The first schedule of the Moscow school is Favorsky Vladimir Andreevich. The artist’s biography includes not only creativity, but also participation in the First World War, and work on numerous theoretical works, and teaching. But first of all, he is known as a book illustrator. Many people unmistakably recognize his drawings for the works of W. Shakespeare and S. Ya. Marshak.
Youth
We can say that Favorsky was destined to connect his life with art as a successor to the family tradition. The artists were his grandfather, mother and great-grandmother. The great Russian illustrator was born in 1886 in Moscow. Constantly observing how his mother draws, he himself took up brushes and pencils. Initially, he perceived painting as a pleasant pastime - no more. But entering the world of art, Tabor remained here forever and set as his goal to introduce as many people as possible to him. He began his career as a painter, giving high hopes. But later he chose graphics as the kind of art closest to the people.
The artist’s childhood, spent in the circle of a loving family, was deprived of adversity. The closest relatives - artists, architects, sculptors - contributed to the growing interest in art. And when it came time to go to school, in addition to basic education, it was decided to send the boy to a private art school of K. F. Yuon.
Study
At the same time as attending Yuon’s school, the young man attended evening classes at the Stroganov School. After graduating from high school, he went to Munich and entered the Faculty of Economics, but soon realized that this was not his occupation at all. In 1906, the young man entered a private educational institution, which was led by a Hungarian artist of Armenian origin Shimon Hollosi. Vladimir Andreevich Favorsky will always remember this teacher with gratitude as one of his favorite mentors. Without a doubt, he had a great influence on the formation of young talent and the formation of his artistic principles.
University of Munich, however, Tabor did not drop out and attended a course in art history. In 1907, he returned to Russia and continued his art studies at Moscow University.
Family life
In his last year at the university, in 1812, Vladimir Andreevich Favorsky married Maria Derviz, a lovely girl with a lively character, to all other advantages, a promising artist. Among her relatives was Valentin Serov, who in every possible way encouraged Maria's craving for art. She studied painting in St. Petersburg and in France. In Moscow, like her future husband, she was a student of Yuon, and then the School of Painting, Sculpture and Architecture. Mary was not destined to become a great artist, but the reason for this is the circumstances of life, and not the lack of talent. Despite this, until the end of days she was a friend and assistant for her husband. The last decade of her life, she worked on memories, thanks to which the researchers of Tabor were able to restore some pages of his biography.

The artist had three children: two sons, Nikita and Ivan, and daughter Maria. Both brothers volunteered for the front when the Great Patriotic War began. The eldest died in the first year of the war, the younger did not live a couple of months before the end. And Maria Vladimirovna became a ceramic artist and keeper of family archives.
Maturity of the artist
After graduation, Vladimir Favorsky was engaged in teaching and worked on the theory of art. With the beginning of World War I, he goes to the front and goes through the whole war. The artist returned to Moscow in 1918 with the rank of ensign. After the army, he quickly became involved in the creative life of the capital.
The artist resumed teaching. In the 1920s, he heads one of the departments of the Higher art and technical workshops (VKHUTEMAS), teaches students engraving and woodcut. In 1923 he became rector of VKHUTEMAS. Favorsky begins work on the design of books by Pushkin and Tolstoy, and since then book graphics have become one of the main tasks of his life.
At the same time, he closely communicates with the philosopher P. A. Florensky. The collaboration, backed up by the friendship and kinship of the characters, enriched both of them. In many theoretical positions of the artist, one can notice the influence of Florensky. Together they joined the Left Front of the Arts (LEF). Because of the belief that the spiritual principle prevailed over the intellectual, they were dubbed the group of “production mystics”.
By the end of the 1930s, the artist was delving deeper into the theory of art. He writes articles and reports, teaches at the All-Russian Academy of Arts. He continues to engage in engraving, draws up books, and collaborates with the Moscow Art Theater. Participates in exhibitions in Venice and Paris.
