Spinal hernia is a rather dangerous pathology, in the absence of treatment of which the development of complete or partial paralysis is possible. The sooner treatment begins, the greater the chances of achieving a long-term remission and leading a familiar lifestyle. Symptoms of a hernia of the spine in women are fairly obvious, and ignoring them can lead to partial immobility. You should completely reconsider your diet and lifestyle after making such a diagnosis. Unlike men, the fair sex is less likely to listen to the signals of their own body and are ready to endure pain and other symptoms of a hernia of the spine. Women have such a character trait as patience and a tendency to deny the problem - this can lead to unpleasant consequences, since the begun degenerative changes in the spine are irreversible.
What is a hernia of the spine
Intervertebral hernia is a fairly common disease, which is increasingly diagnosed in relatively young people. For this pathology, a shift in the pulpous nucleus of the vertebra is characteristic, as a result of which the fibrous ring breaks. After this, the nucleus flows into the canal of the spinal cord, damages the processes of nerve cells. Treatment of the disease can be successful only in the early stages, at a later prognosis is unfavorable.
In order to understand the causes of symptoms of spinal hernia in women and men, you should go a little deeper into the human anatomy. There are no blood vessels in the intervertebral discs - the oxygen in them comes from the spinal muscles. In case of malnutrition, the cartilage tissue begins to collapse. Provoke this process can features of physiological human behavior. This is a forced or voluntary lack of physical activity, a constant presence in one position. Depending on the location of the neoplasm, the intervertebral disc of any part of the spine may suffer:
- cervical;
- breast;
- lumbar;
- sacral.
Causes of the disease in women
So, we can distinguish the following most common causes of symptoms of spinal hernia in women:
- a sedentary lifestyle that provoked venous stasis;
- prolonged deficiency of minerals and vitamins;
- alcohol abuse, which is known to wash out the minerals and vitamins necessary for cartilage;
- genetic predisposition to defects of the musculoskeletal system (quite rare).
Unlike women, the most common cause of spinal hernia in men is injury. Injuries to the spine (and regardless of which department - a hernia can develop in any) can damage the innervation of the intervertebral disc. This can lead not only to the gradual development of a hernia, but also to a number of other pathologies. Women can also injure the spine, as a result of which a hernia begins to develop, but this happens less often with the fair sex than with men.
Medical classification of spinal hernias
There are several criteria by which a hernia of the spine can be classified. The prescribed treatment depends on the accuracy of the diagnosis and the fact whether it will be possible to achieve remission and get rid of the symptoms of a hernia on the spine in women. In the photo below - a hernia in an x-ray.
So, the classification according to the location of the lesion of the intervertebral disc:
- cervical spine (a hernia is formed relatively rarely, only about 3-5% of cases of the disease occur in this area);
- damage to the intervertebral space in the lumbar region (for women, this is the most common place of dislocation - this is due to the peculiarities of the development of the musculoskeletal system);
- damage to the thoracic or sacral region.
It is the lumbar spine that assumes a heavy load if a woman sits at a table for a long time. It is a well-known fact that women are more often involved in office work, which involves spending many hours in the same position. Also, heeled movement contributes to a high load on the lumbar. This is another factor that contributes to the appearance of symptoms of lumbar hernia in women.
Also in orthopedics there is a classification of spinal hernias according to the degree of protrusion:
- protrusion (prolapse) is diagnosed if the protrusion is up to 3 mm;
- prolapses are diagnosed with a protrusion of up to 6 mm;
- extrusion (formed protrusions) if the protrusion of the intervertebral disc is up to 15 mm.
The severity of symptoms of spinal hernia in women depends on the location and degree of protrusion. The treatment, for example, protrusion in the cervical region and in the lumbar region will be completely different. In the first case, physiotherapy and exercise therapy will be required, and in the second case, even exercise therapy will have to be performed with caution, or even completely abandon it, resorting to surgery. The exact classification of hernia and the appointment of treatment should be carried out by an orthopedic surgeon or surgeon. Self-medication in most cases not only does not improve the condition, but also exacerbates the patient's condition.
How does a hernia in the cervical spine
Symptoms of a hernia in the cervical spine in women usually appear between the ages of 30 and 45. You should contact an orthopedist as soon as possible and begin therapeutic measures. In the tissues of the intervertebral structures, changes begin; in addition to a hernia, osteochondrosis can begin to develop. Fibrous rings become fragile, the symptoms are becoming more acute. The course of treatment will depend on the degree of damage.
Symptoms of a hernia of the spine in women (an X-ray photo of a sick person is presented below):
- If the hernia is located between the vertebrae of the cervical CI and CII, the patient complains of insomnia. Sleep problems are characterized by disturbed sleep phases and difficulty falling asleep. The patient suffers from tinnitus, frequent headaches. The neck is often "numb", the vertebrae crunch when you try to turn your head. In connection with insomnia, problems with the psychological state often begin: the patient becomes irritable, intolerant, and may even turn to a psychiatrist for help. However, the true cause of the ailment is the development of a hernia and impaired cerebral circulation.
