Most often, an operation to remove the bladder in men and women is carried out against the background of an oncological disease of this organ. If the cancerous processes that began in the mucous membranes have spread to the muscle walls, a resection is indicated. Currently, among other malignant pathologies, localized in the bladder is quite common, only slightly inferior to the degeneration of the prostate gland. The disease is characterized by a latent course. The first symptom to suspect her is bloody inclusions in urine.
When is it shown?
An operation to remove the bladder is recommended for those who, after the initial surgical intervention for diagnostic purposes, received the results of laboratory histological studies confirming the spread of atypical cell structures outside the mucosa. If penetration of degenerated areas into muscle tissue is observed, it is recommended to remove the organ as soon as possible.
The main reason for the operation to remove the bladder is the risk of additional foci and affected areas. Pathology is considered multi-focal, if you do not remove the organ, over time it will manifest in its other area. If such processes have involved muscle tissue, the probability of metastases is estimated at 50%. The spread of the pathological process can be suspected if the patient notes a violation of the urethra, the study shows the proliferation of lymphatic pelvic nodes. Perhaps the formation of areas of degeneration in the skeletal system, liver.
Case features
Before starting an operation to remove the bladder, the tumor must be clearly localized, specifying all the features of the pathological process. A systematic study of the state of the body is shown. A mandatory instrumental measure is a CT scan of the abdominal cavity, sternum, and pelvic area. For bone skeleton scintigraphy is recommended. The task of doctors is to determine the location of metastases or to exclude their presence. If metastases are detected, it is necessary to continue the course of chemotherapy.
Removal of the bladder in women and men is performed with the aim of removing the tumor process from the body. Lymph nodes are removed from the pelvic area. This event simultaneously pursues therapeutic goals and is necessary to clarify the condition - a tissue sample is sent for histological examination.
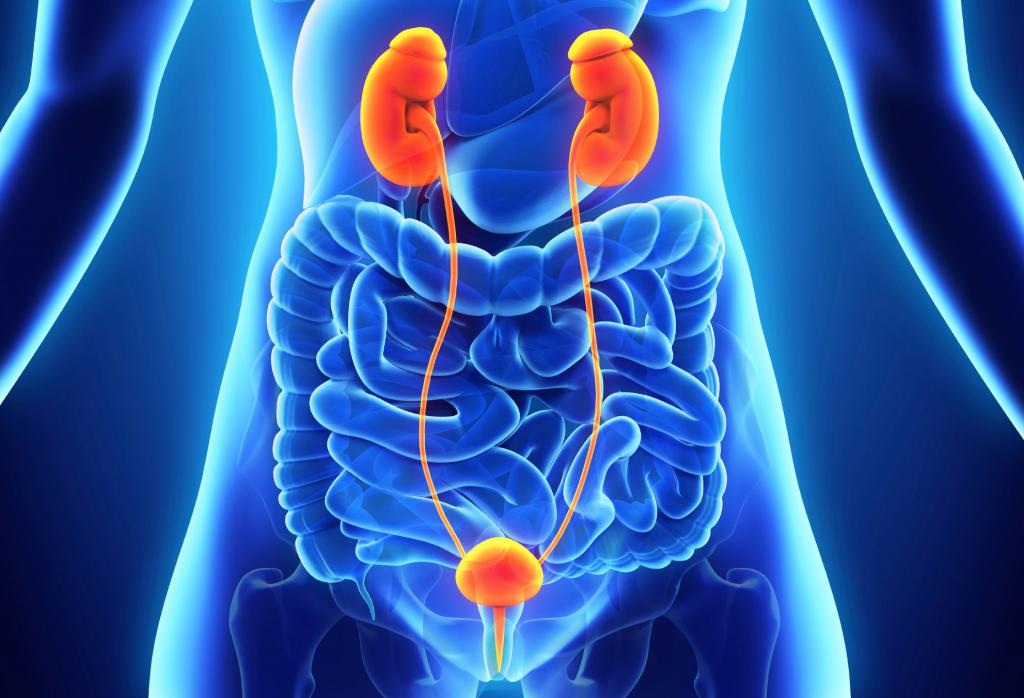
One of the tasks of the planned event is to provide such an option for urine diversion, in which the potency is maintained. In some cases, small intestine tissue is used for this. A bubble can be reconstructed from intestinal tissues, a reservoir can be made from the small intestine. The ability to insert a catheter remains.
