A person’s heart rate, called briefly pulse, can be very different. Infectious diseases usually increase the pulse rate, and the sleep state slows down. But normally in an adult, it should be rhythmic and be in the range of 60-100 beats per minute. Another heart rate will be called tachycardia or bradycardia.
Since ancient times, healers of the East have been diagnosing a person’s condition and determining his illness by pulse, while distinguishing between the most different shades and sounds of a heartbeat, and not just its frequency, which depends on so many factors. The purpose of the article is to understand how bradycardia differs from tachycardia.
Features of the structure of the human heart
To begin, consider the structure of the human heart. The heart is the central organ of the cardiovascular system. It provides the rhythmic contractions of the blood circulation in the body. It is a hollow muscle organ, divided into four chambers: the right and left atria and the right and left ventricles. Both atria and ventricles are separated from each other by partitions. Atria are cavities that receive blood from veins and push it into the ventricles, which eject it into the arteries. Right - in the pulmonary artery, left - in the aorta. So the blood enters immediately into two circles of blood circulation. The right and left chambers do not communicate with each other, and the atria and ventricles are connected by valves. Valves determine the direction of blood flow in the heart: from the veins to the atria, from the atria to the ventricles, from the ventricles to the large blood vessels.
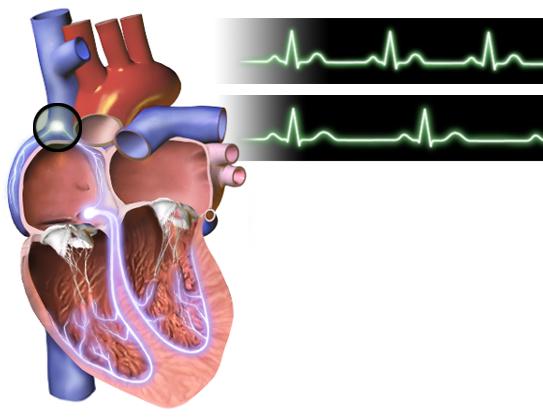
Any painful changes in the valves (rheumatic or other origin) disrupt the proper functioning of the heart and the whole organism. When listening to the heart, the closing of the valves and the reduction of its 4 chambers are perceived as heart sounds. With valve disease, instead of tones or along with them, noise is heard due to the narrowing of their holes.
The heart muscle is pierced by a large number of sensory nerves. Which regulate cardiac activity, but also cause severe pain with any violation of blood supply.
What is cardiac arrhythmia, its types
Arrhythmia (Greek arrythmia - rhythm disturbance) is called a violation of the normal rhythm of the heartbeat. Types of arrhythmias: asystole, extrasystole, bradycardia and tachycardia.
Bradycardia (Greek bradis - slow + kardia - heart) - a slowed heart rate, less than 50 beats per minute.
Tachycardia (Greek tachys - fast + kardia - heart) - the rapid rhythm of heart contractions. The frequency of contractions is from 100 to 180 beats per minute. Thus, tachycardia and bradycardia are two opposite states of the heart according to the number of heart contractions.
Asystole (Greek a - not + systolie - contraction) - a sharp weakening of the heart muscle, causing a decline in the activity of the heart.
Extrasystole (Greek. Extra - over + systolie - reduction) - the occurrence of an extraordinary heart beat or the passage of another stroke.
What determines the heart rate
It is generally accepted that a person’s heart rate directly depends on physical activity or exposure to the nervous system.
The cardiac muscle has the property of automatism, that is, its contractions are involuntary and do not stop for a single minute throughout their lives. Its activity, frequency and strength of contractions are regulated by the central nervous system (depending on the needs of the body) through two nerves: vagus and sympathetic. The first slows down the heart rate and weakens their strength. A sympathetic, on the contrary, speeds up her contractions and increases their strength. Here are the main differences between tachycardia and bradycardia. Muscle contractions of the right and left halves of the heart occur simultaneously. But first, the atrial muscles perform this action, and the ventricles relax. And then both ventricles contract. The strict sequence of contractions of the parts of the heart is due to the special excitation-conducting system of the heart. This is the so-called bundle of His. Violation of this conductive system causes severe dysfunction of the heart.
In healthy people, heart contractions do not cause any subjective sensations. And rhythm disturbances can appear only with significant physical stress (mainly in untrained individuals) or with strong emotional experiences (fear, fear, anger, etc.). With some cardiovascular diseases, arrhythmias can occur even with minor loads. It all depends on the condition of the heart and blood vessels.
Can several rhythm disturbances occur at the same time?
Can tachycardia and bradycardia occur at the same time, for an ignorant in medicine it sounds like a joke. However, such conditions of cardiac activity are quite possible. If the elderly begins to develop a decrease in the number of active cells at the conduction site (sinus) due to fibrosis, then this leads to bradycardia. But fibrosis also affects other heart tissues, especially the atria, causing them to tremble (the so-called atrial fibrillation). As a result, older people can suffer immediately from heart palpitations (tachycardia) and heart weakness (bradycardia). This is the so-called sick sinus syndrome, or bradycardia-tachycardia syndrome. His treatment is serious enough. A dangerous consequence of this syndrome is prolonged dizziness and even loss of consciousness during cardiac arrest, even short-term. Fainting is very dangerous, especially in older people, because it can lead to falls, which means fractures and other injuries.