- Symptoms arising from damage to the intervertebral disc located between the vertebrae CII and CIII are due to the fact that blood supply and innervation of the tissues of the forehead, eyeballs and tongue are carried out in this area. Flies often flash before my eyes, my head often hurts and sweats a lot. The so-called torticollis develops - it is more convenient for the patient to keep her head inclined rather than straight. The taste perception is impaired, vision is reduced, panic attacks may begin, the patient is pursued by a sensation of derealization.
- A protrusion of the intervertebral disc located between the vertebrae CIV and CV leads to a violation of the innervation of the oral cavity, lips and nose. the patient suffers from vague pains in these areas. There may be a suspicion of sinusitis, pharyngitis, etc., however, the otorhinolaryngologist, as a rule, does not find such diseases, since the cause is a hernia of the cervical spine.
- A hernia that affects the intervertebral disc separating the VI and VII vertebrae infringes the root innervating the tonsils and muscle tissue of the shoulders and neck. It is difficult for the patient to turn her head, pains appear in the region of the shoulders and neck. A voice can become hoarse for no apparent reason. The muscles of the neck and arms are weakened. Shortness of breath appears, pains of an unclear nature in the region of the heart.
- When the intervertebral disc is located at the junction of the cervical and thoracic spine, the functioning of the thyroid gland is disrupted. In parallel with the development of a hernia in this area of the spine, patients suffer from frequent bursitis, arthrosis, and thyroid diseases. In this case, it is important to treat the root cause - a hernia, to restore nervous patency. After that, the negative symptoms associated with the main diagnosis will decrease.
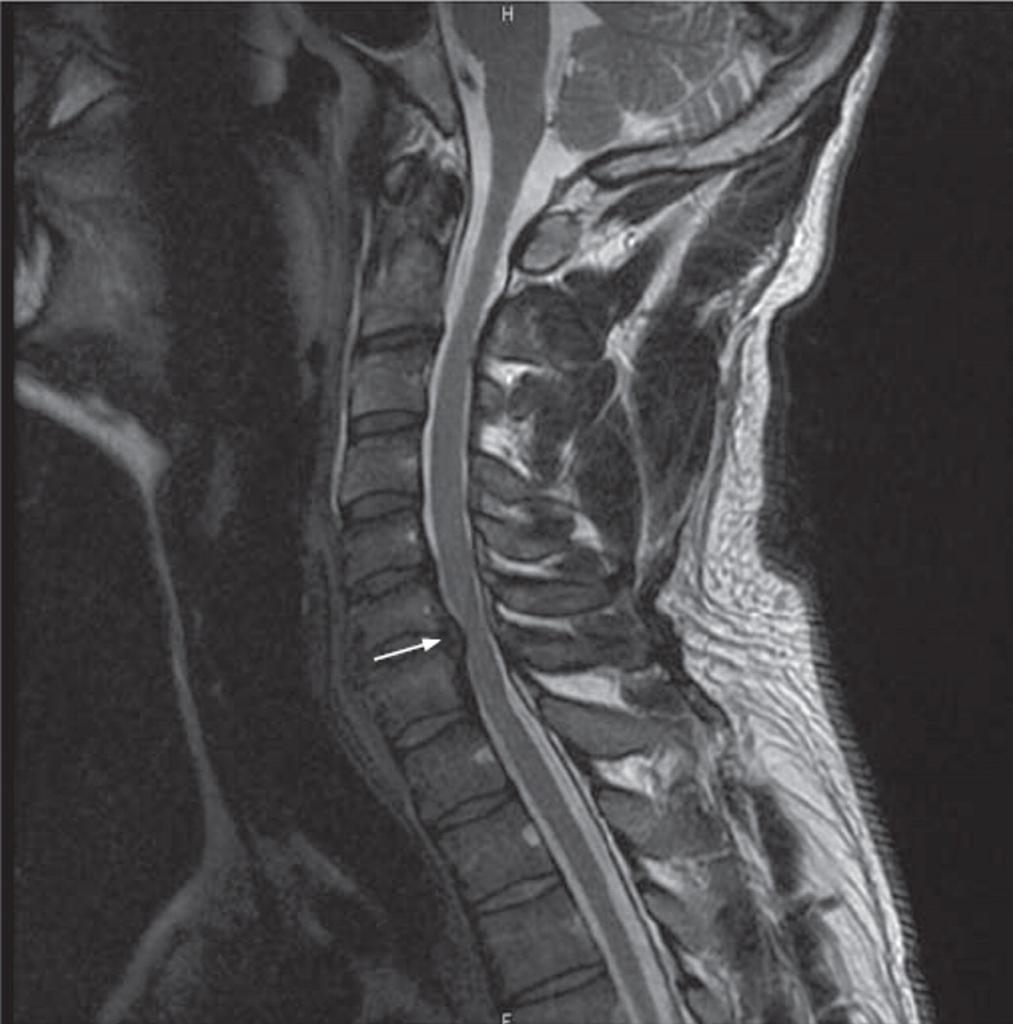
Thoracic hernia: symptoms in women
Pathology occurs in the thoracic spine. The faster the diagnosis is made, the faster it will be possible to proceed to treatment. Symptoms of a hernia of the thoracic spine in women are as follows:
- Pain in the heart of unclear etiology. Patients often believe that they have a heart condition, but an EEG refutes this suspicion. If the pain is permanent, you should definitely visit an orthopedist.
