For some people, sinusitis is associated with a trivial rhinitis, in medicine called rhinitis. Indeed, these two different diseases have one common symptom - nasal discharge, or folk snot. When they appear, many are in a hurry to solve the problem with the help of widely advertised sprays and drops, not suspecting that such therapy only makes itself new problems. And all because the treatment of acute sinusitis, in contrast to rhinitis, must take into account the causes that caused it. In other words, if sinusitis occurs due to an injury, for example after visiting a dentist, the methods of treatment are completely different than sinusitis resulting from a bacterial infection. And treatment of acute sinusitis caused by pathogenic fungi cannot be carried out by the same methods as allergic sinusitis.
Only otorhinolaryngologists can determine what exactly happened to your nose. They prescribe a number of studies, and prescribe drugs based on their results. If you try to get rid of a bothering runny nose on your own, you can stop it for a while, and drive the disease deeper. Then, at best, a runny nose will appear with tedious regularity, and at worst, sinusitis will develop into a more dangerous disease, for example, meningitis or an abscess of the brain.
The concept and characteristic of sinusitis
To understand how effective treatment of acute sinusitis should go, you need to clearly understand what it is. Not everyone knows that sines are not only in geometry. The same term refers to the special sinuses of our nose, and their inflammation, respectively, sinusitis. In total, people have four pairs of sinuses (paranasal sinuses), diseases of which are specific names:
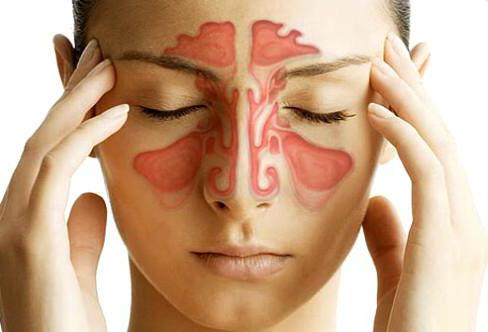
1. Frontite. In the frontal part of the skull, approximately above the orbits, there are two sinuses, similar to the frontal sinuses. In newborns, they are absent and form only when they reach the age of 7 years and older, and in some people they do not form at all. Their posterior walls border the frontal lobes of the brain, and the lower ones - with the walls of the orbits. The sinuses are lined with a thin mucous membrane connected by special fibers to the supraorbital and facial nerves. Inflammation of these frontal sinuses is called "frontal sinusitis." Treatment of acute sinusitis in adults and in schoolchildren must necessarily begin with the establishment of the localization of inflammation and the exclusion of frontal sinusitis, since it is one of the most serious forms of the disease.
2. Ethmoiditis. Approximately in the nose, or rather between the frontal, lacrimal, palatine, palatine and maxillary bones, there is the so-called ethmoid bone. In the context, it resembles a figured labyrinth of cells of various shapes and sizes. The sinuses of the ethmoid bone are also lined with mucous membranes. Their inflammation is called ethmoiditis.
3. Sinusitis. In the maxillary bone there are sinuses, many known as maxillary sinuses. Schematically, they are located on both sides of the nose, approximately from the orbits to the nasolabial fold, and are the largest in size. The maxillary sinuses are lined with a mucosa that is very poor in nerves. Therefore, its inflammation makes itself known not immediately. In a healthy state they are filled with air. Their lower walls are too thin, which creates a risk of infection and even filling material penetrating into them, for example, during poor-quality work of dentists. This greatly complicates the treatment of acute sinusitis of the maxillary sinuses, also called sinusitis, since you have to simultaneously deal with the rehabilitation of the oral cavity and treat dental diseases.
4. Sphenoiditis. In the sphenoid bone there are small sinuses, called by the analogy of the sphenoid. Their inflammation is sphenoiditis.
If several sinuses are inflamed at the same time, pansinusitis is diagnosed.
Causes
The treatment of acute sinusitis in adults and children should begin correctly with the establishment of the causes that caused it. They can become:
- various diseases of infectious etiology (tonsillitis, rhinitis, pulpitis, tuberculosis, as well as tumors and radiation);
- allergic reactions;
- dental treatment (root resection, canal filling);
- injuries of the nose and sinus membranes;
- polyps that appear in the sinuses;
- toxins;
- uncontrolled use of drops from a runny nose, as a result of which a large volume of mucus accumulates in the sinuses (especially in the maxillary sinuses);
- drafts;
- long stay in places with dry and hot air;
- subcooling;
- adenoids and polyps;
- problems with teeth and oral cavity (in case of sinusitis).
