What are autoimmune diseases? Their list is very wide and includes about 80 diseases that are heterogeneous over the course and clinical signs, which, however, are united by a single developmental mechanism: for reasons still unknown to medicine, the immune system takes the cells of its own organism for “enemies” and begins to destroy them.
One organ can get into the attack zone - then we are talking about an organ-specific form. If two or more organs are affected, then we are dealing with a systemic disease. Some of them can occur both with systemic manifestations and without them, for example rheumatoid arthritis. Some diseases are characterized by simultaneous damage to different organs, while for others, systemicity appears only in case of progression.
These are the most unpredictable diseases: they can occur unexpectedly and pass spontaneously as well; appear once in a lifetime and never disturb a person again; quickly progress and end in death ... But most often they take a chronic form and require treatment throughout life.
Systemic autoimmune diseases. List
- Lupus erythematosus is the brightest representative of this group. A serious disease covers many organs and systems: skin, liver, joints, spleen, kidneys, lungs, gastrointestinal tract, cardiovascular system.
- Rheumatoid arthritis is the most common disease. It can occur without systemic manifestations. Joint syndrome is leading, in addition, kidneys, lungs, skin, heart, eyes can be affected.
- Scleroderma, or systemic sclerosis of connective tissue. This chronic disease is unpredictable. It can progress quickly and even lead to death. With scleroderma, degenerative changes and fibrosis of the skin, as well as blood vessels, joints and internal organs are observed.
- Systemic vasculitis is an extensive group of diseases and syndromes, united by a single sign - inflammation and necrosis of the walls of blood vessels. Other organs are involved in the pathological process: heart, joints, skin, kidneys, eyes, lungs, etc. This category includes: Takayasu arteritis, Wegener's granulomatosis, Behcet's syndrome, hemorrhagic vasculitis, microscopic polyarteritis and Kawasaki disease. In addition, giant cell arteritis, vasculitis with rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus, periarteritis nodosa and others.
- Sjogren's syndrome is a chronic inflammatory lesion of the salivary and lacrimal glands, leading to dry mucous membranes of the eyes and oral cavity. The pathological process can affect the lymphatic system, kidneys, liver, spleen, pancreas.
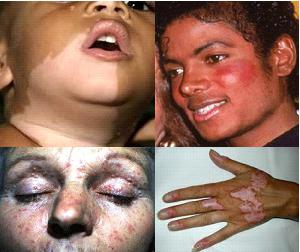
What other systemic autoimmune diseases are there? The list can be continued with pathologies such as:
- dermatopolimiositis - a severe, rapidly progressive lesion of connective tissue with involvement of transversely smooth muscles, skin, internal organs in the process;
- phospholipid syndrome, which is characterized by venous thrombosis;
- sarcoidosis is a multisystem granulomatous disease that most often affects the lungs, as well as the heart, kidneys, liver, brain, spleen, reproductive and endocrine systems, gastrointestinal tract and other organs.
Organ-specific and mixed forms
Organ-specific species include primary myxedema, Hashimoto's thyroiditis, thyrotoxicosis (diffuse goiter), autoimmune gastritis, pernicious anemia, Addison’s disease (adrenal insufficiency), type 1 diabetes mellitus and severe myasthenia gravis.
Of the mixed forms, Crohn's disease, primary biliary cirrhosis, celiac disease, chronic active hepatitis and others should be called.
Autoimmune diseases. List of prevailing symptoms
This type of pathology can be divided depending on which organ is mainly affected. Such a list includes both systemic and mixed, and organ-specific forms.
- Autoimmune joint diseases: spondyloarthropathy, rheumatoid arthritis.
- Lesions of the nervous system: multiple sclerosis, myasthenia graves, Guillain-Baret syndrome.
- Blood diseases: thrombocytopenic purpura, hemolytic anemia, autoimmune neutropenia.
- Endocrine diseases: insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus, Hashimoto's thyroiditis, diffuse toxic goiter.
- Gastrointestinal pathologies: autoimmune hepatitis, autoimmune pancreatitis, biliary cirrhosis (primary), ulcerative colitis, sclerosing cholangitis (primary).
- Skin diseases: psoriasis, vitiligo, isolated skin vasculitis, chronic urticaria, bullous pemphigoid.
- Renal Diseases: Goodpasture Syndrome, Glomerolupathy and Glomerolenephritis, Other Autoimmune Diseases with Renal Syndrome.
- Cardiac pathologies: rheumatic fever, some types of myocarditis, vasculitis with heart syndrome.
- Lung diseases: fibrosing alveolitis, pulmonary sarcoidosis, autoimmune diseases with pulmonary syndrome.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis is based on the clinical picture and laboratory tests for autoimmune diseases. As a rule, a general, biochemical and immunological blood test is taken .