balance has serious consequences. Fluid begins to accumulate in the brain. This results in either a decrease in absorption or an increase in production.
If fluid outflow is disturbed, then the patient develops hydrocephalus. Symptoms can be observed in both newborns and adults. The source of the problem is a narrowing of the channel between the ventricles or a violation of the absorption of fluid by the body. To understand the pathology, you should consider how the brain looks (photo is in the article). Often, an unpleasant ailment is diagnosed in newborns. According to statistics, every 500th child is born into the world, having the aforementioned serious problem.
Sometimes the disease is not a congenital disease. Medicine knows cases where the signs of hydrocephalus were acquired in the process of life. As a rule, the causes of its occurrence lie in the past diseases. Often, it is cerebrovascular disease of the brain that provokes the development of a terrible pathology.
Types of ailment
Hydrocephalus is quite diverse in forms and causes. Today in medicine, there are several classifications of the disease.
At the place of fluid accumulation, the disease is divided into types:
- Internal hydrocephalus. Fluid (cerebrospinal fluid) accumulates in excess in the ventricles.
- External hydrocephalus of the brain. It is also called external. With this type of ailment, the accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid is observed in the subarachnoid space. In other words, the fluid is localized near the cranium.
- Total hydrocephalus. With this form, cerebrospinal fluid is found throughout the brain. It is found in the ventricles and in the subarachnoid space. This form has another name - mixed hydrocephalus.
Causes of the disease in children
The main factor provoking an ailment in newborns is a difficult birth. As a rule, we are talking about a prolonged anhydrous period of the fetus or the birth injury received by the child.
Sometimes there is an accumulation of fluid in the brain of a child who is still in the womb. This pathology is associated with infections and viral diseases suffered by a pregnant woman. Herpes, toxoplasmosis, cytomegaly are especially dangerous.
The most common is congenital hydrocephalus of the brain. Her signs begin to appear in the first months of a child's life. However, in older children, an ailment may occur. There are many sources provoking a serious illness. Among them are:
- brain tumors (both brain and spinal);
- meningitis;
- encephalitis;
- infectious ailments (tuberculosis);
- defects of the brain and blood vessels;
- hemorrhage;
- head injuries;
- genetic disorders.
Sometimes the source of the terrible disease can’t even be established.
Causes of the disease in adults
Not only babies have a terrible diagnosis. It can be delivered at any age. There is hydrocephalus, or, as it is popularly called, dropsy of the brain in adults due to past ailments:
- cerebral hemorrhage;
- stroke;
- brain surgery;
- meningitis;
- oncological diseases of the brain;
- traumatic brain injury;
- atrophy of the brain.
In most cases, it is cerebrovascular disease of the brain (atherosclerosis, stroke, arterial hypertension) that becomes a real focal point for the development of dropsy.
Clinical signs of the disease in children
Cerebrospinal fluid (cerebrospinal fluid) performs an essential function in the body. It feeds the brain with all useful substances and removes toxins from it. Timely outflow of fluid determines the normal functioning of the main organ. Any violation of the withdrawal of cerebrospinal fluid is fraught with consequences. After all, fluid production does not change. As a result, the ventricles overflow. As a result, their expansion is observed.
The most common symptoms of hydrocephalus are:
- a rapid increase in the head (takes the form of a ball);
- the child is very tearful and irritable;
- the baby is abundant and often spits up;
- fontanel rises above the surface of the skull, there is no ripple;
- the eyes of the newborn are shifted down, vision is impaired, sometimes strabismus occurs;
- cramps may occur;
- lag in physical and mental development;
- frequent tipping of the head;
- pallor of the skin;
- chin and limb tremors.
In older children, the head does not increase, because the bones of the skull have already grown together. In this case, the liquid still accumulates. The doctor will see this manifestation when he examines the brain in the picture. The photo will be very different from those images that healthy people have. As a rule, children are tormented by severe headaches, vomiting, a feeling of nausea. There may be a decrease in hearing, vision. The child has a weakness.
Symptoms of the disease in adults
The following signs of hydrocephalus are distinguished:
- dizziness, pain;
- nausea, vomiting;
- noise in the head;
- epileptic seizures;
- disorders of motor and neurological functions;
- decreased performance, the occurrence of apathy, depression;
- visual impairment.