But most often, precisely because of the penetration of pathogenic microorganisms into the sinuses, acute sinusitis begins. Symptoms and treatment in adults depend on the type of microbe that has penetrated the mucous membranes. It can be:
- staphylococci;
- mushrooms;
- streptococci and others.
Classification
Differentiate not only by the localization of inflammation, but also by other signs of acute sinusitis. Symptoms and treatment, depending on the type being diagnosed, may be similar, but may vary significantly.
For the reasons that caused sinusitis, the classification is as follows:
- traumatic;
- viral;
- allergic;
- mycotic (caused by parasitic fungi);
- bacterial;
- medication;
- mixed.
According to the type of mucus formation, the classification is as follows:
- exudative sinusitis (serous, purulent, catarrhal);
- productive (polypous, parietal-hyperplastic).
Chronic sinusitis
By the nature of the course, acute and chronic sinusitis are differentiated. In the acute form, the disease lasts no more than two weeks. In chronic it lasts for years, in remission with almost no symptoms. When factors provoking exacerbations appear, they diagnose acute chronic sinusitis. The treatment in such cases is the same as in the acute form. Causes of chronic sinusitis:
- untreated diseases (acute respiratory infections, flu, bronchitis and others);
- improper treatment (inappropriate antibiotics and the like);
- adenoids and polyps in the nasal cavities;
- decrease in immunity;
- smoking;
- chronic diseases;
- cystic fibrosis;
- asthma is bronchial;
- HIV and others.
During remission, chronic sinusitis can only bother with mild headaches, fatigue, lethargy and not attract attention. Its treatment is complicated by the fact that microorganisms parasitizing in the sinuses have time to adapt to the drugs used by the patient. Therefore, therapy is carried out only in combination: antibiotics, which are susceptible to pathogens, anti-inflammatory and immune-correcting drugs, methods that strengthen the body as a whole.
Acute sinusitis: symptoms
Each type and type of sinusitis has its own characteristic symptomatology. However, there are a number of common signs that help to suspect this insidious ailment. Why suspect, but not diagnose? Because the symptoms of sinusitis, especially at the initial stage, are observed in many other diseases. It:
- general weakness;
- decreased appetite;
- moderate headache relieved by analgesics (if the inflammation is unilateral, then the head hurts on the same side);
- temperature.
In addition, there may be:
- runny nose;
- sneezing;
- nasal congestion;
- pain in the area of the nasal sinuses;
- decrease in sense of smell;
- sleep disturbance;
- sometimes a sore throat.
In addition, with different types of sinusitis, patients experience some characteristic symptoms.
So, sinusitis or acute maxillary sinusitis, the treatment of which in no case can be carried out without consulting a doctor, is characterized by the following symptoms:
- tear;
- chills;
- memory impairment;
- pain in the gums when turning the head.
With frontal sinusitis, characteristic symptoms:
- a feeling of pain and heaviness above the eyes;
- pain in the eyes, aggravated by bending and decreasing when lying down.
With etmoiditis, the symptoms are as follows:
- a feeling of pressure in the orbits;
- tear;
- heaviness in the cheek from the side of the inflamed sinus;
- Signs of toxicosis.
With sphenoiditis:
- a feeling of heaviness, fullness in the nasopharynx;
- aching headache, mainly in the back of the head (the prevailing symptom);
- double vision;
- pain radiating to the ears.
To clarify the diagnosis, the doctor prescribes a blood test (general), x-ray, rhinoscopy and even computed tomography.
So, you already know what the symptoms of acute sinusitis are. And treatment in adults will be later brought to your attention. In the meantime, let's talk about the features of the disease in young patients.
Sinusitis in children
In about one in five cases, acute sinusitis in children is diagnosed. Symptoms and treatment of all types of disease are about the same as in adults. The differences are that babies do not have frontal sinusitis, since they have no frontal sinuses. The causes of sinusitis in children are almost the same as in adults, but the prevailing importance is:
- infection by pathogenic microorganisms;
- adenoids;
- subcooling;
- weakened immunity;
- allergic reactions;
- congenital pathologies in the structure of the nasal septum;
- improper treatment of previous sinusitis ARI, influenza, bronchitis.