Favorsky entered the 40s as a mature master. The artist received recognition and the opportunity to work on the most interesting orders. His skill continues to grow, the technique is being improved. The depth of images and expressiveness of the stroke are honed.
Last years
In his declining years, the artist reaped the deserved fruits of his work. In 1956 he became an Honored Artist of the RSFSR, in 1959 - People's Artist of the RSFSR, and in 1963 - People's Artist of the USSR. He receives gold medals at international exhibitions in Brussels, Leipzig and Sao Paulo. And in the spring of 1962, Favorsky was awarded the Lenin Prize for his achievements in illustration. This does not mean that the artist rested on his laurels - he continues to work on a series of drawings, engravings, and is engaged in painting. The venerable master passed away the artist in late 1963. His grave is located in Moscow at the Novodevichy cemetery.
Theoretical views
Favorsky carefully developed and designed his theoretical program. The concept was based on lectures that the professor gave to his students. With them, he began the design and systematization of his vision of art. As a result, books were born “On Art, on a Book, on Engraving”, “Font, its Types and Connection of Illustration with Font”, “Lectures on Theory of Composition”. In them, Favorsky talked about the process of interaction with the form and its embodiment on the plane. He considered the topic of interpretation of lines, the role of the plane in painting and graphics. Each type of surface, the artist ascribes his own composition and "visualization."
Regardless of what aspect of creativity Favorsky discusses, the idea that the production and ideological components of it should be indivisible and balanced sounded like a refrain. The roll in any direction causes deformation and leads to the degeneration of art. Creativity must be life-affirming, since the concept of truth is inseparable from the concept of beauty. Aesthetization of ugliness for art should be unacceptable.
Book graphics
Tabor often said that he does not illustrate the work, but creates a book. He always approached the task comprehensively, creating not only illustrations, but also selecting the font, format, ornament, proportions. All this should be subject to a single stylistic synthesis. The rhythm of indentation, margins and paragraphs should be in tune with the rhythm of engraving. In the work, Favorsky was guided not only by his creative intuition, but also relied on the experience of antiquity and rebirth. He introduced the concept of “book architecture” - the science of proportionality and harmony of all its components.
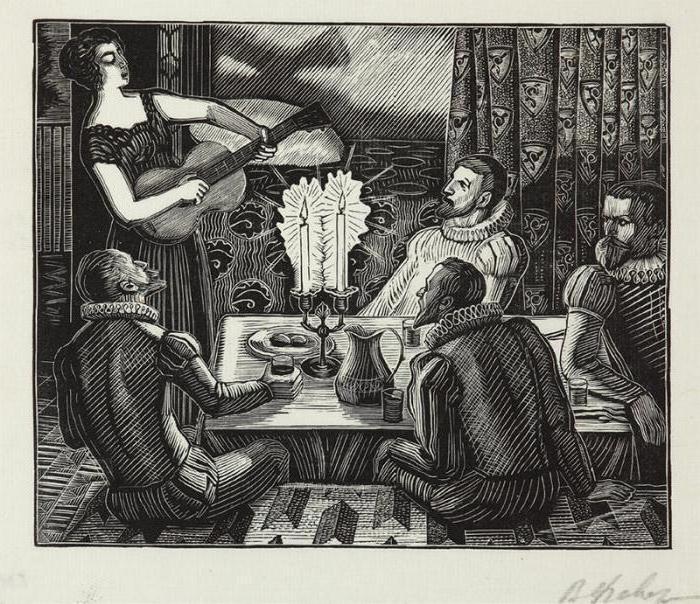

Tabor found his approach to each work. The design of “Words about Igor’s Regiment” was inspired by ancient Russian books. Ornaments and initial letters refer the reader to old handwritten texts. Illustrations to Pushkin's “Little Tragedies” are distinguished by high detail, attention to the smallest details. Heroes freeze in theatrical poses and become a symbol of expressed emotion: greed, grief, anger, fear. In the illustrations for Gogol's “Shponka”, grotesque fantastic creatures appear: giant insects, bird-headed people. The visual series not only complements the text, but also serves as a separate work of art that can provide food for thought. One of the works of a mature author is an illustration to S. Spassky’s work “New Year's Eve”. Their style is dictated by the dramatic plot of the work. Drawings are sharp, bold, dynamic. The artist confidently plays with the composition, while always achieving an impeccable result. Engraving of Favorsky has gained many fans and is still valued among collectors.
