Aneurysm of the brain, the symptoms of which will be described below, can occur at any age. However, more pathology is typical for adults than for children. Next, we learn what aneurysm is, how it manifests itself and what methods are used today to identify and eliminate it.
General information
What is an aneurysm? This is a small formation inside the skull. It appears on the blood vessel of the brain. Education is growing fast enough. Its convex part can press on the surrounding tissue or on the nerve. The greatest danger to life is a rupture of the aneurysm of the brain. In this case, blood enters the surrounding tissue. This condition is called hemorrhage. The formation of small sizes does not lead to complications. Aneurysm can occur in any area of the brain. However, as practice shows, most often it is located on the site of discharge of the artery branches. This place is located between the cranial base and the lower region of the brain. As for the structure, a neck is present in the aneurysm. The three-layer structure of the artery is preserved in it, which makes it the most durable part of the formation. Aneurysm has a body. The elastic membrane in it is broken; the muscle layer is also absent. The thinnest place is the dome. It consists only of vascular intimacy. It is at this point that the gap occurs.
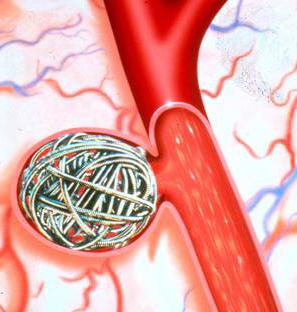
Causes of pathology
The appearance of education can provoke various diseases of the vessels of the brain. The cause of the pathology can be a genetic disorder. In particular, it can be polycystic kidney disease or damage to the connective tissue. Contribute to the formation and formation of cerebrovascular disease associated with circulatory disorders. This, in particular, is a congenital arteriovenous defect. Provoking factors should also include injuries and other head injuries, infections, high blood pressure , and a tumor. Atherosclerosis, a vascular pathology complicated by deposition on the walls of cholesterol, can cause aneurysm. Bad habits aggravate the situation: smoking, alcohol abuse, drugs. According to some researchers, when taking oral contraceptives, the risk of aneurysm increases. The formations resulting from infection are called mycotic. Aneurysms that accompany cancer pathologies are often associated with metastatic or primary tumors of the neck and head. When using drugs, blood circulation is disturbed. In particular, with frequent use of cocaine, vascular lesions develop, as a result of which an aneurysm can occur.
Classification
Treatment of cerebral vessels is carried out in accordance with the type of pathology and the severity of its course. As for the formations under consideration, there are three types of them that are distinguished. The first type includes saccular aneurysm. It has the appearance of a rounded sac with blood. It is attached by the neck or base to the vascular branch site or to the artery directly. The saccular type is considered the most common type of pathology. It is also called “berry” because of its resemblance to a berry hanging from a stem. Typically, such an aneurysm appears in the arteries at the base of the brain. The saccular type of education is most often detected in adults. The second type is a lateral aneurysm. It is like a tumor on one of the walls. Spindle-shaped formation is referred to the third category. It is formed due to the expansion of the vascular wall in one of the sections. There is also a classification of formations by size. Small ones include those whose diameter is less than 11 mm. Formations of 11-25 mm are referred to the average size of aneurysms, and more than 25 mm to giant ones.
Risk groups
Absolutely for all types of aneurysms, there is a possibility of their rupture and hemorrhage. At high risk are people with some congenital abnormalities. It was found that in women aneurysm is detected more often than in men. For every 10 thousand people, about 10 ruptures of aneurysms are recorded annually.
What is the danger of pathology?
As mentioned above, rupture of the aneurysm entails a hemorrhage in the brain. This, in turn, causes quite serious, life-threatening complications. In particular, damage to the central nervous system, hemorrhagic stroke, or death. The first break may be followed by the second. In this case, hemorrhage will reappear. In addition, new aneurysms may form. As a rule, with a break, blood enters the cavity between the brain and the cranial bone. In this case, they talk about subarachnoid hemorrhage. Its rather dangerous consequence is hydrocephalus. This condition is characterized by an increased accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid in the cerebral ventricles, which expand and put pressure on the brain tissue. Another, no less dangerous complication may arise - vasospasm. In this case, we are talking about narrowing of blood vessels, due to which blood flow to the most important areas of the brain is limited. Lack of blood supply leads to tissue damage or stroke.
