Genetic pathologies are rare congenital diseases that are difficult to predict in advance. They arise even at the moment when the formation of the embryo. Most often they are transmitted from parents, but this does not always happen. In some cases, gene disorders occur on their own. One of these pathologies is considered Bruton's disease. It refers to primary immunodeficiency conditions. This disease was discovered recently, in the middle of the 20th century. Therefore, it has not been fully studied by doctors. It is quite rare, only in boys.
Bruton's disease: a history of study
This pathology refers to X-linked chromosomal abnormalities transmitted at the genetic level. Bruton's disease is characterized by impaired humoral immunity. Its main symptom is susceptibility to infectious processes. The first mention of this pathology occurs in 1952. At that time, the American scientist Bruton studied the history of a child who is sick more than 10 times at the age of 4. Among the infectious processes in this boy there were sepsis, pneumonia, meningitis, inflammation of the upper respiratory tract. When examining a child, it was found that antibodies to these diseases are absent. In other words, after infections, no immune response was observed.
Later, at the end of the 20th century, Bruton's disease was again studied by doctors. In 1993, doctors were able to identify a defective gene that causes a violation of the immune system.
Causes of Bruton's Disease
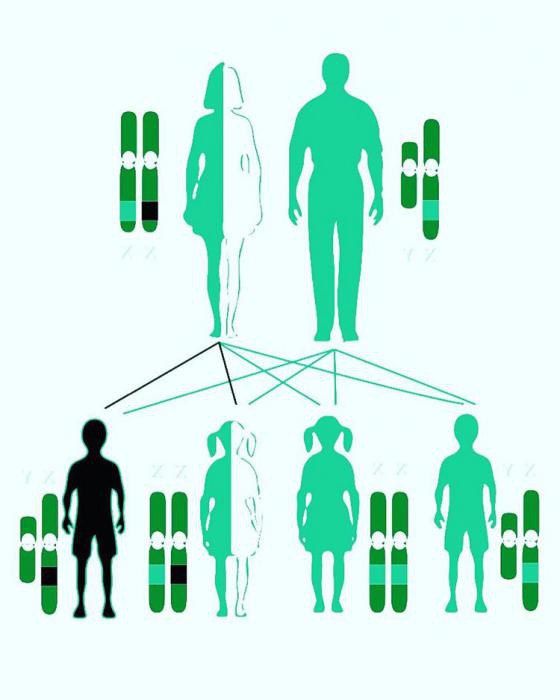
Agammaglobulinemia (Bruton's disease) is most often hereditary. The defect is considered a recessive sign, so the probability of having a baby with a pathology is 25%. Carriers of the mutant gene are women. This is due to the fact that the defect is localized in the X chromosome. However, the disease is transmitted only to the male sex. The main cause of agammaglobulinemia is a defective protein, which is part of the gene encoding tyrosine kinase. In addition, Bruton's disease can be idiopathic. This means that the cause of its appearance remains unclear. Among the risk factors affecting the child’s genetic code are:
- Alcohol and drug abuse during pregnancy.
- Psycho-emotional overstrain.
- Exposure to ionizing radiation.
- Chemical irritants (hazardous production, adverse environment).
What is the pathogenesis of the disease?
The mechanism of the development of the disease is associated with a defective protein. Normally, the gene responsible for tyrosine kinase coding is involved in the formation of B-lymphocytes. They are immune cells that are responsible for the humoral defense of the body. Due to tyrosine kinase failure, B cells do not fully mature. As a result of this, they are not able to produce immunoglobulins - antibodies. The pathogenesis of Bruton's disease is to completely block the humoral defense. As a result of this, when infectious agents enter the body, antibodies to them are not produced. A feature of this disease is that the immune system is able to fight viruses, despite the absence of B-lymphocytes. The nature of the violation of humoral protection depends on the severity of the defect.
Bruton's disease: symptoms of pathology
Pathology first makes itself felt in infancy. Most often, the disease manifests itself by the 3-4th month of life. This is due to the fact that at this age, the body of the child ceases to protect maternal antibodies. The first signs of pathology can be a painful reaction after vaccination, skin rashes, infections of the upper or lower respiratory tract. Nevertheless, breastfeeding protects the baby from inflammatory processes, since breast milk contains immunoglobulins.