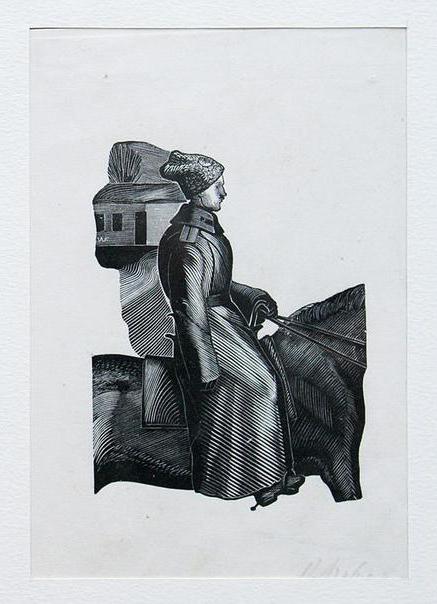

The artist illustrated Pushkin, Shakespeare, Tolstoy, Dante, Gogol, Merime, Burns, and this is not a complete list of his works. Not only adult literature was designed by Favorsky, he also worked closely with the publishing house DETGIZ. The illustration for the poem “If the Children of the Earth ...” is familiar to many from the textbook. Barefoot guys laugh carelessly and run in the meadow, enjoying a peaceful life. Every Soviet child must have read Marshak's collection, where there was an illustration for the poem "Mustachioed-striped" with a naughty kitten.
Other types of creativity
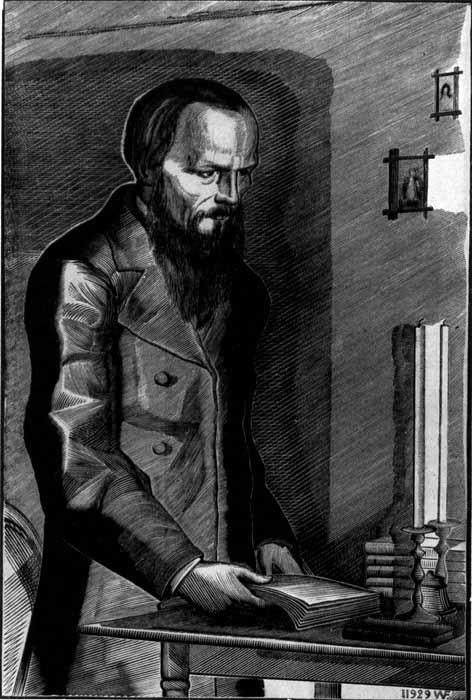
The scope of one art form was close to Vladimir Andreevich. He became famous not only for book illustration. In the second half of the 40s, Favorsky performs the cycle “The Great Russian Generals”, where the portraits of prominent people embody the greatness and power of Russia. One of his best works is a portrait of F. M. Dostoevsky. Serious and focused, the writer appears before the viewer. The artist does not flatter him, does not adorn reality, does not pretend to be caricatured pathos. But in the modest figure of Dostoevsky there is an alarm for the Russian people, love for his country and the extraordinary power of thought.

His favorite technique was woodcut and woodcut, but he was also attracted to linocut. The charming Samarkand cycle was created in this technique. Having started his career as a painter, throughout his life, Favorsky periodically took up brushes. His authorship belongs to the mosaic "1905". He was engaged in sculpture and monumental painting. In addition, the artist collaborated with theaters - made sketches for performances and costumes, and in his youth, even wooden dolls for children's performances. Whatever Vladimir Favorsky undertook, he did everything with love and great skill. But in the memory of his descendants, he remained primarily an outstanding graphic artist and illustrator.