In urological practice, there is such a disease as a paraurethral cyst. At the heart of the disease is a blockage of the glands localized near the urethra in women. Such a pathology is extremely rare. That is why the disease often raises many questions both when making a diagnosis, and in methods of dealing with it.
Disease Description
To understand what a paraurethral cyst is, it is necessary to consider the anatomy of the female body. The urethra (urethra) is surrounded by many glands. They are called paraurethral. In medical practice, they are often referred to as Skin glands, by the name of the scientist who described them in detail.
They have a clustered shape. In their structure resemble the male prostate. Numerous sinuses, ducts form an extensive network of tubular canals. They surround the urethra along the lateral and posterior walls. The ducts of the glands are completely emptied into the urethra. The secret that they produce protects the urethra from pathogens. In addition, it plays the role of a barrier during sexual contact.
In the process of life, the skin glands undergo some changes. During pregnancy, they increase to the maximum size. After birth, they are involutional. Menopause is characterized by their atrophy. That is why a cyst is most often observed in women of childbearing age.
Sometimes the gland exit clogs. In this case, the secret accumulates in them, and does not exit into the urethra. This is how a paraurethral cyst is formed. This formation is a small round seal. It is quite elastic to the touch. Most often, the cyst is localized near the exit of the urethra, near the surface of the skin. However, there are cases when the formation was found in the deep layers.
The causes of the disease
Many sources are known, due to which a paraurethral cyst is formed in women.
The basis for the development of pathology may be:
- inflammatory diseases of the urethra;
- birth trauma provoked by episiotomy (perineal dissection);
- bruises, various injuries of the urethra;
- microtrauma of the urethra provoked by gross sexual intercourse;
- chronic pathologies that provoke a decrease in immunity;
- damage during labor;
- diabetes;
- some intimate hygiene products;
- sexually transmitted infections.
Characteristic symptoms
Pathology can be completely asymptomatic. This is observed if a small-sized paraurethral cyst is diagnosed. Symptoms of large formations are more pronounced, and cause serious discomfort to women.
Most often there are complaints about the following phenomena:
- swelling in the area of cyst formation;
- dysuria;
- a variety of urination disorders;
- discomfort during walking, sexual intercourse;
- urinary incontinence;
- pain during urination, sometimes pain;
- swelling of the urethra;
- hematuria (presence in the urine of blood);
- burning sensation, pain in the area of education;
- urinary incontinence;
- feeling of fullness in the area of the cyst;
- the stream of urine is weakened;
- foreign body sensation in the urethra;
- high sensitivity of the paraurethral zone caused by compaction;
- infectious processes in the area of the cyst, which can provoke suppuration;
- urethral diverticulum formation;
- the presence of secretions (mucous or purulent);
- changes in cysts (hyperplastic, neoplastic);
- the formation of a malignant tumor (extremely rare phenomenon).
If the unpleasant sensations described above in the urethra in women are observed, then you should know that regression and self-resorption for the ailment are uncharacteristic. Therefore, you need to seek help from a doctor.
Disease classification
For pathology, two forms are characteristic:
- Skin cysts. They are formed due to blockage of the glands located in the area of the urethra. In appearance, they resemble a pouch.
- Gartner passage cysts. Such formations are formed as a result of abnormal development of the genitourinary system. The basis of their appearance is the fusion of the wall of the vagina and urethra. This leads to an accumulation of secretion, against the background of which a cyst develops.
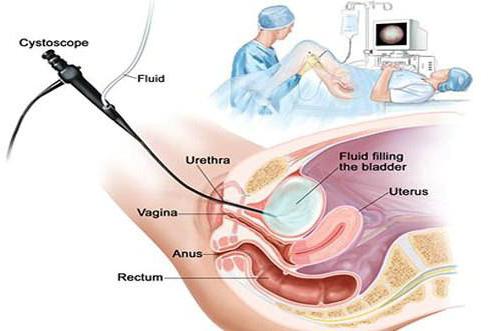
Regardless of the form of the disease, education cannot resolve on its own. Doctors say that prolonged exposure to the cyst near the urethra is quite dangerous. Pathology can lead to the development of inflammation or suppuration. It should not be forgotten that a paraurethral cyst is a favorable environment in which congestive urine accumulates. Of course, against the background of such a clinic, bacteria multiply. The inflammatory process can provoke an abscess. And it is extremely unpleasant if the cyst burst. In this case, the purulent contents are opened into the urethra and diverticulitis develops.
Progression stages
Doctors distinguish several degrees of the development of the disease:
- First stage. There is an infection of the glands. As a result, disorders in the genitourinary system begin to develop. Sometimes they are asymptomatic. But most often it is at this stage that the first unpleasant sensations in the urethra in women can appear. As a rule, patients complain of discharge, pain during urination.
- Second stage. The cyst begins to increase in size. The above symptoms of the disease are joined by pain in the pelvic area, discomfort during intercourse. Foci of chronic inflammation may be present around the lesions.
Diagnostic Methods
If there is unpleasant discomfort in the pelvic area, then you must immediately go to an appointment with a gynecologist. The doctor will conduct an examination, and if he finds a pathology, then you will be advised to see a urologist.
But be prepared for the fact that any urological clinic, in order to confirm the diagnosis, will offer to undergo examinations, such as:
- Analysis of urine;
- Ultrasound of the pelvic organs;
- urine culture (bacteriological);
- MRI
- urine cytology;
- uroflowmetry;
- a smear from the urethra;
- urethrocystoscopy.
Treatment of ailment
The cyst is not able to decrease on its own. Medication will not provide this. And it should be remembered that education is quite dangerous. Indeed, at any moment, suppuration can begin. And, of course, it is completely undesirable to wait for the moment that the cyst bursts.
Given all of the above, it should be strictly understood that with such an education, you must immediately contact a competent specialist. Clearly understand: the only method to combat a parauretic cyst is surgery. In other ways, it is impossible to treat the ailment.
The operation involves a little intervention. During it, the cyst is removed, its walls are carefully excised. A few days later, the postoperative wound heals. Patients who have undergone this intervention are advised to abstain from sexual activity for 2 months.
Regardless of which urological clinic is chosen, only surgery is performed to remove the cyst. Unfortunately, electrocoagulation, various punctures, laser exposure do not allow to achieve complete healing. Such methods only temporarily relieve the patient from unpleasant symptoms.
In the presence of infection or inflammation, the patient is prescribed medication before and after surgery.
Possible consequences
It must be said that a paraurethral cyst can lead to the appearance of extremely negative complications even after surgery.
The likelihood of negative consequences completely depends on the formation itself, its size, the presence of infectious and inflammatory processes, and the location.
Unpleasant complications arising from the operation may include:
- recurrent infection;
- pain urethral syndrome;
- hematoma;
- bleeding;
- relapse of the cyst;
- urethral stricture (such a narrowing is accompanied by inflammation);
- urethro- and vesicovaginal fistulas.
Prevention of ailment
Of course, one should not forget about those measures that avoid the occurrence of pathology. It is much easier to prevent cystic formation than to fight it later.
Doctors recommend the following prophylaxis:
- timely treatment of inflammation of the urethra, genitals, bladder;
- getting rid of sexually transmitted infections (chlamydia, ureaplasmosis, mycoplasmosis, trichomoniasis);
- compliance with hygiene rules;
- use only natural underwear;
- preventive examinations by a urologist and gynecologist.
Timely contact with specialists will allow much easier and faster to transfer surgery. Therefore, in the presence of unpleasant symptoms, do not postpone the visit to the doctor. Remember, the faster you get rid of the pathology, the higher the chances of avoiding the development of unpleasant consequences.