Addison's disease is a complex endocrine disease that causes malfunctioning of the adrenal glands, as a result of which hormones, in particular cortisol, aldosterone and androgens, completely stop being produced in the gland. Pathology can be caused by both external factors: the adrenal cortex or the anterior pituitary gland of the brain is damaged due to injuries, operations, removal of tumors, and hereditary factors. The nature of the second, hereditary cause of Addison's disease is not fully understood. The risk group for the development of pathology includes carriers of HIV infection, patients with tuberculosis, people suffering from drug addiction, as well as patients who underwent a kidney transplant, have cysts and neoplasms.

Symptoms and causes of Addison's disease were described by the English physician Thomas Addison (pictured) back in 1855. He first found a connection between damage to the adrenal cortex and pathological manifestations of the disease, such as increased fatigue, changes in skin pigmentation. These symptoms of Addison's disease manifest themselves in a complex.
A bit about the role of hormones
The adrenal glands are paired organs located in the abdominal cavity. Their malfunctioning is the cause of Addison's disease. Normally, the adrenal glands produce three types of hormones: cortisol, aldosterone and androgens. Yes ... it is male sex hormones that play an important role here. It turns out that androgens, contrary to popular belief, affect not only the development of male secondary sexual characteristics.
They actively participate in lipid metabolism, control cholesterol, have antibacterial and anabolic effects, participate in the synthesis of proteins in all tissues and organs in both women and men. Lack of hormones can lead to infertility, diabetes, impaired perception and confusion, psychosis. Cortisol, in turn, is responsible for the assimilation of nutrients from food, supports energy metabolism in the body.
Synthetic cortisol is prescribed for depression or high fatigue. A hormone deficiency causes disruption of the gastrointestinal tract, adynamia, cardiovascular disorders, lowers blood glucose levels to critical levels, increases insulin sensitivity, and causes a persistent feeling of fatigue.
Aldosterone regulates the optimal balance of sodium and potassium in the body, its lack negatively affects the water-salt metabolism, puts the human blood and cardiovascular systems at risk, the heart muscle loses weight, arrhythmia occurs, and blood pressure decreases.
Where to wait for trouble
The pathogenesis of Addison's disease is quite extensive. In most cases, adrenal gland dysfunction is caused by complications after serious illnesses, such as tuberculosis, syphilis, brucellosis, amyloidosis, scleroderma, tumors of a different nature, inflammation or purulent infections, in some cases radiation exposure.
Only in 30% of cases, Addison's disease, or bronze, occurs when hereditary factors influence. The disease most often affects people aged 30 to 50 years of both sexes. The frequency of diseases is one case per hundred thousand. This is how Addison's disease manifests itself, a photo of the adrenal glands is presented in the article.
A pathological change in water-salt metabolism is observed in the body, the content of chlorine and sodium decreases, the concentration of potassium increases, hypoglycemia develops, and the concentration of lymphocytes and eosinophils in the blood increases.
The first significant test that can confirm the diagnosis is a blood test for adrenocorticotropic hormone. He, as the conductor of the orchestra, controls the work of the adrenal glands, stimulating the secretion of substances. If there is no ACGT in the blood, then the disease is almost confirmed.
Addison's disease occurs for a number of reasons:
- Causes associated with direct damage to the adrenal cortex: disease, infection, mechanical damage, atrophy.
- Disruption of the pituitary gland when its anterior lobe does not produce the hormone already known to us - adrenocorticotropic.
- Reception of synthetic corticosteroids. They are used as maintenance therapy for various autoimmune disorders, for the prevention of tissue rejection during organ transplants. And also with psoriasis, arthritis, lupus erythematosus. The body gets used to getting a portion of "sweet" for free and stops its production on its own. Over time, this can lead to complete atrophy of the gland.
Addison's disease and its symptoms
- A person is bothered by constant fatigue, weakness, and poor health. Moreover, all these symptoms only intensify during the day. It comes to the fact that the patient can not get out of bed.
- Weight goes quickly. Muscle mass is lost, first of all, as a result of disturbances in the electro-hydrolysis metabolism of creatine and creatinine.
- Digestion is broken: there are then constipation, then diarrhea, the patient is tormented by abdominal pain. Often nausea attacks.
- The color of the skin changes. Stains from lemon yellow to dirty brown appear. Fingers darken, mucous membranes, hair can even darken.
