This is the largest gland in the human body, which is a vital organ. It is located in the abdominal cavity, immediately below the diaphragm, on the right side. She participates in metabolic processes, cleanses the body of toxins, promotes digestion, synthesizes cholesterol, bile acids. It accumulates fats, proteins, minerals, carbohydrates and vitamins. It is very important to maintain the liver in a healthy state, and for this it is necessary to know the symptoms of liver diseases and the causes that cause them.
Classification of diseases
In medicine, so far they have not come to a unified classification of diseases of this organ and biliary tract due to the fact that the main criteria by which the systematization of diseases occurs: causes, changes in structure, pathogen, clinical manifestations, are intertwined. According to morphology (pathological processes of the disease), all pathologies of the liver and biliary tract are conditionally divided into three main groups.
- Parenchymal - diseases associated with disruption of the cells, which provide the basic functions of the body. These include: cirrhosis, hepatitis, all neoplasms: cyst, various tumors.
- Hepatobiliary - they include various inflammatory processes in the bile ducts, which are of medical, toxic and infectious origin. The same group includes diseases associated with impaired outflow of bile, resulting from spasm, blockage or neoplasms of the ducts.
- Vascular - any organ malfunction associated with the state of the vessels.
In addition to this classification, all diseases can be divided according to the etiology (causes and conditions of occurrence) of the disease and other criteria.
Causes of the disease
Liver tissue is very resistant to various negative influences. This is the only human organ that can self-repair. Despite this, the constant influence of adverse factors leads to various diseases. The main causes of ailments that are considered in the diagnosis of liver diseases are as follows:
- Injuries. They occur during a fall, at work, in an accident. There may not be any visible signs, and the symptoms will appear much later in the form of cysts, which are discovered quite by accident during an ultrasound examination.
- Viral infections. Hepatitis A, B, and C viruses pose a serious danger. They cause inflammation of the tissues, which occur in acute or chronic form, subsequently causing cirrhosis. The safest of these is hepatitis A, called jaundice. It does not go into a chronic form and does not entail serious consequences. The greatest danger is hepatitis B, which for a long time does not show a clinical picture, goes into a chronic form and has a risk of developing cirrhosis or cancer.
- The presence of parasites. Their various species cause organic and functional disorders. Necrosis appears, combining into an amoebic abscess, the development of liver failure occurs.
- Medicines The unsystematic use of medications, especially antibacterial, hormonal and antifungal agents, leads to disruption of the vital organ.
- Poisoning. The systematic effect of toxic substances on the human body as a result of work in hazardous industries leads to liver damage. A single exposure to fumes of heavy metals or chemical compounds can cause acute necrosis of the gland. There is a liver failure, as a result of which the remaining healthy cells can not perform all the functions assigned to them. Over time, dead cells are replaced by connective tissue, which leads to the development of cirrhosis.
- Alcohol poisoning. Alcohol abuse also leads to cirrhosis.
- Improper nutrition. The high content of fatty, spicy, fried and smoked foods in the diet makes it difficult for bile outflow, which leads to stagnation, resulting in the formation of stones, both in the gall bladder and in the ducts.
- Genetic predisposition. Disturbances in the structure of the liver cause narrowing of the ducts and blood vessels, which complicates the flow of blood and bile, poor development of a vital organ or its parts leads to a decrease in functioning.
- The presence of purulent foci in the peritoneum. This affects the functioning of the biliary tract, the development of cholangitis or abscess.
- Exposure to radiation. Radiation or ionizing phoning causes the degeneration of liver cells into malignant cells.
There are a lot of factors that affect the condition and functioning of an organ, but most of them are related to lifestyle, therefore a person is able to maintain his health.
What are liver diseases?
In medicine, the following are considered the main diseases:
- Hepatitis is an inflammation of a different nature. They are acute or chronic, have a toxic, medicinal or viral nature. In the absence of timely treatment, the general condition of a person worsens significantly.
- Primary cirrhosis. The disease is more common in women. Symptoms of liver disease are manifested by itching, ulcers, yellowing of the mucous membranes and dermis.