Bruton's disease manifests by about 4 years. At this time, the child begins to contact with other children, attends kindergarten. Among infectious lesions, meningo-, strepto- and staphylococcal microflora predominate. As a result, children may be prone to purulent inflammation. The most common diseases include pneumonia, sinusitis, otitis media, sinusitis, meningitis, conjunctivitis. With untimely treatment, all these processes can go into sepsis. Also, a manifestation of Bruton's disease can be dermatological pathologies. Due to the reduced immune response, microorganisms multiply rapidly in place of wounds and scratches.
In addition to the manifestations of the disease include bronchiectasis - pathological changes in the lungs. Symptoms include shortness of breath, chest pain, and sometimes hemoptysis. It is also possible the appearance of inflammatory foci in the digestive organs, genitourinary system, on the mucous membranes. Swelling and soreness in the joints are periodically observed.
Diagnostic criteria for the disease
The first diagnostic criterion should be attributed to frequent incidence. Children suffering from Bruton's pathology suffer more than 10 infections per year, as well as several times during the month. Diseases can be repeated or replace each other (otitis media, tonsillitis, pneumonia). When examining the throat, there is a lack of hypertrophy of the tonsils. The same applies to palpation of peripheral lymph nodes. You should also pay attention to the reaction of the baby after vaccination. Significant changes are observed in laboratory tests. In the KLA there are signs of an inflammatory reaction (increased white blood cell count, accelerated ESR). In this case, the number of immune cells is reduced. This is reflected in the leukocyte formula: a small number of lymphocytes and an increased content of neutrophils. An important study is the immunogram. It reflects a decrease or absence of antibodies. This symptom allows you to make a diagnosis. If the doctor has doubts, you can conduct a genetic examination.
Differences of Bruton's disease from similar pathologies
This pathology is differentiated with other primary and secondary immunodeficiencies. Among them - Swiss-type agammaglobulinemia, Di Georgy syndrome, HIV. In contrast to these pathologies, Bruton's disease is characterized by a violation of only humoral immunity. This is manifested in the fact that the body is able to fight viral agents. This factor differs from Swiss-type agammaglobulinemia, in which both the humoral and cellular immune responses are disrupted. In order to conduct differential diagnosis with Di Georgi syndrome, it is necessary to take a chest x-ray (aplasia of the thymus) and determine the calcium content. To exclude HIV infection, palpation of the lymph nodes, ELISA is performed.
Agammaglobulinemia treatment methods
Unfortunately, it is impossible to completely defeat Bruton's disease. The methods of treatment for agammaglobulinemia include replacement and symptomatic therapy. The main goal is to achieve a normal level of immunoglobulins in the blood. The amount of antibodies should be close to 3 g / l. To do this, use gamma globulin at a rate of 400 mg / kg body weight. The concentration of antibodies should be increased during acute infectious diseases, since the body cannot cope with them on its own.
In addition, symptomatic treatment is performed . Most often prescribed antibacterial drugs Ceftriaxone, Penicillin, Ciprofloxacin. With skin manifestations, local treatment is necessary. It is also recommended to rinse the mucous membranes with antiseptic solutions (irrigation of the throat and nose).
Forecast for Bruton's Agammaglobulinemia
Despite lifelong replacement therapy, the prognosis for agammaglobulinemia is favorable. Continuous treatment and prevention of infectious processes minimize incidence. Usually patients remain able-bodied and active. With the wrong approach to treatment, complications can develop up to sepsis. In case of advanced infections, the prognosis is poor.
Bruton Disease Prevention
If there is a pathology in relatives or suspected of it, it is necessary to conduct a genetic examination during the first trimester of pregnancy. Also, preventive measures include airborne exposure, the absence of chronic infections and harmful effects. During pregnancy, stress is contraindicated for mothers. Secondary prevention includes vitamin therapy, the introduction of gamma globulin, a healthy lifestyle. It is also important to avoid contact with infected people.