A fracture of the neck of the hip joint is attributed to severe and fairly frequent damage to the musculoskeletal system. At a young age, this is rare. The fact is that this requires a fairly strong blow - a fall from a height or a serious injury received, for example, in a traffic accident.
A completely different picture is observed in elderly people. Over the years, bone strength decreases significantly. The reason for this is osteoporosis, in which their thinning and rarefaction occur. Bones become brittle and brittle.
Clinic of the disease
A fracture of the femoral neck is difficult to tolerate in old age. The consequences can be of the most unpredictable nature - lead to disability or even death. Fractures are divided into three types:
- in the area of the femoral neck;
- in the area of the femoral head;
- in the area of the greater trochanter.
They are also divided into:
- median (medial) - intraarticular fracture;
- lateral (lateral) - extraarticular fractures;
- fractures in the trochanteric region, which are characteristic of older people, even with moderate injury.
Symptoms
Fracture of the femoral neck in old age - the consequences of injuries, infections of bone tissues, malignant or benign bone tumors. Damage is manifested by pronounced symptoms:
- Moderate concentrated in the groin pain increases with minor blows to the heel from the side of possible damage.
- A broken leg is unnaturally turned slightly outward.
- Shortening of a broken leg is noted - a damaged bone enables the muscles to pull the limb closer to the thigh.
- Symptom of “sticking heel” - with a possible flexion-extensor movement, maintaining the weight of a straightened leg is impossible.
If the patient received a hip fracture in old age, the consequences of this are primarily detrimental to his psycho-emotional state. There is nervousness, moodiness, frequent mood swings. First of all, due to forced immobility. Immediately problems arise that require endurance and patience.
Treatment
The likelihood of self-healing of bones is very small, primarily because of the structural features of the femoral neck and its blood supply. Therefore, it is very difficult to treat the fracture of the femoral neck in old age (it is impossible to predict the consequences of possible complications). In many countries, this issue is resolved radically - through surgical intervention.
1. Fixation of fragments of the femoral neck with cannulated screws - osteosynthesis. Complete freedom of movement (independently) after surgery is possible after four months. But even with this method, there are failures. Due to bone non-growth, there is a high probability of the formation of a false joint.
How to treat a hip fracture depends on many factors. The older the patient and the longer the period from the moment of injury, the greater the risk of failure. The optimal age of the patient in this case is up to 60 years.
2. Replacing the hip joint with an artificial joint - endoprosthetics.
The optimal age of the patient is from 60 to 80 years. After confirming the diagnosis of "hip fracture", treatment, surgery (the method of its implementation) are determined by the doctor, taking into account the individual and age characteristics of the patient.
3. Patients with multiple concomitant diseases that have contraindications (heart disease, diabetes mellitus), and those who have practically no chance of successfully undergoing surgery, are given non-surgical conservative treatment .
This we said about the official side. But the long-term practice of treating such fractures has shown that no conservative treatment will help if there is a hip fracture in old age, the consequences will still lead to death. Doctors were forced to go to the trick and apply the tactics of "lies to save." Patients were informed that there was no fracture, there was only a strong bruise. Painkillers were prescribed, a plaster splint or orthopedic boot was applied to fix the outer foot. But the main emphasis was on the need for active movement, which is an excellent and most important prevention of consequences:
- Formation of pressure sores.
- Violations of pulmonary blood flow, which inevitably leads to pneumonia.
- Hypodynamia, which negatively affects the work of the intestine and is the cause of constipation.
- The absence of loads on the caviar muscles causes a violation of venous circulation, which will lead to venous thrombosis of the lower extremities.
- Asthenic syndrome. After two months of bed rest, the patient’s physical weakness is so pronounced that he cannot not only walk, but also sit down.
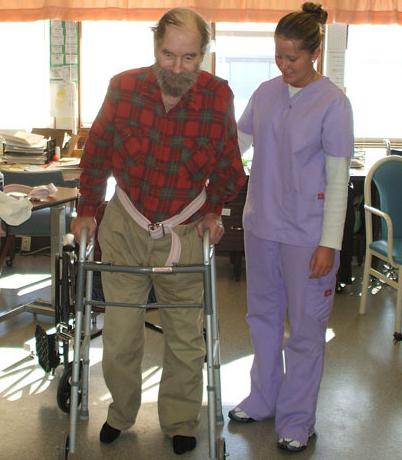
As soon as the pain subsides a little, the patient is allowed to sit with his legs down from the bed. After two weeks you can stand with a walker or crutches. After three weeks, you should move as much as possible, relying on something.
The method of such treatment is aimed not at ensuring fracture fusion - at this age it is simply impossible, but at adapting the patient and teaching him to live with such damage.
Surprisingly, it was this position that allowed many patients to save life and activity. The tactics of early activity of patients today is generally recognized.