Despite the high level of development of medicine, some pathologies remain not fully understood. One of these diseases is Tolosa-Hunt syndrome. Currently, only the symptoms of this pathology are known, while the causes are not yet fully disclosed. Most likely, this is due to the fact that the disease is very rare and open not so long ago. In addition, Tolos-Hunt syndrome is often "masked" by other pathologies, and it is easy to confuse it. The main symptom is damage to the eyes and cranial nerves. It is known that one of the properties of this disease is that it lends itself to hormone therapy, after which there is a rapid improvement. However, relapse can occur at any time.
Description of Tholos-Hunt Syndrome
The first mention of this disease appeared relatively recently. It was described in 1961 by the English ophthalmologist Hunt. In addition to the main name, pathology is also called in another way, for example, “chameleon”. This is due to the fact that its symptoms resemble many other ailments. Among them: head tumors, infectious encephalitis, orbit myositis, and even diseases of the hematopoietic system. In addition, the Tholos-Hunt pathology is called a symptom of the upper orbital fissure, which does not accurately reflect the essence of the problem. The clinical picture of this disease depends on which particular nerves of the brain were affected. Most often, Tolos-Hunt syndrome is characterized by pain in the orbit, the inability to move one's eyes, and diplopia. With timely initiation of hormonal therapy, a complete cure or achievement of stable remission is possible.
Etiology of Tholos-Hunt syndrome
Due to the fact that the pathology has various manifestations and begins suddenly, it has not yet been possible to establish the exact etiology. It is also associated with a low incidence of the syndrome. For this reason, doctors do not have the opportunity to properly study this disease. There are several suggestions according to which pathology can develop. The following etiological factors are distinguished among patients with Tolos-Hunt syndrome:
- Malformation. This term refers to the abnormal development of the vascular system of the eyes. As a result of malformation, a mixture of arterial and venous blood occurs, which should not be normal. This disorder is more common among the female population.
- Autoimmune aggression. This factor is the trigger of many diseases. Nevertheless, it is not possible to answer the question why immune cells begin to destroy body tissues. In most cases, “aggression” occurs after stresses and long-lasting infection processes.
- Various neoplasms of the brain and cranial nerves. It can be either benign tumors or cancerous.
The mechanism of the development of the syndrome
Given that the etiology of the disease remains unknown, pathogenesis also cannot be fully studied. Regardless of the reasons why the pathology develops, only certain structures of the eye and nerve tissue are affected. As you know, the second name of the disease is the syndrome of the superior orbital fissure. This is due to pathogenesis, because the nerves and blood vessels that pass through it are affected. First of all, there are changes from the orbital vein and artery. As a result, trophic tissue is disturbed. In addition, the cavernous sinus is damaged, which is adjacent to the upper orbital fissure. Arteries supplying it become inflamed, and the tissue hypertrophies. As you know, the following cranial nerves pass through the gap: block, abducent, part of the trigeminal and oculomotor. In some cases, all of these pairs are affected. In this case, the ability to rotate the eyeball suffers. Sometimes the function of one or two pairs of nerves is disturbed.
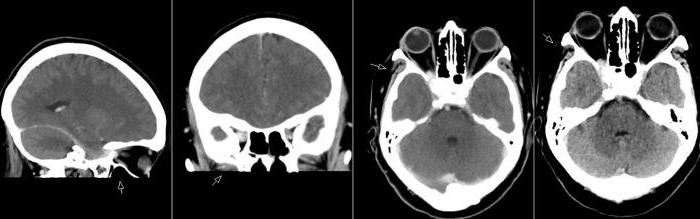
Tolos-Hunt syndrome: symptoms of the disease
Pathology most often makes itself felt in the elderly and senile. This syndrome can be affected by both women and men. The clinical picture of the disease develops suddenly, without any prerequisites. The following symptoms are distinguished:
- Pain in the orbital region. Unpleasant sensations first appear in the area of the forehead, eyebrows, head. Later, the intensity of the pain intensifies, it spreads to the eyes.