In addition to the main symptoms of sinusitis, parents can alert:
- the appearance of blue circles under the eyes of the baby;
- complaints of pain in the ears;
- refusal of food;
- moodiness;
- hard breath;
- deterioration of the child in the evening and improvement in the morning;
- prolonged (more than two weeks) cough, runny nose.
Treatment of acute sinusitis in children in no case should be carried out independently. An ENT doctor is required to prescribe a series of tests for the child (blood, swab from a nose), in particularly difficult cases an MRI or CT scan is performed. At home, you can perform the following therapy methods:
1. Nasal instillation with one of the vasoconstrictor drugs: “Nazivin”, “Sanorin”, “Xilo”, and after that - with one of the antiseptic drugs: “Etericide”, “Protargol”. Nose lavage is not recommended for very young children.
2. Treatment with antibiotics: Amoxiclav, Augmentin or their analogues.
3. Treatment with antiallergic drugs: Claritin, Tavegil.
Inhalations can be performed on the recommendation of a doctor. Usually use decoctions of chamomile, calendula. Also, in agreement with the doctor, you can give your child homeopathic medicines and use physiotherapy. Acupressure and gymnastics give a good effect.
Severity
Regardless of the location and type, acute sinusitis can occur easily or extremely severely. Symptoms and treatment with different degrees of severity differ significantly:
1. Light form. The patient feels a slight malaise, a slight weakness, although it remains operational. Symptoms that give the right to suspect sinusitis:
- runny nose;
- wheezing when breathing;
- not very severe headaches;
- nasal congestion;
- a slight increase in temperature (not always).
If an X-ray is taken, there may be no signs of sinusitis in the images.
2. Moderate form. Marked malaise is noted. Other symptoms:
- quite noticeable headaches;
- high temperature (over 38 ° C);
- nausea, sometimes vomiting;
- swelling of the eyelids;
- Sore sinuses;
- swelling of the soft tissues near the sinuses.
3. Severe form. The patient is weakened, indifferent, complains of soreness throughout the body. Other symptoms:
- heat;
- lack of appetite;
- nausea, often with vomiting;
- sometimes diarrhea;
- severe headaches;
- the temperature is increased significantly, sometimes to critical levels.
Rhinosinusitis
The mechanism for the development of sinusitis in a simplified form is as follows: the holes (mouth) with which all the sinuses communicate, in fact, with the nose, due to inflammation of the mucosa, narrow or completely close. Because of this, in the sinuses there is excessive pressure, which, in turn, provokes a new formation of mucus. Since the exit is blocked for her, she stagnates. This leads to a change in the acidity of the flora in the nose, and the cilia of the epithelium wrapped in mucus cease to move. All this creates paradise conditions for pathogenic microorganisms. They begin to multiply at an accelerated pace, destroy the membrane of the mucous membranes and penetrate their cells.
At the initial stages of nasal discharge, they have a serous character (color is transparent, specific gravity is low). The body sends an army of white blood cells to the area of inflammation to fight uninvited guests. When they die, they form a turbid, greenish-yellow liquid of a higher density, called pus, and the disease is already diagnosed as rhinosinusitis or acute purulent sinusitis. Treatment of the disease should be carried out only professionally, otherwise complications such as meningitis, subdural empyema, orbital abscess can be obtained.
Purulent sinusitis, like any other, proceeds in three stages. Light and medium can be treated according to general rules, but it is necessary to take a swab from the nose to determine the type of pathogen and choose the right antibiotic. Also, the complex of treatment includes preparations that thin the mucus, narrow the vessels of the mucous membrane, antiseptics, anti-inflammatory, antihistamines and strengthen the immune system. At the third stage of the disease, such conservative measures may not be enough, therefore, sinus punctures are performed. Such measures are also taken in cases where other methods of treatment do not give results.
Acute sinusitis: treatment. Preparations
The meaning of the treatment of any sinusitis is to relieve inflammation of the mucosa, ensure the removal of exudate from the sinuses and destroy the pathogenic pathogens.
If a patient encounters polyps or adenoids, they are surgically removed.
With an allergic etiology of sinusitis, they find out what exactly provokes it, they conduct anti-allergic therapy, at the same time they restore breathing with special exercises and prescribe drugs that increase immunity.
With advanced sinusitis, a puncture of the maxillary sinuses is prescribed with the removal of accumulated masses from them, washing them with saline and injecting antibiotics and anti-inflammatory drugs inside. However, this procedure can cause complications, such as otitis media, edema, vascular embolism, meningitis. Therefore, if possible, you should not start the disease.