- Cholangitis. Inflammatory processes occur in the ducts of the organ.
- Vascular anomalies - congestive liver, vein thrombosis.
- Tuberculosis - bacteria usually enter the intestines through the hematogenous or lymphogenous pathways, and sometimes spread through the bile ducts.
- Fatty degeneration - organ cells are replaced by adipose tissue.
- Hepatic failure - characterized by a violation of one or more functions. Appears in connection with the defeat of the parenchyma.
- Hepatomegaly is a pathological increase in the size of a vital organ. This condition is characteristic of many diseases.
- Volumetric (focal) liver formations are single and multiple sites of structural change, the origin of which can be very different: benign and malignant.
- Steatosis is a fatty organ infiltration. The cells accumulate fat.
- A cyst is a benign cavity formation filled with fluid inside. It is located in various segments of the liver.
- Hepatic coma - caused by deep oppression of the organ. A person loses consciousness, his blood circulation and breathing are disturbed.
Most often, examination of patients reveals hepatitis, cirrhosis and liver steatosis.
First signs of the disease
To recognize the symptoms of the disease, you need to know where the liver is. Its shape is similar to an obtuse triangle, which consists of two lobes and has rounded edges. The liver is located in the peritoneum on the right side. Its upper part is located from the left nipple to the right, and the lower part is at the right ribs. In the early stages of the disease, there may be no signs. This organ does not contain nerve fibers, so pain may not occur for a long time.
In liver diseases, the very first sign is weakness and fatigue. But it should be remembered that such symptoms have a number of other diseases, or simply they can appear with excessive load. With the constant presence of malaise, for no apparent reason, it is advisable to consult a doctor. In diseases, these symptoms are associated with intoxication of the body, since the liver ceases to cope with its cleansing. In addition, there may be a violation of metabolic processes: vitamin, carbohydrate and protein. Only a doctor can figure out all the intricacies. The most important thing is to turn to him in time at the first sign of liver disease.
The main symptoms of pathology
Diseases of this organ for a long time pass without any signs, the pain appears even with severe liver damage, when it increases in size and begins to compress the fibrous membrane, where the pain receptors are located . For various liver diseases, the following symptoms may appear:
- weakness and general malaise;
- heaviness under the ribs on the right side;
- yellowness of mucous membranes and skin;
- dark color of urine;
- feces of liquid consistency and grayish-white color;
- the appearance of puffiness;
- the formation of hematomas as a result of fragility of blood vessels;
- increased sweating;
- frequent bleeding;
- in the morning there is a bitter taste in the mouth, a yellow coating and an unpleasant smell on the tongue;
- papules on the skin, burning and itching;
- sudden weight loss;
- the appearance of a venous pattern on the abdomen and an increase in its volume;
- frequent headaches, loss of memory and mental abilities;
- hormonal failure and dysfunction of the nervous system;
- significant increase in volume.
Symptoms of liver disease are numbness of the muscles, a feeling of cold fingers and toes, nails become brittle, brittle with white stripes or spots. Hepatitis and cirrhosis are accompanied by a slight increase in temperature. With its values greater than 39 degrees, it should be expected that a purulent process develops. The nervous system reacts to sleep disturbances, apathy, fatigue due to incomplete elimination of toxins due to poor organ function.
Diagnostics
To establish a diagnosis, the doctor conducts the following studies:
- Conversation with the patient - listens to the patient's complaints.
- Inspection - a visual examination: the volume of the abdomen, the color of the skin and tongue, the presence of rashes.
- Palpation - it turns out the size of the vital organ, density, shape.
- A biochemical blood test for liver disease helps diagnose hepatitis, metabolic disorders and cirrhosis.
- General analysis of urine - color, transparency, smell, character of the foam are examined.
- Fecal analysis - determine the physical and chemical parameters.
- Analysis for viral hepatitis and HIV infection.
- Ultrasound - to identify the focus of the disease.
- CT and MRI - the lesion is determined, the sizes and condition of the tissues are specified.
- Puncture - for the collection of material for histology.
- Duodenal sounding - the function of the gallbladder, bile sampling for analysis is evaluated.
