Currently, oropharyngeal diseases occupy a leading position among pathologies of ENT organs.
The value of the disease
What is acute pharyngitis? Pharyngitis (or in the people - tonsillitis) - the process of inflammation of the mucous membrane of the tonsils, pharynx, which occurs under the influence of many factors.
History
The world learned about such a medical concept as otolaryngology back in the 5-6th century BC. e., when there already existed people who knew how to gargle to treat a sore throat. After many millennia, a generalized concept of otolaryngology appeared - a science that studies the causes of formation, stages of development, methods of diagnosis and treatment of various pathologies of the mouth, nose and ears.
Thus, the concept of otolaryngology is so extensive that it covers many diseases in the human body. Conditionally otolaryngology can be divided into children and adults.
Common diseases of the ENT organs include pharyngitis - local inflammation of the pharynx and tonsils. Acute pharyngitis (ICD 10 - J02) includes both acute sore throat and inflammation caused by other etiological factors.

Causes of the disease
Currently, more and more specialists in the field of medicine call the cause of many diseases a bad ecology, an accelerated rhythm of life and unhealthy diet. Of course, one must agree with this, but other reasons for the development of pathologies cannot be ignored:
- Infections, mainly airborne.
- Inhalation of non-adapted air (too cold or hot air).
- Chemical damage to the area.
- Fungal or viral infections of the oropharynx.
- Reaction to an allergen.
- Injuries to the oropharynx.
High risk groups
As it became clear from the above text, in otolaryngology there is no age or social framework, but there is a certain risk group - people who most often suffer from problems with pharyngeal inflammation:
- elderly people;
- persons leading an asocial lifestyle;
- patients with chronic infectious diseases;
- children;
- persons often in contact with infectious patients.
It is important to understand that any disease must be treated in the early stages of development, preventing the formation of advanced forms and complications. Therefore, the appointment of an ENT doctor should not be postponed for a long time. A specialist will not only tell you what acute pharyngitis is, but also prescribe a therapy that will help prevent complications.
Classification due to occurrence
Acute pharyngitis (ICD code - J02) is classified by source of infection into:
- bacterial;
- viral;
- fungal;
- allergic;
- post-traumatic.
With the course of the inflammatory process in the pharynx
There are such forms:
- Catarrhal or simple pharyngitis occurs with the formation of a large amount of mucus.
- Granular or hypertrophic - swelling and an increase in the volume of the pharyngeal mucosa.
- Subatrophic or atrophic, on the contrary, thinning of the throat mucosa.
According to the ICD, acute pharyngitis is classified as follows:
- J02.0 - complicated by streptococcal infection;
- J02.8 - caused by other pathogens specified during diagnosis;
- J02.9 - unspecified, i.e. the etiology of this disease is not known.
Diagnostics
Any disease requires qualified treatment and diagnosis. A simple layman cannot always clearly differentiate the causes of sore throat. During the examination of the patient, the ENT or therapist will diagnose on the basis of complaints, objective examination data. During pharyngoscopy, it will be clearly visible that the posterior pharyngeal wall is swollen, hyperemic, there are granular inclusions, plaque or plugs.
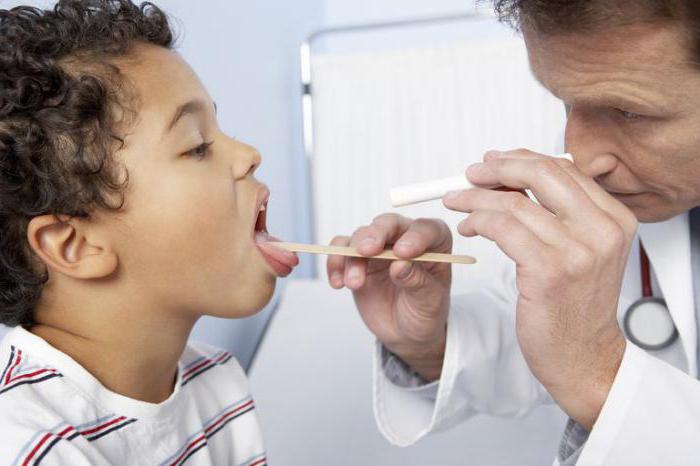