Comparison of various rhythm disturbances
No disease pleases, so what is worse - tachycardia or bradycardia, it’s hard to say.
Chronic rhythm disturbances indicate a malfunction in the heart, the need to consult a doctor and conduct treatment. Some people tolerate bradycardia really well, while for others it changes their whole lives. People simply don’t notice a small tachycardia.
But there are times when the decrease in heart rate only means that the person is young and well trained, his blood vessels are well developed, and forty beats per minute (and sometimes thirty) is enough for the body to be perfectly supplied with blood - it functions normally .
Age-related heart rhythm disturbances and pacemaker
Usually, “senile” doctors call such heart diseases as angina pectoris, ischemia, atrial fibrillation and others associated with tissue degeneration, decreased motor activity, including due to concomitant diseases. Most of these people who have tachycardia and / or bradycardia have had infectious diseases or have cardiovascular, endocrine and other diseases.
If abnormalities in the sinus node become chronic, associated with the aging of the body and are not treatable, the “artificial pacemaker” can correct the situation, or more simply, a pacemaker. Sometimes it is much more effective than drug treatment, because it prevents fainting.
Children's heart rhythm disturbances
A child can have the same numerous cardiac arrhythmias as an adult: tachycardia and bradycardia simultaneously or separately, extrasystole, blockade, and others. You need to know that in healthy children there are periods when the heart rhythm can be disturbed.
Moreover, the most dangerous periods are:
- newborns;
- from 4 to 5 years;
- from 7 to 8 years;
-from 12 to 14 years.
The causes of rhythm disturbances in children can be both congenital anomalies and diseases that are infectious in the first place (diphtheria, bronchitis, tonsillitis, pneumonia, intestinal infections, etc.).
The heart rate in children of different ages is different: in newborns - 140 beats per minute, in one-year-olds - 120, in five-year-olds - 100, in ten-year-olds - 90. In adolescents - 60-80 beats per minute.
Teenage heart rhythm disturbances
In adolescence, when there is a jerky, uneven development of various organs and systems, many have arrhythmia (every second teenager). But usually there is no health hazard. Teenagers do not feel it, usually it does not bother them and is detected only during a routine examination. And arrhythmia (usually bradycardia) passes by itself.
However, if even after two years, tachycardia or bradycardia does not go away (or intensifies), you must consult a doctor and undergo an examination.
A few recommendations from a cardiologist
One way to relieve a tachycardia attack is as follows. Relax first, then exhale completely and hold your breath for as long as possible. This raises blood pressure and helps normalize heart rate. Usually one time is enough, but if necessary, you can repeat more. This exercise usually reduces heart rate, returning the pulse to normal.
Exercises that cause vomiting, slight pressure on the eyeballs, squeezing the abdominal press also help relieve an attack of tachycardia, as they increase the pressure.
It is advisable to remove bouts of bradycardia under the supervision of a doctor or on his clear recommendation with the help of drugs. Before the doctor arrives, Validol or Corvalol according to the instructions is used to stabilize the rhythm.
Prevention of heart rhythm disturbances
Prevention and treatment of heart disease is best done according to the specific recommendations of a doctor, but general principles still exist, and the most important is a healthy lifestyle.
This very broad concept includes not only the absence of such bad habits as tobacco, alcohol, gluttony, lingering on your favorite sofa, many hours of communication with a TV or computer.
This is, firstly, the ability to enjoy every day of life. Heart disease provokes a fear of death, so you need to try and live happily, breathe deeply, and forget about anxieties. It is difficult, but necessary. Only when every day you meet with hope and desire to live (and exercise!), The heart will be fine.
- This is followed by physical activity. This is not fussy running around “about business,” full of petty anxieties and worries that destroy health. It is necessary to allocate at least half an hour daily to give the body a good load. Walking, swimming, gymnastics with regular repetition will make anyone healthier and more fun. The rhythm of classes is selected together with the doctor or himself, if it comes to prevention.
A friend after a heart attack recovered only when he began to walk up to 10 km per day, walking, and not "on business."
- It is necessary to include more various products in the food, which helps in normalizing the metabolism and uplifting. You can not drink strong tea, coffee, cocoa, eat a lot of fat and sweet. Fish, vegetables, cereals should be on your table constantly. When bradycardia is not recommended: honey, dried apricots, baked potatoes, cherries, cherries, cranberries, peaches.
- To relieve seizures that arose after stress, you can use aromatherapy, such as lavender, and better laugh therapy - daily comedy viewing, fun reading.
- Further, you can recommend thinking less and doing more with your hands, sitting less at the TV (and a computer in general, like a microwave, can provoke arrhythmia!), And walking more, even slowly, is better in the park, but you can even on the balcony, doing simple exercises.
- You need to see a lot of people. Look at them from the windows if you are not able to go outside. Communication for the cores is a necessary component of recovery.
It is difficult to say what is better - tachycardia or bradycardia, but one thing can be stated for sure: spare your heart, move and communicate more, enjoy life!