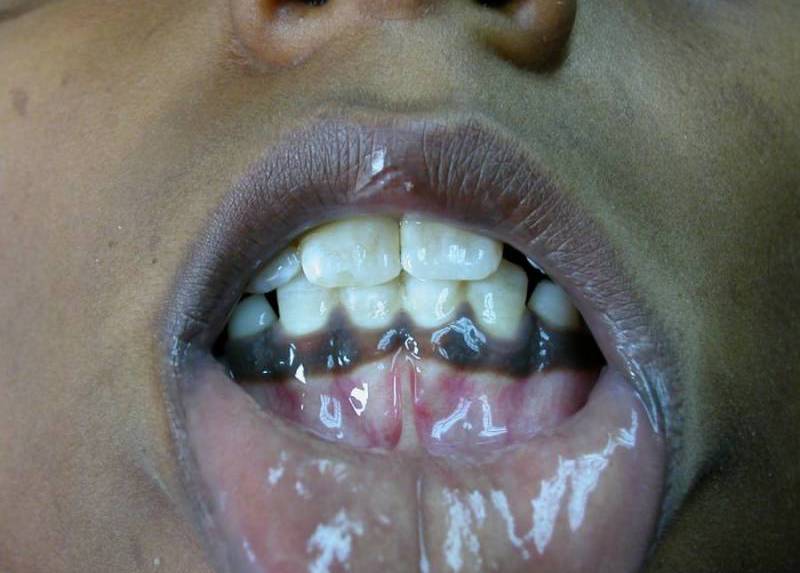
- The person is tormented by attacks of shortness of breath, palpitations become more frequent. This is due to some pathological decrease in the heart (and we know that this is also a muscle), heart failure, rhythm disturbance occurs. Pressure decreases, anemia develops, dizziness is frequent.
- Body temperature is often below normal. People constantly freeze, catch a cold.
- Decreases libido.
- Depression, memory and attention disorders, sleep disturbance.
- Short temper and irritability.
- Craving for acidic or salty foods, constant thirst.
- Lowering blood glucose.
- Menstrual irregularities (in women).
- Impotence development (in men).
- Increased neuromuscular irritability due to an excess of phosphates.
- Possible tremors or impaired sensation of the extremities caused by an excess of potassium. Possible dysfunction of swallowing (dysphagia).
Important! When to get tested
Symptoms of Addison's disease may sometimes not manifest in acute form. The patient does not have a fever, there are no drastic changes in the state of health. Symptoms, seemingly unrelated to each other, are attributed by a person to fatigue or nervous strain, colds, poisoning, etc. This disease does not “hit” in any one area or system of the body, it acts unnoticed immediately in several directions. Therefore, often from the first signs to the correct diagnosis can take years.
Is there a threat to life?
Sometimes, against the background of the absence of any symptomatology, the disease can appear suddenly and in an acute form - a person's blood pressure and blood sugar drop sharply, which most often leads to fainting and even coma. The causes of death in Addison's disease are failure to provide assistance during an attack. This condition in medicine has received the name "Addison crisis." It can be “triggered” by a protracted cold, trauma, blood loss, surgery, adrenal vein thrombosis, embolism of the adrenal arteries, or hemorrhage in the tissues of an organ.
Signs of Addison crisis:
- Dizziness and loss of consciousness.
- Sharp pain in the stomach, back, or legs.
- Dehydration on the background of severe vomiting and diarrhea.
- A sharp drop in blood pressure.
- Decrease in glucose level.
- Confusion.
- Excess potassium in the blood.
- Change in skin color, the presence of specific spots.
This condition is especially dangerous if a person does not even suspect about the disease and begins self-medication, which in most cases does not bring relief, especially if the skin with Addison's disease has not yet changed pigmentation, as in the photo.
In this case, a timely diagnosis can save a person’s life. Sometimes this condition occurs in patients who are aware of their diagnosis, but for some reason do not receive treatment, or the doses of synthetic hormonal drugs do not meet the required ones. As you know, taking synthetic hormones contributes to the "addiction of the body", and it begins to reduce the production of its own, even in minimal doses. Periodically, to control the hormonal background and adjust the therapy, it is necessary to repeat the tests.
Emergency help
Intravenous administration of hydrocortisone, saline and dextrose allows you to stop the crisis. Resuscitation teams are equipped with such drugs in full. Further, the patient is required to be hospitalized in a hospital, or in the endocrinology department, or, in life-threatening cases, in the intensive care unit. In addition to the dose of hormones, the patient undergoes a series of procedures that normalize the water-electrolyte balance, as well as normalize blood sugar levels.
Three main degrees of the course of the disease can be distinguished, depending on the state of the person and the clinical picture.
- Easy degree. The manifestation of symptoms is not so pronounced. To alleviate the condition, it is enough to adhere to a potassium-free diet, increase the intake of sodium or ordinary salt and ascorbic acid.
- Medium degree. Usually this form of the disease occurs most often. Hormone therapy is prescribed with drugs containing cortisone, hydrocortisone, prednisone.
- Severe form. Usually, the course of the disease is complicated by addison crises. Life-long therapy is prescribed with the above drugs, as well as drugs containing deoxycorticosterone.
When making the correct diagnosis of bronze (Addison's) disease, the endocrinologist usually excludes other diseases with similar manifestations. And there are a lot of them: melanosis, hemochromatosis, malaria, tuberculosis of the kidneys, scleroderma and even arsenic poisoning. In any case, a blood test is not enough. The doctor will prescribe a number of procedures, having studied the medical history and interviewed the patient.