Acute pharyngitis in adults and children is differentiated by the causative agent of the disease by taking biological material from the throat for sowing before treatment. In this case, the patient should not treat the pharynx with local antibacterial agents. The result of this analysis will not only determine what caused the inflammation, but also find out the sensitivity of this microbe to antibiotics. It will be much easier for the doctor to determine the choice of the drug for treatment.
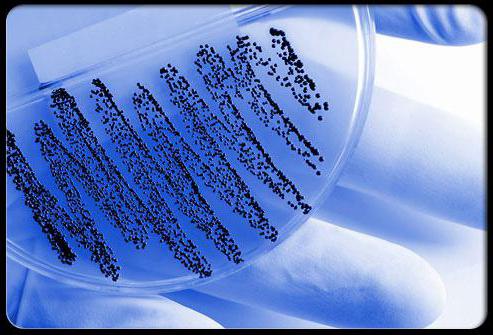
If the results of bacterioscopy (smear from the mucosa) do not give a result, it is necessary to conduct immunological studies for the presence of antibodies to infections in this patient.
The following shows how the material is sampled.

Also, patients need to undergo a general blood test, because in the presence of a large number of white blood cells (indicates an inflammatory process) or other changes in the analysis, treatment will need to be adjusted.
Symptomatology
Symptoms and treatment of acute pharyngitis are interrelated. Any disease begins with a violation of the general condition: increased fatigue, weakness, loss of appetite, and only then the specific signs of the disease join. Symptoms of acute pharyngitis in adults:
- Change in volume, color, shape of tonsils.
- Soreness and discomfort when swallowing.
- Sore throat.
- Fever.
- When pharyngitis is formed as a symptom of another disease, signs of this disease join it.
What is acute pharyngitis of fungal origin? This lesion is characterized by the appearance of a white coating with a clear outline. With all forms of sore throat, local inflammation of the lymph nodes in the lower jaw and neck can occur. They become painful on palpation.
In small patients
Symptoms of acute pharyngitis in children are very similar to the manifestation of the disease in adults:
- the child becomes tearful, restless;
- fever may appear;
- crying while eating;
- pain on palpation of the submandibular lymph nodes;
- cough due to drainage of mucus along the back of the throat or perspiration;
- with an objective examination, swelling, redness, plaque.

