Catarrhal otitis media is a pathological process of an inflammatory or infectious nature that occurs in the middle ear. This disease is characterized by damage to the tympanic cavity, the auditory canal and the cellular structure of the mastoid process. Catarrhal otitis media, the most common causative agents of which are pneumo-, strepto- and staphylococci, is found in representatives of all age groups, but most often affects the children's body. This is due to the fact that in children the auditory tube is shorter and wider than in adults. This facilitates the penetration of pathogens into the middle ear cavity .

Among the total number of patients with pathologies of ENT organs, according to official statistics, catarrhal otitis media is diagnosed in about every fourth case. Therefore, timely diagnosis in combination with the right treatment tactics are extremely important for the prevention of various complications and possible adverse effects of this pathology. It is also important to know the causes and symptoms of this disease, which will help identify catarrhal otitis media at an early stage of its occurrence.
Among the factors contributing to the development of the disease, there are a decrease in the body's resistance, vitamin deficiency, the presence of various infectious agents, and diabetes mellitus. As a rule, acute catarrhal otitis media is observed against a background of various chronic pathologies of the nasal cavity, which are accompanied by swelling of the mucous membrane. Also favorable conditions for the development of this ailment are influenza, acute respiratory viral infections and acute rhinitis. It is important to note that the spread of pathogens that provoke catarrhal otitis media is also possible through the circulatory system in tuberculosis, measles and scarlet fever.
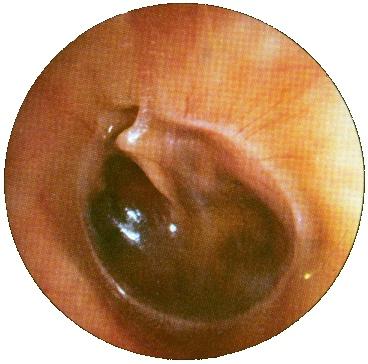
Symptoms of this pathology are manifested by severe headaches, a feeling of stuffiness in the ears, fever, hearing loss, and general well-being. In addition, in the acute stage of the disease, radiating pains of a shooting and pulsating nature appear, which can give into the teeth, temporoparietal region. Also, the pain is greatly enhanced during sneezing, blowing your nose, coughing and swallowing.
Dysfunction of the auditory tube may be accompanied by exudative otitis media, which is characterized by the presence in the tympanic cavity of a mucous-serous effusion. The leading pathogenic factor of such otitis media is a persistent violation of the ventilation and drainage function of the auditory canal. This form of otitis media is characterized by increased secretion of mucus and a protracted course of the disease.
The main diagnostic method here is otoscopy, often with an increase. To clarify the nature of the course of the disease, a study of the functionality of the auditory canal is also carried out using some publicly available samples. In addition, an impedance examination is often prescribed to identify a flattened curve. The patient’s hearing status is checked with tuning forks and audiometric methods.
Treatment of otitis media in the absence of additional complications and adverse factors is carried out mainly at home. The patient is prescribed bed rest, local painkillers (usually ear drops containing analgesics). In addition, various warming agents are needed: half-alcohol compresses, a heating pad, an ultraviolet lamp, UHF physiotherapy, and others. It should be noted here that warming procedures can be carried out only in the presence of a normal temperature, otherwise you must first take an antipyretic.
Vasoconstrictive drops in the nose can also be very effective for otitis media, which will reduce swelling and restore patency of the auditory canal. For the treatment of acute catarrhal otitis media, antibiotics and restorative drugs are often prescribed. With adequate therapy, the entire course takes no more than a week. It is important to remember that self-medication of otitis media is highly not recommended, since it can go into a more severe form (internal or purulent) and give intracranial complications.