- Manifestations of intercostal neuralgia. Tingling pains in the sternum of an unknown etiology - this is most often precisely intercostal neuralgia, one of the symptoms of a hernia of the spine in women. Lumbar or thoracic - this can be confirmed with accuracy only after a CT scan.
- Numbness of the hands, deterioration of fine motor skills is also a common symptom.
How does a hernia of the lumbar spine manifest itself?
Depending on the stage of the process, the symptoms of a lumbar hernia in women can be as follows:
- Pain of aching, dull character in the lumbar region. In some cases, it can hurt not in the center, but on the sides of the lower back. In this case, the pain becomes less pronounced in the supine position. Often, patients confuse this symptom with kidney disease. In fact, the reason is a hernia of the spine in the lumbar region.
- Patients often complain of a feeling of "sagging" in the lower back. When you try to stretch or bend, there is a rather sharp pain sensation.
- In the mornings, numbness may be felt in the lumbar region, as if the blood flow in this place was impaired or the place was treated with anesthesia. This symptom of a lumbar spine hernia in women occurs in the initial stages. Later, when the disease progresses, pain appears.
Symptoms of a hernia of the sacral spine in women
The sacrum is located at the very bottom of the back, in front of the tailbone. This area of the body gets a lot of stress in those people who lead a sedentary lifestyle.
Symptoms of a hernia of the lumbosacral spine in women are as follows:
- sharp pain in the sacrum and tailbone when trying to bend or rotate the body;
- in the morning, a feeling of numbness in this area of the body, while trying to get up, pain may appear (its intensity depends on how far the pathological process has gone);
- the pain gives to the lower abdomen, to the pelvic area, sometimes it is a symptom of diseases of the bladder, so for an accurate diagnosis it is necessary to undergo an examination.
Methods for the treatment of hernia of the spine
Depending on the location and stage of the hernia, the treatment will be different. In some cases, regular exercise therapy is sufficient, and in others it is impossible to do without surgical intervention.
Many patients have been suppressing pain with painkillers for years, while hernia progresses. Do not let the pathology go by chance - you should regularly take physiotherapy courses, take all the drugs prescribed by the orthopedist and surgeon (even if at first glance it seems that taking the prescribed drugs will not bring any benefit).
Conventionally, three stages of treatment are distinguished in orthopedics:
- pain relief with medication and complete rest;
- massage and complex therapy;
- if necessary, surgical intervention;
- rehabilitation, recovery.
If after 3 months the condition worsens (neurological deficit syndrome, potency decreases, limbs go numb, pain increases), then surgery is prescribed as an extreme measure of treatment due to the increased risk of complications.
The use of pharmacology in the fight against hernia of the spine
The following groups are usually used as pharmacological preparations:
- Muscle relaxants can achieve relaxation of the problematic muscle group, as well as balance the pathological distortion of the spinal column. The parallel use of physiotherapy allows for remission in the early stages.
- Painkillers for the symptoms of a hernia of the spine in women (the lumbosacral region was damaged, the thoracic or cervical - it does not matter) can relieve the patient from pain. This is not a treatment in the literal sense of the word, but just a way for a while to get rid of the manifestation of pathology. The most commonly used painkillers are Tizanidine, Tetrazepam, Midokalm.
- Gels, ointments and other painkillers are for local, external use. This is Tylenol, Indomethacin. With regular use, they allow you to get rid of pain, relieve inflammation, but do not directly affect the hernia.
- Paravertebral blockade with novocaine (providing for the introduction of an anti-inflammatory hormone), which can instantly - for two to three weeks - relieve the patient from pain. It is permissible to perform three to four blockades during the course of treatment.
- Vitamin-mineral complexes with components that have a positive effect on the quality of cartilage and improve the functioning of nerve fibers - Milgamma, Neurovitan.
- Drugs that improve blood flow and lymph flow in the affected areas. Such drugs also help relieve swelling, sometimes inflammation. This is "Actovegin" in injectable form, "Berlition", "Pentoxifylline".
- