The pineal gland or pineal gland is a small formation (about 0.5 mm in size) in the brain that has an endocrine nature. The hormone melatonin, which regulates circadian rhythms, is produced in the pineal gland. Melatonin is a product of its predecessor, serotonin. Adrenoglomerulotropin is also released from the pineal gland, which stimulates the release of aldosterone by the adrenal glands. From the article you will learn what it is - a cyst of the pineal gland of the brain, whether it can dissolve and what the consequences may be.
Causes
Unfortunately, even today, humanity knows only a small part of the reasons for the formation of cysts in the human brain:
- cysts caused by parasites - echinococci;
- blockage of the excretory channel of melatonin;
- hemorrhage in the gland;
- damage to the brain in the fetus during childbirth;
- intrauterine pathology of the fetus;
- infectious disease in the postnatal period.
Parasitic disease of the pineal gland
Small cysts of the pineal gland of the brain caused by parasites (worms), in most cases, are formed as a result of constant intoxication due to the vital activity of echinococcus. It is this parasite that can be infected from domestic animals, in particular dogs, and there can also be infection from livestock. This form of cyst is quite rare in humans. And, unfortunately, it is this type of cyst that can increase in size very rapidly, which subsequently leads to compression of the brain, as well as damage to surrounding tissues in the organ. This occurs as a result of the penetration of parasites into the gland through the outflow of blood, where the helminths form the protective capsule in which they live.
This neoplasm, unfortunately, is invulnerable to human immunity. During the life of parasites in this capsule, more precisely in its shell, the products of their vital activity accumulate, it is due to this that cysts grow and progress many times faster. Scientists also consider autoimmune diseases of the human body and hormonal changes as the cause of such cysts. But many are interested in the question of whether the cyst of the pineal gland can resolve itself. Definitely yes, if it is small.
Outlet obstruction
Blockage of the excretory canal occurs only in a few moments: if the secretion of the pineal gland is too viscous and with too winding excretory canals. From this we can conclude that the pineal cyst of the pineal gland can dissolve and rarely grows to large sizes. If there is a blockage in the excretory pathways of the gland, then melatonin accumulates in the so-called sac, which will be constantly filled, which in the future will provoke an increase in the formation. This all happens due to impaired brain function, the causes may be various injuries, operations, as well as a hereditary predisposition.
Iron hemorrhage
Since in the pineal gland there is a very abundant blood supply, as well as nearby tissues, this is a very large risk factor for hemorrhage in the gland. This hemorrhage in the tissue is considered another cause of cystic degeneration.
In childhood, the following factors can be the causes of the cyst of the pineal gland cyst:
- intrauterine pathology of the fetus;
- traumatic damage to the brain of the fetus during childbirth;
- fetal hypoxia;
- infectious diseases in the postnatal period.
Until today, other reasons why cysts occur are not fully understood. One of the explanations of scientists is that the disease proceeds without obvious symptoms.
Symptoms
The pineal cyst is hollow inside and contains fluid. The disease has a benign nature and is rarely malignant. Distinguish cystic formation of the pineal gland, associated with difficulty in the outflow of secretion from the gland, as well as the presence of echinococcal bladder. Symptoms in this disease are absent if the size of the cyst does not exceed 1 cm. If the size becomes larger, then symptoms appear. Their severity depends on the size and growth rate of education. Symptoms are more pronounced with an echinococcal cyst :
- Patients complain, as a rule, of headaches for no apparent reason, which are often attributed to fatigue, stress, lack of sleep.
- With a severe headache, nausea and even vomiting can occur.
- Also, patients may have disorders such as double vision, decreased visual acuity, blurry contours of objects and other visual disturbances.
There is a very revealing symptom that neurologists test. They ask the patient to look up, and if pain occurs, the doctor begins to suspect the presence of problems with the pineal gland. There are problems with sleeping and falling asleep. Echinococcal cyst can cause convulsive seizures, psychoses and dementia. Small cysts of the pineal gland of the brain do not cause severe harm to their owner. The only thing is that they need observation to prevent an increase in education in volumes. If the cyst is voluminous and long-existing, then hydrocephalus and atrophy of the brain develop.
Kinds
Cysts of the pineal gland (pineal gland) of the brain are:
- arachnoid;
- colloidal;
- pineal;
- dermoid;
- epidermoid.
Cysts are divided into types depending on the type of tissue from which they are formed.