The drugs of choice in the treatment of acute sinusitis are prescribed based on the condition and age of the patient, the presence of chronic diseases, as well as on the basis of the results of a study of pathogenic microflora in the nose. For mild to moderate forms of sinusitis, medications are taken orally. In severe form, part of the drug is injected.
Treatment Algorithm:
1. Nasal instillation. Most people with the appearance of snot immediately run to the pharmacy for vasoconstrictive drops from a cold. It is advisable to use them only during acute attacks and, as a rule, at night to ensure a quiet sleep. But even if you do not adhere to this and bury your nose according to indications, such treatment can be carried out no more than 5 days. Popular drugs are Protargol, Ingaron, Derinat, Grippferon, Pinosol, Euphorbium (suitable for children).
2. Nasal lavage. This technique provides an outflow of mucus from the sinuses and sanitizes the nasal cavity. Recommended preparations are Dioxidin, Miramistan, Furacilin, Chlorophyllipt. According to many patients, such a simple technique as washing the nose can not only relieve the disease, but also prevent acute sinusitis. Effective treatment, reviews of both doctors and patients about which are only positive, is the use of bacteriophage solutions for washing the nose. Using them, you can do without antibiotics, which for some categories of patients is fundamentally important. The only condition without which the method does not work is that before preparing a solution of bacteriophages, it is necessary to determine the type of bacteria that occupied the sinuses.
3. Antipyretic. At a temperature prescribed drugs "Paracetamol", "Aspirin", "Ibuprofen", "Nalgesin". Also used anti-allergic drugs "Loratadin", "Cetirizine."
4. Mucolytic drugs. Be sure to include in the complex therapy "Libexin", "Mukodin", "Fluditec." They thin the mucus, which helps its rapid elimination.
5. Antibiotics and antiviral. They are prescribed for almost all types of sinusitis. The following groups are used:
- penicillins: Amoxilav, Unazin, Ampisid;
- cephalosporins: "Cefixime", "Pantsef", "Suprax" (have a large number of adverse reactions);
- Macrolides: "Josamycin", "Clarithromycin" (term of use - up to 3 days);
- fluoroquinolones (only for adults): Ciprofloxacin, Levofloxacin, Ofloxacin and others.
6. Physiotherapy - treatment with a laser, UHF, microwaves and pulse currents.
Folk remedies
Treatment of acute sinusitis with folk remedies is quite possible provided that the disease is at the very beginning or as an additional remedy to the main course.
1. Washing the nose with a solution of salt, especially sea. For adults, they put a teaspoon without a slide of salt in half a liter of water, and for children - per liter, mix thoroughly so that all the crystals dissolve. In severe cases, a drop of iodine can also be added to the solution on the tip of a baking soda knife. The prepared solution can also be used for a kind of mask. In it, gauze is moistened, squeezed slightly and cover her face for a quarter of an hour.
2. Thuja oil. It is used as an antiseptic, immunomodulator, a means to relieve mucosal inflammation and as a prophylaxis of polyps. Thuja oil can be instilled into the nose or inhaled. For instillation, the nose is first washed with saline, then 3 drops of purified (distilled) water are instilled into each nostril, and only then 2 drops of oil. The nostrils are pinched.
3. Cyclamen. One of the most effective treatments for acute sinusitis. Treatment at home with this method is long, at least 2 months every day, but eliminates the disease forever. The cyclamen root is washed, triturated, squeezed juice and diluted with water (1: 1). Store the product in the refrigerator. They instill 2 drops in each nostril.
4. Prepare a mixture of cyclamen, aloe, Kalanchoe and onion juices, add Vishnevsky ointment. The resulting ointment with ear sticks is placed in each nostril.
5. Laurel. Three large bay leaves are poured with water and brought to a boil. In the resulting solution, a rag is moistened, squeezed out a little, put on the forehead and nose bridge, kept until cool. Repeat the process 3 times.
Some people try to treat sinusitis by heating the sinuses with a hot egg or other items, which is a mistake. If there is an accumulation of mucus in the sinuses, especially purulent, warming up will facilitate the rapid multiplication of microorganisms and the further spread of infection. You can warm your nose only when the recovery phase has begun and your sinuses have already been cleared.
There are dozens of other popular recipes for sinusitis, it is impossible to cover them all in one article.