A feature of the ailment of the elderly is a normal or slight increase in intracranial pressure. A small deviation from the norm characterizes normotensive hydrocephalus. Squeezing gray matter through fluid leads to brain damage.
If mixed replacement hydrocephalus is diagnosed, then internal pressure does not increase at all, since most often the cause of the disease lies in brain atrophy. Thus, the liquid simply fills the free space. This space arises as a result of atrophy.
Features of external hydrocephalus
As noted above, this ailment is characterized by the accumulation of fluid near the skull. Liquor can freely communicate between places of its localization. Such external hydrocephalus of the brain is called open. The closed form involves the complete separation of all spaces with liquid.
The main symptoms of the disease are increased fatigue, weakness, drowsiness. There may be double vision, a headache. In some cases, nausea, vomiting. Accompanying the disease is a violation of coordination of movement, a change in gait. At times, urinary incontinence is added to these symptoms.
There are known cases in which the development of hydrocephalus imperceptibly occurs. Symptoms are completely absent for a long time. The patient does not have an increase in pressure. Headache does not occur.
A very insidious form is considered moderate hydrocephalus. It is characterized by the absence of symptoms for several years. At one point, the patient's condition deteriorates sharply. The source of the problem is cerebrovascular accident. As a rule, the diagnosis of moderate cerebral hydrocephalus in most cases is made by chance. The doctor observes pathology during the examination of the fundus.
The nuances of internal hydrocephalus
This type of ailment characterizes the accumulation of fluid in the ventricles. Internal hydrocephalus can develop as a result of poor absorption of cerebrospinal fluid in the tissue. The causes of this phenomenon can be in the past infections, strokes in the subarachnoid region, clogged veins.
A characteristic manifestation of the disease is a severe headache. Nausea, a violation of visual and auditory functions are often connected to it. However, as with the above form of the disease, moderate hydrocephalus may not be manifested at all by any symptom.
General form of the disease
The development of such hydrocephalus is associated with accumulation of fluid in the ventricles and in the areas near the cranium. It is believed that the mixed hydrocephalus was provoked by the progression of brain atrophy . The expansion of the ventricles and subarachnoid space leads to this form of the disease. However, their increase provokes a decrease in brain tissue during atrophy.
Mixed replacement hydrocephalus is a serious illness in which the space of the brain replaces the cerebrospinal fluid. The risk group for this form of the disease includes people of the age who are diagnosed with hypertension, atherosclerosis. This category is supplemented by patients with instability of the vertebrae of the neck who have suffered a concussion. People who are addicted to alcohol are at risk for getting a terrible diagnosis.
With this form, symptoms may be completely absent. Or manifested by frequent dizziness, constant drowsiness, nausea, vomiting.
Diagnosis of ailment
A diagnosis is possible only after a complete examination of the patient. Initially, the fundus is carefully studied. Further, the patient is recommended to undergo additional studies, such as neurosonography, MRI, CT. A therapist (pediatrician), neonatologist, neurosurgeon or neuropathologist can suspect a terrible ailment according to characteristic symptoms and make an initial diagnosis.
For babies under 2 years old, an effective method is often used - neurosonography. This procedure is possible until the fontanel of the newborn is closed. In infants, there are other areas of the skull characterized by a very thin bone. These locations are also excellent "ultrasound windows." For example, the temporal bone is well suited for this study. This method allows you to determine the expansion of the ventricles, to detect the presence of volume formations (cysts, hematomas, tumors), to diagnose some brain defects. For all this, the above method is not accurate enough. Therefore, babies are better off doing an MRI.
A distinctive feature of diagnosing adults is the ability to listen to patient complaints. It is a thorough data collection and neurological examination that suggest the development of this pathology. However, such an examination is not enough to finally determine the diagnosis. Therefore, for adults, the doctor recommends an MRI scan. It is this study that allows you to identify any pathology of the brain.
For adults, angiography, x-ray of the skull can be used instead of a tomographic study. If the onset of the ailment is associated with a viral infection, a laboratory test for DNA or antibodies of pathogens is prescribed. In adults, hydrocephalus is differentiated with brain tumors. In children - with complications of rickets.
Drug treatment
With the slow progression of the disease, conservative therapy can be selected. In adults, this method of treatment determines the open form of the disease. It should be understood that the choice of the method of combating the disease is selected solely by the doctor.