Brain Aneurysm: Symptoms
Very often, pathology does not manifest itself. Signs of aneurysm of the brain begin to appear when it reaches a large size or bursts, which, in turn, can happen against the background of perfect well-being, only after physical or emotional stress. Small, non-increasing formations may not be accompanied by any manifestations throughout a person’s life. At the same time, the constantly growing aneurysm of the brain, the symptoms of which are quite easy to confuse with other pathologies, exerts constant pressure on the tissues and nerves. The average age of patients with a pathology is 30-50 years. Many live quite a long time despite the fact that they have an aneurysm of the brain. Symptoms of the pathology are as follows: pain in the eye area, paralysis, numbness or muscle weakness on one side of the face. Blurred vision, dilated pupils are also noted.
Signs of aneurysm in the posterior artery are a distortion of the outline of objects, loss or narrowing of the visual fields. With damage in the anterior part, transient weakness of the lower extremities is noted. Vascular aneurysm in the back is accompanied by peripheral paresis of the facial nerve, hearing loss (one-sided). There is also a strong blowing noise in the ear. When an aortic aneurysm of the brain bursts, a person feels a sudden and very severe pain. Vomiting or nausea also begins, stiff neck muscles occur. Even loss of consciousness is likely. As patients themselves say, describing this condition, this is the most terrible headache that can happen in life. The condition is characterized by intensity and severity. In some cases, before the rupture of the aneurysm, a person has warning pains in the head. They can last several days or even weeks after an attack occurs. Other symptoms of pathology include a lowered eyelid, changes in mental state, increased anxiety, and the appearance of sensitivity to light. In rare cases, the patient may fall into a coma. With localization of pain in the fronto-orbital area, a lesion is likely in the antero-connective and antero-cerebral, in the temple and occiput, in the back, and in the half of the skull, in the basilar artery. If periodic paroxysmal pain appears, combined with other symptoms indicated above, you should immediately visit a doctor.
Diagnosis of cerebral vessels: general information
In some cases, the pathology is detected by accident, during examinations related to other conditions. Differential diagnosis is carried out with brain tumor diseases. The risk of hemorrhage from the detected formation is quite high. The probability is higher, the larger the size of the lesion. Also, the risk will depend on somatic status (general), the location of the aneurysm. Subsequent hemorrhages increase the likelihood of death and proceed much harder than previous ones. Most often, aneurysm of the brain, the treatment of which should be carried out exclusively in a specialized department, is detected in the process of rupture. The patient may lose consciousness, he has cramps, an epileptic seizure, anisocoria, and fever are likely. It must be remembered that only a doctor should carry out the treatment of cerebral vessels. When these manifestations of the patient appear, it is urgently necessary to hospitalize. With aneurysm, vasospasm is likely with an increase in the area of ischemia, a breakthrough of blood into the ventricular system, and the appearance of intracerebral hematoma.

Research methods
Diagnosis of cerebral vessels allows you to get the necessary information about the lesion. And then, based on it, prescribe adequate therapy. As a rule, studies are carried out after subarachnoid hemorrhage. The following diagnostic methods are available:
- Angiography. This type of X-ray examination is carried out with the introduction of a contrast medium. Intracerebral angiogram allows you to identify the degree of narrowing or destruction of the vessels of the neck, head, brain. With the help of the study, you can identify venous or arterial changes, including the appearance of formations. Angiography is used for circulatory disorders. It allows you to accurately determine the location, shape and size of a tumor or aneurysm. Angiography is performed in specially equipped rooms. After anesthesia, a flexible catheter is inserted into the artery. It is promoted to the affected vessel. A certain amount of contrast medium is released into the bloodstream. After it spreads through the vasculature of the neck and head, the required number of x-rays are taken.
- CT scan. This is a fairly informative non-invasive, quick and painless diagnostic method. With its help, you can detect the presence of aneurysm, and if it breaks, determine whether a hemorrhage in the brain has occurred. Typically, a CT scan is prescribed first if there is a suspicion that the formation may burst. X-ray processing is carried out on a computer in the form of two-dimensional images of cross sections of the skull and brain. In some cases, a contrast agent is injected into the bloodstream before a CT scan. Such angiography gives a clearer and more detailed image. CT is carried out in special rooms equipped with appropriate equipment.
- MRI is a type of study in which a magnetic field and radio waves are used. MRA (magnetic resonance angiography) allows you to get even more clear and detailed images of blood vessels. Pictures can be viewed both in three-dimensional form and in the form of two-dimensional cross-sections. MRA is painless. During the study, you can determine the shape and size of the unexploded aneurysm, as well as determine whether a hemorrhage has occurred.
- CSF analysis. If you suspect a rupture of the aneurysm, a specialist can refer the patient to take cerebrospinal fluid. The procedure is performed under local anesthesia. Using a needle, a small volume of material is extracted from the subarachnoid space. Cerebrospinal fluid is then examined for hemorrhage and bleeding. The material is taken in a special office of the hospital.