What to do?
How to treat acute pharyngitis? This disease is treated by a local therapist or otolaryngologist. For all patients with inflammatory diseases of the oropharynx, there are general recommendations:
- consume more liquid during the illness (in the form of heat compotes, fruit drinks, teas with lemon and honey);
- eat at least 2 fruits a day;
- the food should be sufficiently high-calorie, based on your needs, but without the content of irritating food and drinks (soda, spices and cold and too hot drinks);
- in the room where the sick person is located, regular ventilation, humidification and wet cleaning are necessary.
If the temperature rises above 38.5 degrees, it is recommended to use:
- Ibuprofen
- "Paracetamol";
- "Aspirin";
- "Ibuklin."
It is necessary to familiarize yourself with the instructions of each drug, to make sure that the person taking them is not contraindicated. Do not exceed the indicated maximum daily dosage of tablets. Control of temperature decrease in 20-30 minutes after the use of the drug.
If the doctor suspects a viral etiology of sore throat, then he will prescribe one of the drugs:
- Arpetol;
- "Kagocel";
- Ergoferon;
- Cycloferon;
- Ingavirin.
It should be noted that the 100% effectiveness of the above drugs has not yet been proven, however, some patients have a positive effect in the first days of treatment.
Treatment of bacterial pharyngitis
As described above, when bacterial pharyngitis is detected, antibacterial drugs are prescribed (based on sensitivity):
- Amoxiclav;
- "Flemoxin Solutab";
- "Azithromycin";
- Clarithromycin;
- Zinnat
- Suprax.
Treatment of acute pharyngitis in adults with drugs of this series is prescribed exclusively by specialists, self-medication is strictly prohibited and can cause irreparable harm to the body. It is known that these medicines negatively affect the intestinal microflora. Therefore, their combined use with dyspeptic drugs is recommended.
Many specialists prescribe these funds not only for allergic pharyngitis, because they relieve swelling of the mucous membrane:
- Cetrin
- "Suprastin";
- Parlazine
- Loratadine;
- "Diazolin";
- Fenistil;
- Zirtek.
Local treatment
External treatment of acute pharyngitis is relevant for any etiological factor. So, this: gargling, lubrication of the mucosa with antiseptic solutions, sprays, inhalation therapy.
Rinses are carried out with the following solutions:
- Chlorhexidine;
- "Furacilin";
- Soda and iodine;
- Hexoral;
- A decoction of chamomile, calendula, sage.
Sprays and sprays for local use:
- Hexoral;
- Stopangin
- "Proposol";
- Ingalipt;
- "Cameton";
- "Lugol."
Currently, the pharmacy chain offers many lozenges for resorption:
- Septolete;
- "Falimint";
- "Dr. Mom";
- Strepsils.
With the advent of home portable inhalers, these procedures can be done at home. It is only necessary to correctly determine the mixture for inhalation. Some experts themselves recommend to patients which solution is best for inhalation. Important: oil solutions have many contraindications, so you should not use them yourself. But a decoction of chamomile water - an excellent anti-inflammatory agent. It is also possible to carry out inhalations with mineral water without gases.
Remember: thermal procedures, including inhalation, should not be carried out at elevated temperatures.
Additionally, a course of immunostimulating therapy is recommended for patients: Immunal, Echinacea, as well as a multivitamin complex. With viral pharyngitis, it is better to drink Group B vitamins.
As for the treatment of this disease in childhood, it is jointly carried out by pediatricians and ENT doctors. There are some features of the use of drugs in children's practice, which your doctor will tell you about. At home, it is difficult to make a child inhalation, therefore, if possible, it is better to resort to physiotherapy in the walls of the hospital.

Symptoms and treatment of acute pharyngitis are directly related . If the patient complains of any additional signs of the disease, it is necessary to prescribe therapy regarding them.
Complications
With untimely or ineffective treatment, any disease can spread, resulting in complications. This is due to untimely initiation of treatment or failure to comply with the timing of therapy.
The most common complications are:
- acute tonsillitis (tonsillitis) ;
- otitis;
- sinusitis;
- tracheitis;
- laryngitis;
- bronchitis.
The disease is dangerous because with a prolonged spread of the process, the inflammation "goes down" to the lungs, pneumonia or bronchitis can form, in more severe cases an lung abscess.
Herpetic pharyngitis as a variant of the viral is also dangerous . The process quickly affects the nerve endings and spreads everywhere. In this disease, the most serious complications are most common, in case of untimely treatment.
As for acute bacterial pharyngitis, its streptococcal variety is most dangerous. Complications of streptococcal inflammation can be on the heart, and on the lungs, and in the joints. In this case, the treatment process is quite long and serious. In the manuals you can find a description of the case of sepsis - a general seeding of the body by pathogenic microorganisms, which was preceded by banal pharyngitis.
Prevention
For patients with chronic pharyngitis, the prevention of an acute process is daily hygiene and pharynx toilet (rinsing in the morning with a solution of chamomile, calendula).
For people who do not have a chronic form of the disease, it is worth avoiding hypothermia, breathing only through the nose in the cold season, and treating all diseases of the nasopharynx in a timely manner. Quitting smoking will also serve as a preventive measure for the formation of inflammatory processes in the throat. Fans of spicy foods, too cold or hot drinks should reconsider their taste preferences. And, of course, to increase immunity by hardening and proper nutrition.
The oropharynx is the most common “entry gate” for all kinds of infections, because it is there that the optimal environment for the reproduction of many pathogenic microbes. Now it becomes clear what acute pharyngitis is and how to prevent its occurrence .