Who are they doing?
If, as part of the treatment of a tumor, removal of the bladder seems to be the most effective and promising option, the patient's condition is first assessed in order to clarify how much surgery is possible and permissible in a particular case. It is necessary to remember the inoperability of some cancer patients. If invasive cancer processes are detected, the tumor is large enough, local removal is not feasible, the only option is organ removal. Such an event is indicated if the patient is recommended a combined therapeutic course - surgery and chemotherapy.
Removal of the bladder in cancer is considered complex, time-consuming, requiring a lot of time and operation. The rehabilitation period takes a long time. This places a particular responsibility on the doctor who decides to advise the patient to agree to the intervention. When assessing forecasts, the presence of chronic diseases is considered - ischemia, arrhythmia, stroke, diabetes. An important aspect is the age of the patient. Surgery is possible only if a person is under 70 years old, his renal system is functioning normally. For patients older than this age, reconstruction is not recommended, since the main majority determine the weakness of the sphincters, which in the future will lead to urinary incontinence.
How does it go?
The procedure for removing the bladder requires complete anesthesia. During the intervention, doctors directly remove the bladder, remove the lymph nodes from the pelvic area. Men are shown removal of the seminal and prostate glands. If the erection was normal before the patient’s intervention, doctors take measures to maintain the nerve fiber responsible for this. If the procedure is performed for a woman, it is usually recommended to remove the uterus, ovaries. According to statistics, it is here that metastases are most often detected in malignant processes localized in the bladder.
When the resection is completed, it is necessary to choose the optimal method of urine diversion. The ureter can be attached to the wall of the abdominal cavity or lead to a new bladder reconstructed from intestinal tissues. A specific option is chosen based on the features of the bladder removal procedure for cancer. Take into account how old a person is, in what condition he is, what surgical interventions have been previously transferred. An important aspect is the presence of intestinal pathologies. Often, even before the operation, the doctor together with the client decides on the best option.
Resection: before, during and after
Before starting the removal of the bladder, the patient should be prepared for the intervention. A course of laxatives is prescribed to cleanse the intestinal tract. This is usually enough. The duration of the operation itself varies about five hours, possible deviations are usually within an hour up and down. After completion of the event, the patient is transferred to the intensive care unit, intended for newly operated people, where they monitor the condition for at least a day. The initial recovery period involves the intravenous infusion of analgesics and other medications necessary in a particular case.
A few days after removal of the bladder, the intestinal tract restores normal performance. A week after the event, it is necessary to remove temporary stents from the patient's body. After another week or a half people are discharged from this department. If the patient received a reconstructed bladder, he is shown a second dose after ten days - temporary catheters should be removed from the body.
Rehabilitation
As is known from statistical studies, after removal of a bladder tumor accompanied by reconstruction of the removed organ, up to 95% of patients can normally control urination in the daytime. Several months are needed to develop control skills at any time of the day. The majority of patients who underwent surgical manipulations successfully master the skills of controlling the bladder, regardless of the time of day.
Erectile function is largely determined by the potency of the patient before the intervention. Important aspects will be the age and features of the event. In some cases, it is not possible to remove the bladder so that the nervous system remains in its original state. If it was not possible to save the nerves, after removing the bladder, the man will not have the desired sexual strength.
Diagnoses and treatment: features of the issue
An invasive process is called a cancer process in which pathological changes encompass not only the mucous membranes of the organ, but also the layers below them, including the muscular ones. In the patient’s diagnostic card, the diagnosis will be recorded in stage T2 and more. Such a disease requires an intensive treatment of the patient. Resection is currently the only reliable method that gives relatively good results. The operation helps to take control of the case, reduce the risk of relapse. The official name for bladder removal surgery is radical cystectomy.