Therapeutic measures: general information
It must be said that education does not always burst. As mentioned above, a person can live his whole life with an aneurysm, which will not manifest itself in any way. Such patients need constant monitoring of the dynamics of the development of education. You should constantly monitor the level of blood pressure, undergo appropriate therapy with high cholesterol, and also treat (if any) the effects of traumatic brain injury and infectious diseases. It is also necessary to note new manifestations that may be accompanied by aneurysm of the brain. Treatment in this case will be prescribed as soon as possible. The results of research and observation allow you to choose the most effective tactics. It should be noted that each defeat is unique in its own way. Treatment of cerebral vessels should be carried out taking into account the location, type and size of the damage. Equally important is the patient's age, heredity, medical history, general health. The risk of aneurysm rupture is also taken into account.
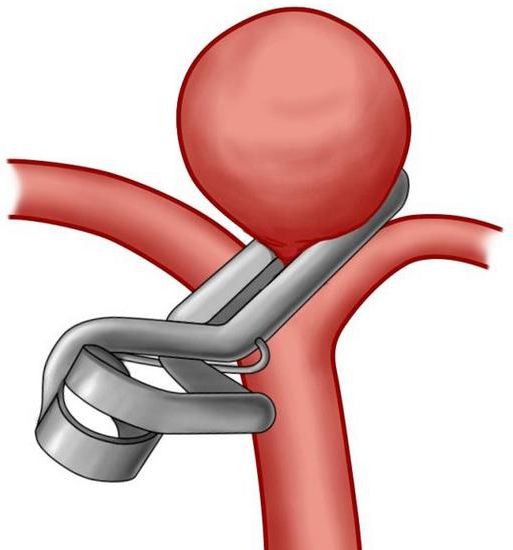
Surgical intervention
Treatment of cerebral vessels in this case can be carried out in two ways. The first method is the so-called clipping. Any brain surgery is risky. These interventions pose the greatest danger to patients. The operation of the aneurysm of the cerebral vessels by the clipping method is a “shutdown” of the damaged area and preservation of blood circulation along the main channel. A clip is put on the formation, the spilled blood is eliminated. There is an alternative method by which aneurysm is removed. Surgery for endovascular embolization can be performed several times during the life of the patient. During the femoral artery intervention, special agents are administered. They are filled with aneurysm of the brain. The operation is carried out using the latest drugs or micro spirals gluing damage. This technique is currently considered the most progressive.
Is it possible to prevent the development of pathology?
Currently, measures have not yet been developed with which to prevent the emergence and increase in the size of education. Patients at risk should carefully monitor their health, observe the daily regimen, control blood pressure, do not smoke or take drugs (cocaine and others). In addition, you must consult your doctor about taking drugs such as Aspirin and other blood thinners. Women should consult with a specialist on the use of oral contraceptives. These are the main activities for people who have a predisposition or already have aneurysm of the brain. The operation is considered necessary with an intensive growth of education and an increase in the risk to the patient's life.
Consequences and forecast
An unexploded aneurysm in the brain may remain undetected over a long period, and in some cases, throughout life. In other situations, a burst formation can cause death, hemorrhagic stroke, or vasospasm. The latter complication is the main factor provoking disability or death due to rupture of the aneurysm. A bursting formation can provoke coma, hydrocephalus. Irreversible or temporary brain damage is also likely. The prognosis after hemorrhage will depend on the age of the patient, the characteristics of his body, and other concomitant neurological conditions. The importance is the location of the formation, its size, the degree of bleeding, and also, whether it is repeated either primary. In assessing the consequences, the period between care and the hemorrhage itself should also be taken into account.
Patients who have received treatment for an unexploded formation need less time to recover than patients who have an aneurysm. The recovery period in the latter case may be several weeks or months. Rehabilitation after a particular operation should be under the supervision of a doctor. As supportive therapy, medicinal herbs can be used.
General preventive measures
Many vascular pathologies can be completely prevented. First of all, you should pay attention to the way of your life. In the conditions of a sufficiently high rhythm of modern life, it is necessary to find time for the right rest. In this case, we are talking about active sports, preferably in the open air. Experts recommend using all possible methods to deal with physical inactivity. The emotional background of a person is also of great importance. If possible, it is necessary to eliminate stressful situations, mental stress. All this extremely negatively affects the state of the vessels. All drugs that are prescribed by a doctor should be taken exclusively in accordance with the scheme of use, do not exceed the dosage. , , . . - . , . , , . , . , . .