Typically, brain hydrocephalus needs the following conservative treatment:
- Decrease in high rates of intracranial pressure. For such purposes, the doctor prescribes the means "Diacarb", "Furosemide." Reception of these drugs is a long period. Often we are talking about a few months.
- Reduced fluid The most optimal drugs are “Glycerin”, “Mannitol”.
- Strengthening blood vessels with complete preservation of electrolyte balance. To achieve this effect, potassium preparations are used.
- Decreased CSF production. An excellent remedy is Acetazolamide.
- Therapeutic puncture. This procedure is only suitable for infants. This is a method of removing excess fluid from the brain through an overgrown fontanel.
- Restorative therapy. Patients are usually prescribed coniferous, salt baths. A special course of vitamins is selected. Complementing this therapy with desensitizing drugs.
- Treatment of ailments that provoked the development of hydrocephalus. The relevance of this therapy is due to the acquired form of the disease.
If the above treatment is ineffective, doctors recommend surgery. This procedure allows patients to achieve recovery, in some cases even complete healing. And sometimes the operation is aimed at saving a sick person’s life.
Surgery. Contraindications
Unfortunately, effective medical methods to combat the disease at any stage have not yet been developed. The above treatment is used for mild forms of the disease. As a rule, such methods perfectly reduce intracranial pressure and protect the patient from complications. Doctors strictly control the dynamics of hydrocephalus.
If there are prerequisites for surgical intervention, several contraindications should be considered. None of the following operations can be performed if the patient has:
- ongoing inflammation in the shell of the brain;
- irreversible processes (blindness, deafness, epilepsy, mental disorders).
Bypass surgery
In the event that the brain does not restore the mechanism of fluid withdrawal, the doctor prescribes surgical intervention. In such cases, only surgery can help. In the recent past, hydrocephalus has been quite effectively eradicated by the only method - bypass surgery.
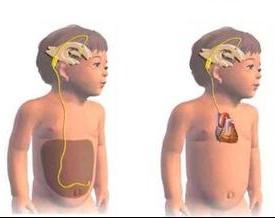
The purpose of this intervention is to restore the withdrawal of cerebrospinal fluid from the brain. For this, a shunt is installed. A ventricular catheter is located in the lateral ventricles. A special valve controls the outflow of fluid. A peripheral catheter is inserted into the atrial region or into the abdominal cavity. This helps optimize cerebrospinal fluid absorption. In some cases, after excision of one kidney, fluid is removed to the ureter.
This operation has a number of possible complications and disadvantages. Among them are the following:
- shunt infection;
- mechanical damage to the embedded system;
- violation of the functionality of the shunt;
- slow outflow of cerebrospinal fluid.
Under these circumstances, there is a need for repeated surgical intervention.
Endoscopic surgery
This method is the most common today. Endoscopy involves small incisions. This significantly reduces the risk of any complication. For the patient, the rehabilitation period is reduced. During the operation, the surgeon directs the outflow of fluid into the tanks of the brain, which are able to normally absorb cerebrospinal fluid. Thus, normal fluid circulation is restored. Successful operation completely eliminates the need for a shunt. The patient returns to normal.
Craniotomy
This intervention requires brain hydrocephalus, the causes of which lie in various obstacles to the outflow of fluid. As a rule, we are talking about aneurysms, tumors. Depending on the localization, they are able to block liquor-conducting paths. In such cases, craniotomy is used. As a rule, during the surgical intervention, new pathways for fluid outflow are created.
The consequences of the disease
This disease can lead to encephalomalacia - tissue necrosis. As a result of a violation of the blood supply to the brain, atrophy occurs. These processes are irreversible. Quite often, hydrocephalus can lead to disability. Symptoms are quite damaging to the body. The patient may lose mental and motor abilities.
A common complication of the disease is dislocation syndrome. It is characterized by compression of the brain and the emergence of oppressed consciousness, and often coma.
Congenital illness can stop its development at any age. With this outcome, the patient is fully or partially cured. In the case of rapid progression, babies very rarely survive to the age of 5-6 years.
Preventive measures
The most important rule is full compliance with all the doctor's recommendations during pregnancy for taking medications. At this stage, any infections, especially viral infections, should be carefully avoided. It is recommended before pregnancy to get vaccinations against those ailments that the expectant mother had not previously been sick with. Alcohol and tobacco should be completely excluded.
Adults need to be careful about their health. In time to diagnose ailments, treat them correctly. , , , . . – , . . . !