Pathologies of the liver, which are caused by partial or complete blockage of the bile duct, are quite common. Their symptoms, as a rule, are the yellow color of the skin and mucous membranes. And this condition is called mechanical jaundice. The description, symptoms, signs and treatment of it we will consider in this article.
Causes of occurrence
Previously, obstructive jaundice (ICD-10 code - K83.1) was perceived as an independent disease, however, numerous studies have shown that this is only a symptom. It is caused by violations in the hepatobiliary tract and the formation of calculi of bile. In the registry of the international classification of diseases (ICD-10 code - K83.1) obstruction of the bile ducts is called obstructive jaundice. Its other names are subhepatic or obstructive jaundice.
The main reason for the development of the syndrome is compression or closure of the duct, which interrupts the flow of bile into the intestine. And most often the named phenomenon is caused by the following pathologies:
- The formation of stones in the hepatobiliary tract as a result of bile stasis, that is, cholestasis, or an increase in the content of salts in bile as a result of a failure in metabolic processes.
- The development of cholangitis, pancreatitis, cholecystitis, etc.
- Tumors and cysts in the bile ducts, pancreas or gall bladder and other oncological neoplasms.
- Diverticulum of the intestine, atresia of the biliary tract and other developmental abnormalities. Often obstructive jaundice is associated with these diseases in newborn babies.
- Infection with parasites, including echinococcus and ascaris.
- Chronic jaundice (ICD-10 code - K83.1., As already indicated) in chronic form may be a sign of cancer in the head of the pancreas.
But the Klatskin tumor, or cholangiocarcinoma, is accompanied by this disease only when it reaches large sizes.
Signs of the disease
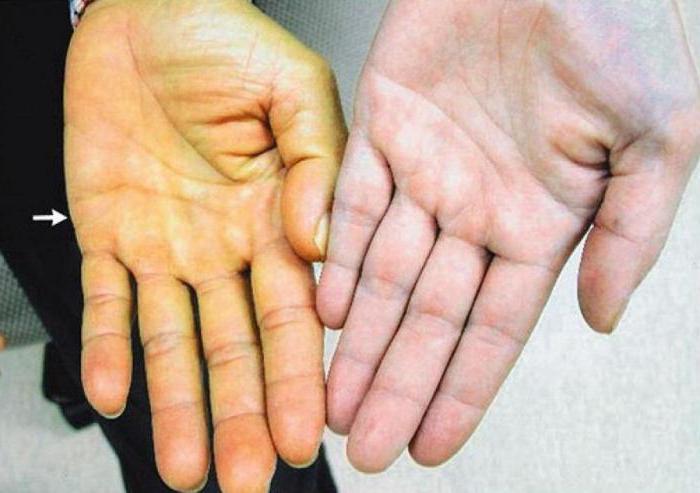
The main sign of obstructive jaundice (the ICD-10 code has already been indicated earlier) is the yellowing of all tissues in the body, including the eye proteins and mucous membranes. This phenomenon is due to an increased concentration of bilirubin. Other signs are:
- Biliary colic. They are characterized by sharp bouts of pain in the upper right abdomen. The pain gives to the right shoulder, shoulder blade or collarbone and is usually caused by physical activity, the intake of fried or fatty foods, as well as the use of alcoholic beverages.
- An increase in the size of the liver, or hepatomegaly.
- Elevated body temperature.
- Nausea and vomiting of bile.
- Itching on the skin.
- Light feces and dark urine.
Symptoms
Jaundice can also occur as a result of another disease that invariably accompanies cholestasis. Symptoms in this case are:
- Dyspeptic syndrome, which is characterized by nausea and heaviness in the epigastric region.
- Symptom of Courvoisier, when an enlargement of the gallbladder is obvious even with palpation due to its overflow with bile. There is no soreness when feeling.
- Abnormal weight loss.
Chronic form
In chronic form, obstructive jaundice causes anxiety in the right side, in the hypochondrium. Pain aching and dull, aggravated by vibration, bending and during lifting weights.
Nausea with jaundice is constant, worse after eating fatty foods and alcoholic beverages. In addition, this condition is characterized by weakness, fatigue and dizziness, which are signs of asthenic syndrome.
Next, we will find out what complicates mechanical conjugation jaundice (ICD-10 code - P59).
Complications
Regardless of what causes disruptions in the outflow of bile, this can cause cirrhosis. This disease is characterized by the formation of nodes in the liver, which consist of connective fibrous tissue. Such a pathology develops as a result of the death of active hepatocytes. In the future, cirrhosis runs the risk of developing into liver failure and dysfunction.
Another complication of unspecified obstructive jaundice (ICD diagnosis code is R17) is intoxication with metabolic products that are not properly excreted from the body, being absorbed from the intestine into the bloodstream. This disease is called toxemia. First of all, the tissues of the kidneys and liver are affected, which ultimately leads to the failure of these organs.
With the penetration of toxins into the brain, hepatic encephalopathy occurs, which is typical for the defeat of the entire nervous system. This occurs as a result of a violation of the blood-brain barrier.