The most dangerous is an arachnoid cyst, which most often occurs in men. Such a cyst is formed in the arachnoid membranes of the brain, filled with cerebrospinal fluid. If the pressure in the cyst rises, adjacent parts of the brain can be squeezed, which causes symptoms that help determine the presence of a cyst. Usually arachnoid cysts are congenital in nature, but sometimes arise as a result of inflammatory and infectious processes.
Colloidal cysts are also usually congenital, which are laid during fetal development. They do not manifest themselves in anything, but in case of a violation in the circulation of cerebrospinal fluid, they can lead to dropsy, a hernia of the brain and death. During intrauterine development of the fetus, dermoid and epidermoid cysts also form. In the cavity of such formations, accumulations of fat and hair can be detected. They pose a serious threat to the development of the baby, as they are able to grow quickly, so they are removed immediately after the birth of the baby.
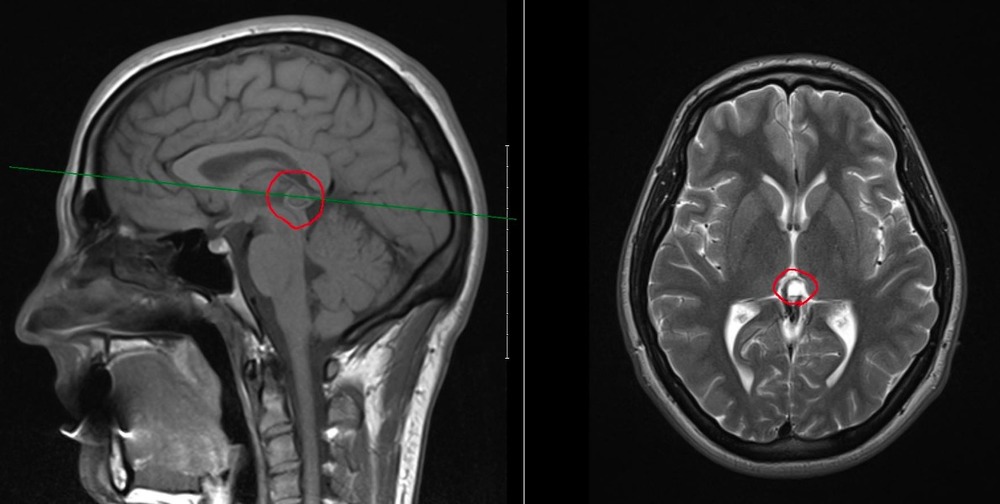
The pineal cyst is always small in size and is a tumor of the pineal gland. Pineal, dermoid, epidermoid and colloidal cysts are considered benign formations. With such cysts, it is usually enough to observe them, they are removed only if they begin to develop and squeeze adjacent tissues and parts of the brain, interfering with its normal functioning. After removal, the cysts are examined for histology, in case of detection of cancerous, pathogenic cells, chemotherapy or radiotherapy is prescribed.
Echinococcal cysts can only be cured surgically, they can not be treated with medication. If there are contraindications for surgery, for example, advanced age or concomitant chronic diseases, they do not perform surgery, then only conservative treatment can help. True, with this method of treatment, cysts cannot be completely stopped, but you can slightly reduce their size, prevent growth, and alleviate symptoms. For conservative treatment, sedatives are used, drugs that promote fluid outflow, pain medication.
Diagnostics
Diagnosing a cyst of the pineal gland of the brain can be difficult, since the symptoms of the disease are practically absent. Typically, a cyst is recognized during a random examination. The main methods that allow you to diagnose a cyst of the pineal gland of the brain are MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) and CT (computed tomography) of the brain. These examinations can also reveal the size of the formation, as well as whether the cyst affects adjacent sections and brain tissue.
CT scan is not suitable for young children and pregnant women, since there is x-ray exposure. Computed tomography is prescribed in the absence of contraindications, as well as when the exact area for the study of the affected area is determined. In this case, a three-dimensional image model is created, which allows a more detailed examination of the cystic formation.
MRI is the safest test that can be done for every person. This examination is also the most effective for the diagnosis of various formations in the brain. Typically, MRI is prescribed to all patients who complain of frequent headaches to check for the presence of a variety of formations. During an MRI, the neoplasm can be seen as a capsule with a liquid content. If the cyst is parasitic in nature, adjacent tissues will be inflamed. In this case, additional examinations and tests may be prescribed.
Features of the course of the disease
The pineal cyst of the brain can form as a result of parasitic infection of this tissue site. Indeed, echinococcus, getting into the human body, leaves this kind of formation. You can get this parasite from dogs or some farm animals. The considered type of cyst is rarely diagnosed. However, it should be noted that this benign formation increases over time and begins to interfere with neighboring areas of the brain. The second cause of this disease may be blockage of the excretory canal. This is due to a viscous fluid of the pineal gland or too sinuous duct. Therefore, here the cyst of the pineal gland can not increase.