The diagnosis of liver diseases allows you to accurately establish the diagnosis and prescribe the appropriate treatment.
Skin changes in diseases
In diseases associated with this internal organ, specific modifications occur on the skin. They can be the following manifestations:
- The icteric color of the dermis. First of all, the mucous membranes, eye sclera, the lower surface of the tongue, palms, feet, face, and then the whole body change their color to a yellowish tint, especially noticeable in natural light.
This process is associated with an increased content of bilirubin in the blood.
- Skin rash. Rashes with liver diseases are manifested in the form of: pustular foci, boils, dermatitis, eczema, hemorrhagic rash. All this is associated with functional disorders in the functioning of the internal organ - the inability to synthesize immunoglobulin, neutralize toxic substances, and produce prothrombin.
- The appearance of stretch marks. Often they appear on the stomach in the form of thin strips of bluish color. A hormonal malfunction occurs in the body, since the liver cannot cope with excess steroid hormones.
- Itching of the body with liver disease is explained by an increased concentration of toxic substances in the epidermis as a result of poor organ function. Irritated skin on the abdomen, hips and forearms is combed and very difficult to treat.
- Spider veins are small blood vessels. They appear on the face, neck, and then spread throughout the body and are considered signs of cirrhosis.
- Marked pallor of the skin. Impaired absorption of nutrients and a reduced amount of protein for the formation of hemoglobin leads to anemia.
- Stains on the skin with liver diseases. They appear in the inguinal and axillary regions. Pigmentation has a bronze or smoky color and is a symptom of hemochromatosis.
Pain in the liver
By the intensity and nature of the pain, we can assume the type of gland disease:
- Acute - occurs with pathological phenomena in the gallbladder. There is a spasm of the bile ducts, which leads to a violation of the outflow of bile, hepatic colic begins.
- Burning - appears with acute cholecystitis. In this case, bitterness appears in the mouth, the temperature rises, nausea and vomiting begin. Pain in liver diseases can be given to the right arm and collarbone.
- Dumb - inherent in chronic inflammatory diseases: cholecystitis, hepatitis. Additional signs will be: poor digestibility of food, flatulence, nausea.
- Aching - characteristic of cirrhosis or malignant tumors.
In some cases, pain in the right hypochondrium can cause diseases that are completely unrelated to the internal organ in question.
Clinic for men
Various ailments of the key organ of a person suffer all people, regardless of age group. There is no difference between the signs of liver disease in men and women. According to medical statistics, it is believed that women are less likely to be subject to these diseases than men. This is most likely due to the lifestyle, and not to the constitutional characteristics of a person. Some diseases are more common in women. For example, prolonged use of hormonal contraceptives provokes disruptions in the hepatobiliary system (excretion of metabolic and digestive products from the body). Others suffer more often than men. For example, cirrhosis, which arises from excessive alcohol consumption or working conditions with toxic substances. Certain types of pathology affect the sexual activity in men. Signs of liver disease that appear with mass death of hepatocytes lead to a decrease in potency.
Blood analysis
When studying the analysis of blood biochemistry, its composition is revealed, the results of which are recorded in a specific form, which lists the main components and their content in the blood. The values of the indicators can be different depending on the age and gender of the patient. Deviations from the norm are a symptom of an organ malfunction. Correctly evaluate all the results of the analysis, compare them with other signs and causes of the disease can only the attending physician. The main indicators of liver diseases in blood biochemistry are:
- proteins - total, creatine, albumin, uric acid, urea;
- lipids and lipoproteins - cholesterol, apolipoprotein, triglycerides;
- carbohydrates - fructosamine, glucose;
- specific proteins - transferrin, C-reactive protein, ferritin, myoglobin, troponin;
- electrolytes;
- pigments - bile acids, bilirubin;
- vitamins.
Only blood biochemistry reflects the functional state of the internal organ and will significantly help the doctor make a diagnosis.
Tongue plaque
Language is not only a participant in the digestive process, but also an indicator of human health. When visiting a doctor, you often hear the phrase: "Show the tongue." This interest of doctors is not accidental, the language is one of the first to feel the beginning anomalies in the body. An experienced doctor can identify the symptoms of some ailments by the appearance of this vital internal organ. The color of the tongue in liver diseases usually turns yellow.