The operation is recommended if an invasive cancer process is established, with metastases or not, or only regional ones identified, which can be removed during the operation. In some cases, removal of the bladder in men and women is practiced if superficial cancer processes are established. Resection is indicated if transurethral surgery has been postponed, after which several relapses have occurred. They can prescribe an event in case of a large area of lesions and the spread of the pathological process to the prostatic zone of the urethra.
Diagnoses and Patients
Sometimes bladder removal for men, women is shown against a background of flat cancer. The operation is prescribed if the intravesical immune treatment, the chemotherapeutic approach did not give the desired result.
The type of intervention under consideration is useful in T1, an early stage of the malignant process under the condition of low differentiation of degenerated cells. For such a disease, the risk of relapse is rated as high.
With an oncological disease detected at a late stage, they can resort to resection in order to improve the patient's condition, weaken pain and improve the quality of life. The event is aimed at eliminating the main symptoms - frequent urges to urinate, bleeding. The measure is considered palliative.
Nerve-Saving Intervention
Men are more often interested in such an operation. In an impressive percentage of cases, removal of the bladder is associated with impaired functioning of bundles of nerve fibers and vessels that feed the reproductive organs, and after surgery the patient becomes impotent. If erectile function was good before the event, the patient is usually interested in maintaining it. The recommended intervention will be very similar to nerve-sparing prostatectomy.
In addition to the obviously positive aspect of preservation of the nervous system, there is a likelihood of undesirable consequences - removal of the bladder in men may not give the desired cure, the likelihood of maintaining foci of atypical degeneration in the body increases. An operation that allows you to keep the nervous system of the reproductive organs normal, automatically significantly worsens the prognosis of the case. Doctors, when selecting individuals for such an intervention, are required to maximally responsibly evaluate all the features of the condition. Preservation of the nervous system is possible if invasive oncological processes are localized in the posterior region, on the side or in the trigonal plane. In the absence of an invasive process and the need to remove the bladder against the background of cancer, nerve preservation during bilateral surgery is possible if the pathology is localized on the dome of the bladder, the wall in front.
Responsibility is the key to success
Both before and after the operation to remove the bladder, the patient is shown a course of specialized treatment. Radiation therapy, chemical treatment before the event is carried out to reduce the size of the neoplasm, to reduce the amount of tissue that must be removed from the body. After the intervention, the decision to continue such treatment is made, focusing on the characteristics of the case.
Neoadjuvant drug treatment, followed by total resection, has recently been used more and more often. Many note that this approach is one of the most promising. Given the consequences of bladder removal, the likelihood of relapse, and other technical issues, many agree that it is the format mentioned in the near future that will be recognized as the standard approach for invasive oncological processes in the bladder. The studies clearly demonstrated that the combination of preliminary chemotherapy with subsequent radical resection significantly increases survival, and the difference among patients with oncology at stages T3, T4 is especially evident.
Features of supportive measures
Sometimes the doctor, evaluating the condition (for example, after removal of the uterus) of the bladder affected by cancer processes, recommends that the patient agree to the course of radiation. This kind of treatment before surgery in the general case practically does not affect the results of the resection. Therapy increases the likelihood of complications due to surgical intervention, complicates the formation of a reservoir for urine, if it is decided to use intestinal tissues. If earlier, radiotherapy was the standard beginning of the course, recently resorted to it only in the presence of strict indications.
As can be seen from the medical reviews, the removal of the bladder is an event of increased complexity, so it is important to carefully examine the condition of the patient. If possible, it is necessary to improve the health of the patient - how realistic is it, based on the starting conditions. If a patient has diabetes, chronic high blood pressure, anemia, or another disease, it is important to responsibly compensate for the pathology. A month before the operation, alcohol and tobacco products are completely excluded. This will improve the condition of the body, reduce the likelihood of complications during anesthesia.