Cholecystitis, cholangitis and other bacterial infections can also accompany obstructive jaundice. Lack of timely therapy and generalization of the process can create a risk of septic shock.
Note that different types of jaundice have similar symptoms, and this can complicate the diagnosis. So, hemolytic jaundice is characterized by increased decay of red blood cells and excessive production of hemoglobin, which is transformed into bilirubin. And for parenchymal jaundice , an inflammatory process in the tissues of the liver is characteristic.
In diagnostics, in addition to external signs, special attention is paid to the results of studies, and specifically to bilirubin fractions (direct or indirect) and enzyme levels.
Jaundice of the newborn
The code for ICD-10 - P59 - indicates unspecified neonatal jaundice, which affects newborns. It is physiological and pathological. The first of them appears in the first week of the baby’s life and after a while passes on its own. But sometimes this can be a symptom of some kind of concomitant illness.
In newborns, a violation of the metabolism of the bilirubin enzyme is possible. This leads to pathological pigmentation of the mucous membranes and skin.
If jaundice is of a physiological form, then this does not affect the state of health, appetite, sleep and wakefulness of the child. In the case of a pathological form of the disease, the clinical picture is supplemented by the following symptoms:
- The baby appears significant yellowness of the skin and sclera.
- He is sleepy, his condition is lethargic.
- Refuses to feed.
- Body temperature is elevated.
- Often cries, while tilting his head, bends the body.
- There is profuse vomiting.
- Cramps.
How is obstructed jaundice, we will consider below.
Diagnostics
Instrumental and laboratory research methods in the diagnosis of obstructive jaundice should not be underestimated, the code according to ICD-10 of which is indicated in the article. After all, only they can help find out the true causes of the development of the named syndrome. The prognosis for recovery depends on the timeliness of the patient’s placement in the surgical department. To identify the causes of obstructive jaundice, the following diagnostic methods are used:
- General blood analysis. If anemia is detected, which is characterized by a decrease in the level of hemoglobin and red blood cells, this indicates a chronic form of the disease. An increase in ESR and leukocytosis indicates the presence of an inflammatory process.
- Blood test for biochemistry. In this case, attention is drawn to an abnormal increase in the level of ALT, AST, gamma-glutamyltransferase, alkaline phosphatase, cholesterol, etc. This type of study also reveals the advantage of a direct fraction of bilirubin in relation to indirect.
- Computed tomography and abdominal examination of the abdominal organs help determine the size and structure of the gallbladder and liver, detect the presence of gallstones and evaluate blood flow and cholestasis.
- Esophagogastroduodenoscopy. It is an examination of the organs of the gastrointestinal tract through an endoscope. The latter is a flexible optical tube and helps to detect the existing pathology.
- Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography. It is carried out by introducing a contrast fluid, which allows you to visualize the bile ducts.
- Scintigraphy. During the study, radiopharmaceuticals are distributed over the tissues, which are controlled by the established time parameters.
- Laparoscopy and biopsy. The collection of material from the tumor for further research and cytology.
Obstructive jaundice: prognosis and treatment
What is it, discussed earlier. Now it’s worth learning about the methods of treating the disease. The presence of obstructive jaundice requires immediate medical attention, regardless of whether the child manifested it or an adult patient. The first goal of therapy is to eliminate biliary stagnation. This is achieved through the use of drug treatment with the following drugs:
- hepatoprotectors, which include vitamins from group B, ursodeoxycholic acid, Gepabene, Essentiale, Silymarin, and others;
- Pentoxil, which helps stimulate metabolic processes;
- amino acids such as methionine and glutamic acid;
- hormonal drugs, including Prednisolone;
- Neorondex, Reosorbilact, and Reopoliglukin medicines that stimulate blood circulation in the liver.
If a secondary infectious disease is added, antibiotic therapy with drugs such as Imipenem, Ampicillin, etc.
Operation
Patients who have cholestasis often need surgery. But icteric syndrome is a contraindication for such measures, since this is considered a great risk to the life and health of the patient. Therefore, at the initial stage of the disease, the pressure in the bile ducts decreases by the endoscopic method. Lithotripsy is also allowed.
Subsequent actions establish a stent or anastomoses. These measures are aimed at expanding the bile duct and removing the accumulated substance.
Complete removal of the gallbladder is prescribed to patients who have found calculous cholecystitis in chronic or acute form. This surgical intervention does not pass without a trace for the state of the body. Complications after surgery can be vomiting, nausea, pain on the right. In this case, it is recommended to observe the sleep and work regimen, adhere to proper nutrition and take antispasmodic drugs and hepatoprotectors. Sometimes enzyme therapy, such as Pancreatin, may be prescribed.
Diet
Absolutely everyone who has experienced obstructive jaundice is recommended to follow certain nutritional principles, refuse fried, fatty and spicy foods, and drink alcohol. It is necessary to eat fractionally, in small portions. Intense loads should be excluded. Therapy of obstructive jaundice is a complex and lengthy process in which the main thing is patience and adherence to all specialist advice.
We hope the information presented in the article about obstructive jaundice, treatment, diagnosis and the causes of this disease will be useful to you.