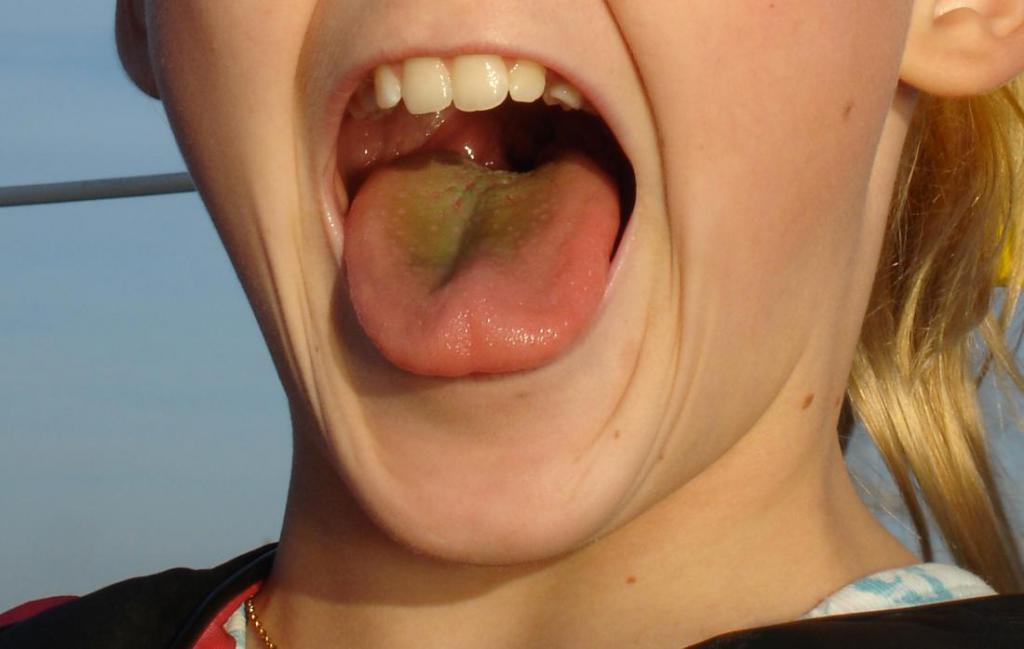
This color is caused by violations that are associated with the outflow of bile from the gallbladder. The most common cause of this phenomenon is the occurrence of cholecystitis due to stagnation of bile or infection with hepatitis. In addition, there is a bitter aftertaste in the mouth and pain in the right hypochondrium. Sometimes the appearance of yellow plaque indicates diseases of the stomach or prolonged smoking. Diagnosis of the color of the tongue, of course, is impossible. For this, it is necessary to take into account other symptoms and causes that caused a discoloration of the tongue and the results of laboratory tests. With liver disease in complex cases, instrumental studies are also carried out.
How to eat
With the help of dietary nutrition, liver function, bile formation and biliary excretion, as well as metabolism are restored. Due to violations in the functioning of the body, food should cause appetite and be quickly absorbed. It should contain protein that is easily absorbed, fiber, minerals and vitamins. Animal fats and foods that increase the secretion of gastric juice should be excluded. Food is recommended to be taken often.
What to eat with liver disease:
- all dairy products;
- low-fat varieties of fresh boiled fish;
- vegetables and fruits;
- some flour products;
- low-fat boiled meat;
- jam, honey, fruit candy, marmalade.
It should be limited to:
- butter;
- eggs
- caviar of sturgeon and salmon fish;
- cheese;
- boiled sausage;
- Tomatoes
When symptoms of liver disease are prohibited:
- alcohol-containing drinks;
- spicy seasonings;
- goose, duck, pork and lamb meat;
- cakes, pastries;
- chocolate;
- fried, smoked and pickled products;
- nuts
- tomato juice.
Due to the nature of the disease, the doctor may prescribe some dietary restrictions and recommend diet food for a certain time. , . , .