Intestinal tract: why is it so important to prepare?
If it is supposed to carry out a resection in such a way that, based on its results, a bubble from intestinal tissues will be restored in the body, it is important to be especially responsible for preparing for the intervention. The intestines should be as clean as possible. Three days before the planned event, they begin to eat liquid products, porridge-like. 36 hours before the intervention, you should drink water, but do not use any dairy products. Juices are allowed. For a day, it is shown to take laxatives, put an enema.
Cleansing measures involve the exclusion of pathological microflora - decontamination. For this, the patient is prescribed antibacterial compounds that are active in the intestinal lumen. Such therapy allows you to completely destroy the microscopic forms of life.
Safety Above All
It is necessary to inform the attending physician, and before the operation, the person responsible for pain relief and the surgeon, if the person is taking vitamin E, aspirin or drugs containing it, if the patient has taken Plavix or Agrenox, as well as similar medicines that weaken the blood's ability to clot. A week or two before the planned operation, the patient should refuse to use these funds, so that the likelihood of unwanted bleeding was minimal. If it is impossible to completely exclude medications, reduce their dosage to the minimum possible.
Any surgical interventions that affect the pelvic area are associated with a high risk of complications caused by the formation of blood clots. To reduce the risk of undesirable consequences, the patient on the eve as a preventive measure is given low molecular weight heparin drugs. In addition, the inguinal region is shaved in order to minimize the likelihood of infection. Lack of hair significantly improves the ability to maintain sterility.
And on the eve of the operation, and in the morning before its implementation, the patient is strictly contraindicated food, drink. If this rule is neglected, anesthesia can cause severe complications. The event obliges the patient to make general anesthesia. During the period of the manipulation, the person does not regain consciousness, and ventilation of the lungs is provided by connecting to the breathing apparatus. To minimize dangers, you should trust your health to the clinic, which has modern equipment. In this case, there is no doubt - all performance indicators of internal systems and organs will be read in a timely and accurate manner.
Features
In some cases, epidural anesthesia is recommended, which allows to increase the effectiveness of general anesthesia. A catheter is placed in the back to hold it. This option of anesthesia helps to reduce discomfort both during the surgical procedures and within a few days after it.
In a reliable clinic, all activities related to analgesia are implemented by a highly qualified anesthetist. This doctor may also be qualified as a resuscitator.Before the start of the surgical intervention, a specialist examines the patient, specifies the features of the anesthesia being performed, reports all the risks, possible undesirable consequences. Only if the patient is aware of them and agrees with the conditions, which is confirmed by his signature on a special form, does the surgeon begin work. Often in the evening of the day preceding surgery, the patient is given sedatives. This helps to get rid of stress, the mental state becomes more comfortable.
Technical aspects of the operation
– . , . , . . , . – . , . . , , – , .
The basic principle of resection is radicalism. And the affected organ itself, and all the lymph nodes, and nearby tissues, covered by malignant processes, must be removed once with a whole block. An equally important principle is ablaplasty, that is, preventing the spread of atypical cell structures through the wound through the body. The doctor, guided by the rules of the event, follows measures to reduce the likelihood of such a complication. The third key principle is anti-blast. His idea is that all atypical cells scattered over the wound surface must be destroyed. For this, the area is washed with medical alcohol, iodine solution or another suitable preparation.
Concluding the review
Surgical measures involve the removal of the bladder, lymph nodes, tissues, while it is important to clearly follow the indicated principles. The process is long, but only it is not all. Next, the doctor forms the path by which urine will be excreted. The final step is suturing the wound. Catheters and a drainage system are left here. All seams are fixed with sterile dressings. Seized organs and tissues must be examined in a laboratory setting.
When the effect of the pain medication ends, the patient is transported to the ward intended for this, and then to the general intensive care unit of intensive care. It is noted that even in the case of a successful operation and a well-proceeding recovery period, patients often become withdrawn, avoiding society, and unsure of themselves.