The purulent inflammatory process of finger tissues in medicine is called panaritium. The causative agent of this disease is usually staphylococcus, sometimes streptococcus. Infection occurs by infection through minor damage to the integrity of the skin (injections, splinters, cracks, wounds).
There are several types of panaritium:
1 - cutaneous - suppuration located between the skin and the epidermal integument. With this form of the disease, the temperature and general condition of the patient are normal. The pain has a weak intensity, localized in a certain area, which has redness and swelling. Recovery occurs with a breakthrough of pus. If measures are not taken in time, subcutaneous panaritium develops. The treatment comes down to peeling with sharp scissors to release pus. A slightly disinfecting ointment is applied to the wound.
2 - subcutaneous. The most common type of panaritium. Inflammation is formed in the subcutaneous tissue, accompanied by its necrosis. The patient’s temperature rises from 37.5 ° C and higher; there is a throbbing pain at the site of inflammation. Tension of tissues and swelling are noticeable in the bent position of the finger. With the spread of the process, pandactylitis, articular, bone or tendon panaritium can develop. Treatment begins with the introduction of a solution of novocaine and penicillin intraarterially. Within 3-4 days, the pain subsides, recovery occurs, sometimes opening an tissue to break through pus is required.
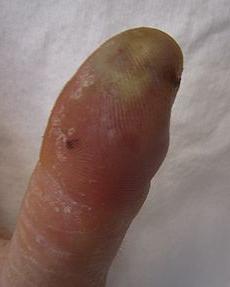
3 - bony felon. It is formed after damage to the bone, periosteum with infected wounds or as a result of a complication of subcutaneous panaritium. In the early stages, the symptoms are the same as with subcutaneous panaritium. But more pronounced. The temperature rises to 40 °. Pain is observed throughout the phalanx, which has a bulbous thickening. On an x-ray after 2-3 weeks from the onset of the disease, destructive changes are visible. Surgical treatment is required.
4 - articular panaritium - inflammation of the metacarpophalangeal and interphalangeal joints. The pain is present even at rest, the joint forms a spindle shape. Gradually, the lateral ligaments are destroyed, a crunch appears during movement and lateral mobility. The X-ray diffraction pattern shows uneven, pitted contours at the ends of the joints of the phalanx. Treatment of such a felon is carried out only promptly.
5 - tendovaginitis (panaritium tendon) - inflammation of the vaginas of the tendons. The cause of the occurrence is an injury to a sharp tendon of the vagina, a complicated skin wound, or a subcutaneous panaritium. Surgical treatment.
6 - paronychia or periungual felon - suppuration of the periungual platen. If you press on the nail, pus is released from under it. It is treated by removing the nail root, without damaging the bed.
7 - subungual panaritium - inflammation developing under the nail. The ingestion of a foreign body under the nail or suppuration of the hematoma causes subungual panaritium. Treatment consists in trepanation of the nail to ensure the outflow of pus.
8 - pandactylitis - suppuration of all tissues of the finger. Usually due to improper treatment of articular, bone panaritium or tendovaginitis. Purulent fusion of soft tissues, joints, bones and tendons occurs. Leukocytosis is present in the patient’s blood. The finger is significantly increased in size, does not move. The treatment is finger amputation.
Thus, in order to prevent serious consequences, you need to monitor your health very carefully.