- Diplopia. This symptom appears after the development of pain. It seems to the patient that all the objects he is looking at are bifurcated. It is hard to concentrate your gaze.
- Impaired mobility of the eyeball - ophthalmoplegia. More often observed on the one hand. Its degree depends on the intensity and number of affected nerves.
- Conjunctival edema.
- Exophthalmos. It is observed in the absence of treatment and frequent relapses.
- Strabismus. It occurs when the nerves are affected only on one side.
- Low-grade fever and worsening condition.
These symptoms usually increase gradually and succeed each other. In some cases, they are all observed simultaneously. Signs of the disease can suddenly disappear, just as they appeared. Nevertheless, without treatment, the pathology always makes itself felt again. The relapse rate is different for everyone, as is the duration of the remission.
Tolos-Hunt syndrome: diagnosis of pathology
It is not easy to identify this pathology, since its symptoms are similar to many other diseases. Therefore, Tolosa-Hunt syndrome is considered a diagnosis of exclusion. First of all, the patient is asked about the features of the course of the disease (how it started, how the symptoms developed). After this, laboratory tests and instrumental diagnostics are performed. It is very important to conduct an ophthalmological and neurological examination. To exclude brain tumors, an MRI scan is performed. It is also important to conduct an ultrasound and X-ray examination of the eye orbits. The presence of vascular malformation is determined by angiography. In addition, one of the diagnostic criteria is the effectiveness of hormone therapy. If during laboratory and instrumental examinations no pronounced changes were found, and the symptoms quickly stopped after treatment, then, most likely, the diagnosis is Tolos-Hunt syndrome. Prednisolone is used for treatment most often.
Differential diagnosis with other diseases
This disease is compared with other pathologies of the eyes and nervous system. First of all, it is necessary to exclude the inflammatory processes of the brain and its membranes, as well as tumors. If meningitis or encephalitis is suspected, spinal puncture is performed. In order to exclude benign neoplasms and cancer, the patient undergoes MRI, CT of the brain and X-ray of the skull. The disease is differentiated with lymphomas, a cavernous sinus cyst and its thrombosis. Also, similar symptoms can be observed with systemic pathologies, such as sarcoidosis, orbit myositis, migraines, etc. To make an accurate diagnosis, the patient should be examined by various specialists: an ophthalmologist, neuropathologist, vascular surgeon, endocrinologist.
Treatment for Tholos-Hunt Syndrome
Treatment for Tolos-Hunt syndrome is to prescribe drugs that suppress the immune system. For this, hormone-containing medications are used: Prednisone, Hydrocortisone. These drugs also have an effect on other autoimmune pathologies, but with this disease the symptoms disappear after 3-4 days. Treatment of the Tholos-Hunt syndrome with prednisone is carried out at a rate of 1-2 mg / kg body weight. If the drug is used in the form of a solution, then from 500 to 1000 mg per day is prescribed. In addition, painkillers and vitamins are used.
Disability in the Tholos-Hunt syndrome
Usually, with this diagnosis, the working capacity of patients is preserved. It is necessary to be sure that the patient has Tolos-Hunt syndrome. Disability with this pathology is rare. However, with frequent relapses, group 3 may be prescribed. The patient should be transferred to light work that does not require visual effort. Also, with persistent nerve damage, the patient cannot drive due to impaired eyeball movement and diplopia.
Prevention of Tholos-Hunt Syndrome
It is impossible to predict the development of Tolos-Hunt syndrome in advance, therefore, primary prevention does not exist. If symptoms such as pain in the eyes and forehead, diplopia are present, a thorough diagnosis should be made. With Tolos-Hunt syndrome, secondary prevention is necessary. It includes timely hormonal therapy, immunity support. You also need to avoid stressful situations and inflammatory processes.