Various disorders in the process of cell formation in physiological tissues provoke the formation of tumors. In turn, neoplasms are classified as benign and malignant. The former are characterized by relatively slow growth. Benign tumors do not cause disorders of other systems and organs. This type of neoplasm includes osteoma of the frontal sinus. Next, we consider this pathology in more detail.
General information
Sinus osteoma is a process of improper differentiation of bone tissue. This neoplasm does not form malignant cells. Sinus osteoma does not provoke brain dysfunction. Pathology can begin its development in childhood (early) age and complete its full formation by 18-20 years.
Features
The initial course of the disease is almost imperceptible. Osteoma of the frontal sinus can be detected quite by accident, in the process of any associated laboratory tests. For example, often a neoplasm is detected by radiography due to head injuries. In the process of tumor development, cell metastasis is not observed. The neoplasm does not affect the conjugate areas of physiological tissues.
Causes
Specialists currently do not know the exact factors that trigger the neoplasm. Nonetheless, some of the most common alleged causes are mentioned. Among them:
- Frequent colds complicated by sinusitis and other sinusitis.
- Disorders in the genetic differentiation of bone tissue in the prenatal period of development. These disorders can be triggered by viral and bacterial infectious pathogens.
- Vitamin D deficiency and calcium deficiency.
- Injuries and various consequences of laboratory diagnostic procedures that are associated with a puncture of the maxillary sinus.
- Radiation, including radiological.
- Adverse environmental conditions.
Osteoma of the bone as a whole can develop not only in the sphenoid, frontal, ethmoid bone of the skull. Often, a neoplasm is detected in the bodies of the vertebrae and lower extremities. Osteoma in spinous processes is less often observed. In these cases, it is necessary to conduct a differential diagnosis, excluding the development of osteophytes on the basis of a prolonged ongoing change in the structure of the vertebral column of a degenerative type.
Frontal sinus osteoma: description
This localization is considered the most common for this type of tumor. The course of the disease is almost asymptomatic, prolonged. In general, frontal sinus osteoma without special research measures is very difficult to diagnose. The specialist may suggest a disease in case of a change in the patient’s voice, in the presence of severe pain in the head of a constant nature. A unilateral lesion, for example, an osteoma of the right frontal sinus, is accompanied by visual impairment in one eye. The bilateral form develops quite quickly. It manifests itself against the background of Gardner's disease. It is believed that this is one of the most dangerous forms in which the frontal sinus osteoma is manifested. The operation should be carried out in this case as soon as possible. Against the background of this type of pathology, neoplasms can be detected by local groups in the bones of the lower extremities, the spinal column.
Clinical picture
How is the frontal sinus osteoma manifested? Symptoms of the pathology appear only in those cases when the tumor, growing, begins to affect the associated physiological tissues. In this case, there may be a violation in the blood circulation of some areas. This, in turn, provokes atrophy in the tissues. As a result, the normal functioning of one or another site is disrupted. As observations show, manifestations of a pathology depend on its classification. For example, specialists isolate a hyperplastic tumor. It develops as a result of the rapid growth of ordinary bone cells, layered on the physiological layer. As a result, a pathological thickening is detected in a certain section of the element. Along with this, thinning of bone tissue is observed near the hypertrophic area. This, in turn, increases the likelihood of fractures and cracks.
Hyperplastic form
This type of tumor is formed from cells of connective and cartilage tissue, followed by calcification and deposition of various kinds of salts. For the most part, the hyperplastic form of pathology is the initial stage of osteophyte. It is localized in the spinous processes of the spine. Pathology can manifest itself in the form of typical symptoms of osteochondrosis. During the examination, a dense neoplasm can be detected on the spinous processes. It is painless and motionless on palpation. The physiological volume of mobility remains within normal limits.
Manifestations of the hyperplastic form of pathology
Symptoms of the disease can be visible physical defects. For example, this may be the formation of a growth, a thickening of the bone, distinguished by asymmetry in the face or other part of the body. Against the background of compression of blood vessels and nerve fibers, pain and numbness sensations may appear. In particular, clearly these manifestations are noted in the region of the lower extremities. In some cases, neuropathy may begin, and insufficient blood supply to the affected part of the body may develop. With hyperplastic osteoma in the frontal sinus there is a feeling of compression inside the nasal cavity and in the forehead. The nasal mucosa is usually dry and very susceptible to infection. This leads to the presence of chronic runny nose in patients, which cannot be eliminated by vasoconstrictors. The most dangerous manifestation that accompanies a one-sided pathology, in particular, osteoma of the left frontal sinus, is considered to be a sharp decrease in the visual acuity of one eye. Over time, attacks of severe pain in the head, as well as epileptic clinical seizures accompanied by clonic seizures, may be added to this. In early childhood, this can provoke paralysis of the nervous system, cardiac arrest and breathing.
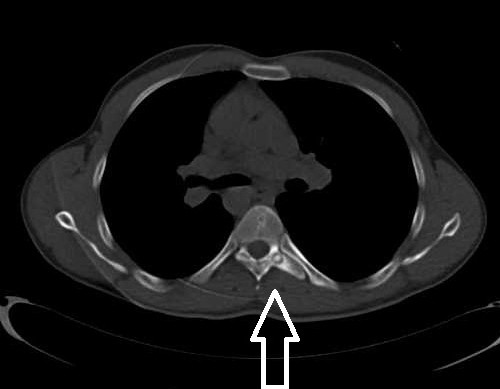
Pathology diagnostics
As mentioned above, it is quite difficult to identify the disease, because throughout the entire growth of the neoplasm (and this is 3-4 years), patients turn to specialists with complaints typical of other syndromes and conditions. Differential diagnosis is carried out after a patient undergoes an x-ray examination. Identification of the disease is carried out using histological analysis of hypertrophied tissue. In this case, a specialist should exclude a malignant tumor, polio, rickets. The initial examination is performed using the x-ray method and computed tomography. At this stage, it is important to exclude sarcoma and Ewing's tumor. These neoplasms are characterized by a high degree of malignancy and, rapidly progressing, will soon cause death.
Frontal sinus osteoma: treatment
Today, there is only one way to eliminate pathology. It is a dissection of excessively overgrown bone tissue. The removal of the frontal sinus osteoma is carried out using general anesthesia. During the intervention, an autopsy of the skin is performed. In special cases, craniotomy may be required. After that, the surgeon conducts a thorough resection of the altered area. In this case, areas of osteosclerosis with damaged blood vessels are also subject to removal. During the intervention, not only the neoplasm itself is eliminated, but also part of the plate of healthy bone tissue on which the tumor was located. Removal of the frontal sinus osteoma is prescribed if the lesion is actively growing and there are sufficiently pronounced signs of deterioration of the patient's health. If the neoplasm does not develop and does not cause concern, it is enough to conduct a regular examination and dynamic observation.
Rehabilitation period
After surgery, the patient undergoes recovery. At the first stage, rehabilitation takes place in a surgical hospital. Here, measures are taken to prevent the secondary appearance of tumors and to accelerate regenerative processes. In the future, rehabilitation consists in the correct organization of the regime of rest and work. The patient is prescribed a special diet with a large amount of calcium. To successfully prevent the development of pathology, it is necessary to carry out preventive measures. They should be aimed at reducing the likelihood of colds during at least the first six months after surgery. In general, to prevent complications in both the primary and secondary development of the disease, it is necessary to visit a doctor in a timely manner. Early diagnosis in many cases avoids the grave consequences of osteoma.