When it comes to pineal brain formation, patients rarely experience any discomfort associated with such a pathology. Most often, the cyst of the pineal gland of the brain is found randomly during an MRI or CT scan. But the large size of the benign formation of the pineal gland causes certain symptoms. For example, a person may have impaired coordination of movements, headaches, vision problems and nausea. Therefore, it is necessary to start taking certain medications. A large parasitic cyst of the pineal gland of the brain often causes epilepsy attacks and even mental disorders. Usually the treatment of the disease depends on the nature of its occurrence.
Therapeutic measures for cyst detection
MRI results can show the presence of microcysts of the pineal gland. In this case, doctors do not prescribe any drugs or procedures. But then once a year it is necessary to conduct additional examinations in order to observe the size of education. If patients at the same time experience discomfort in the form of frequent headaches or nausea, doctors recommend taking diuretics, which can reduce the amount of fluid in the cyst.
Drug therapy and operations for the detection of a parasitic formation
When the cause of the appearance of the pineal gland cyst is echinococcus, after an MRI scan in patients, doctors observe areas of small hemorrhages, the presence of softer tissues and the onset of inflammatory processes near the tumor. Here you can not do without additional examinations. Then the patient will need to take tests for allergens. Now the neurologists are dealing with the disease in question. They direct to other specialists if such a need arises. Detection of a parasitic cyst requires consultation with an infectious disease specialist and a neurosurgeon.
At the initial stages of the disease, you can still resort to a conservative treatment method, which consists in the use of special drugs (Nemozol, Vermox). Such drugs can still affect the soft membrane of echinococcus, eliminating it. Drug therapy is used in cases where patients cannot be operated on. Often, these include the elderly with the presence of other serious diseases. They are prescribed drugs that relieve severe pain (Etodin Fort, Ketorol, Nalgezin), calm the nervous system (Novo-Passit, Persen, Grandaksin) and prevent the occurrence of epileptic seizures (Depakin "). Diuretics ("Uregit", "Furosemide") can also help in diagnosing this disease.
Surgical treatment of the cyst of the pineal gland of the brain is prescribed by neurosurgeons to those patients in whom the size of the neoplasm has increased significantly. You can get rid of a small cyst using the endoscopic method, which avoids serious damage and the formation of scars. Naturally, such a formation interferes with the normal functioning of the surrounding tissues, since it compresses them. The parasitic cyst must be removed due to the presence of inflammation of the pineal gland and impaired normal movement of the cerebrospinal fluid. This complex operation involves opening the skull, after which the neurosurgeon penetrates the damaged tissues. After surgery, all concomitant symptoms of the disease immediately disappear. In order to exclude the presence of cancer cells in the brain, doctors send fluid from the cavity of the pineal gland cyst to the analysis. After all, a benign tumor can turn into a malignant one over time. In other words, doctors diagnose malignancy. When a malignancy is detected, patients are prescribed chemotherapy and radiation treatment.
Forecast and Prevention
The pineal gland cyst (pineal gland located in the midbrain) is quite difficult to diagnose. Symptoms of the development of the disease are practically absent, so it is difficult to recognize the disease. Modern diagnostic methods do not allow timely notice of the pineal gland cyst, so a person can walk for years and not know about his disease. Pathology is detected by chance. The cyst of the pineal gland of the brain is a benign formation, but, like any tumor, it requires attention. Usually small formations of a cystic nature are not hazardous to health, but require observation by specialists. Symptoms appear only if the cyst begins to grow, and even then not always, very often the symptoms are vague, which makes diagnosis difficult.
A small cyst is not dangerous, only a growing and large formation is a danger. We should also dwell on the consequences. A cyst of the pineal gland of the brain increases the risk of developing hydrocephalus. In addition, a person’s hearing and vision are reduced, information is perceived and stored worse, intelligence decreases, and limbs lose their sensitivity. All this threatens with irreversible consequences, even death, if measures are not taken.
After you know what it is - a cyst of the pineal gland of the brain, the consequences of which can be the most deplorable, it is worth paying special attention to preventive measures.
To prevent education, it is recommended:
- Establish a full sleep.
- Lead an active lifestyle, engage in mental activity.
- Eat ration, give preference to oily fish, seafood, proteins of plant and animal origin.
- Have regular medical examinations.