Specific studies of the disease
- Detailed blood test. First of all, the doctor is interested in the levels of the following substances: potassium, chlorine and sodium.
- A blood test for the presence of ACGT, as well as the hormones cortisol and aldosterone.
- Adrenocorticotropic hormone injection. The specialist takes blood twice, before and after the procedure. The goal is to provoke a reaction of the adrenal glands to a portion of the hormone. If the adrenal function is normal, then the concentration of steroids in the blood immediately rises. If the damage to the gland is critical, then there will be no changes associated with an increase in cortisol.
- Hypoglycemia test with insulin. On the contrary, he studies the reaction of the pituitary gland to an increase in blood sugar. The laboratory assistant makes several samples over a period of time. If the patient is healthy, then after the intervention of ACGT, the glucose level decreases, and the adrenal glands immediately begin to produce cortisol. If there is no increase in hormones in the blood, then the problem is with the pituitary gland. To confirm the diagnosis, an MRI of the brain is performed.
- Computed tomography of the adrenal glands. The doctor examines their size, looks to see if there are visual changes, tumors or inflammation.

Tactics of treatment of Addison's disease
In case of confirmation of the diagnosis, the patient is shown hormone therapy. Treatment for Addison's disease is carried out both courses and for life. Doses are selected individually by the endocrinologist depending on the condition of the patient, stage of the disease and the presence of concomitant diseases.
In the case of a chronic course, patients are usually prescribed tablets containing synthetic hormones or corticosteroids.
List of drugs:
- Florinnef is a synthetic aldosterone.
- "Cortinef" is a synthetic cortisol, or hydrocartisone.
- Drugs - androgen substitutes - "Dehydroepiandrosterone".
If a person cannot take therapy orally, for example, due to vomiting, the doctor prescribes injections.
An important rule of recovery is self-control
With Addison's disease, how do people live? The most important condition for the success of any therapy is the desire and responsibility of the patient himself.
Even if your appearance changes dramatically, it can be beneficial. As Winnie Harlow did, suffering from a genetic disease similar in manifestation to Addison's disease. She has become a world famous model and is not at all shy of herself, on the contrary, she is proud.
Unfortunately, for Addison patients, life is divided into two parts - “before” and “after”. This applies to working hours, diet and even sleep. Those who work on weekends will have to abandon processing, otherwise the disease will manifest itself again.
Among other things, you should refrain from alcohol and nicotine. The human body is already experiencing considerable chemical stress.
It is necessary to change the diet. First of all, the menu should be as useful and high-calorie as possible. It is necessary to enrich the body with vitamins, especially A, E and C, as well as the necessary amount of animal protein and amino acids, in particular tyrosine. It helps synthesize adrenaline. Particular attention should be paid to foods rich in potassium, it is better to exclude it altogether.
Prohibited foods: potatoes, dried apricots, raisins, peas, beans, mushrooms, dried fruits, coffee, nuts and others, rich in potassium.
Recommended products: vegetables, cereals, meat broths, watermelons, pumpkin, sea fish and dairy products. It is important to include more salt in the diet, as well as meat and seafood. So-called “fast” carbohydrates (sugar, honey, jam) are allowed, and currants and rose hips, as well as brewer's yeast, are best suited to maintain the level of vitamins B and C.
Alternative therapy
Teas and infusions in folk medicine have always had special properties. Old recipes for liver or kidney teas have been passed down from generation to generation. There are a number of recipes that stimulate the adrenal glands.

- Infusion of geranium leaves. For cooking, the leaves are torn into small pieces, brewed with a glass of boiling water. The plant is rich in radium, which helps restore the gland. Take the infusion warm after eating.
- Horsetail. Affordable, growing in almost every forest, and a useful source of ascorbic acid and carbohydrates. It has a pronounced anti-inflammatory and restorative property. Dry crushed leaves are brewed in the ratio - 1 teaspoon per glass of water. Take two to three times a day after meals.
- Tincture of snowdrop leaves. It is necessary to take 80 snowdrops, pour half a liter of vodka. Put in the sun. Wait 40 days. Take 20 drops daily before meals three times a day.
- Decoction of bearberry and ledum. A mixture of dry herbs 1: 1 pour one and a half glasses of boiling water. Cool. Drink half a glass once or twice a day before meals.
It is important to understand that traditional medicine is only an auxiliary therapy in the treatment of Addison's disease. Infusions and teas only alleviate the patient’s condition, they do not remove the causes, but support the adrenal gland in the volume that is possible at this stage of the disease. In any case, the endocrinologist is obliged to give advice on how to use these plants in each specific case, to select an adequate dose and course of their use.
In general, with the correct and timely treatment of patients with Addison's disease, its manifestations may become invisible to the environment: acquaintances, friends. The only amendment is not to interrupt treatment yourself, undergo examinations and only then adjust the volume of therapy together with specialists. Remissions can be short-lived, and the consequences can be severe.
In general, subject to the recommendations of the attending physician and replacement therapy, the life expectancy of patients with this diagnosis does not differ from healthy people.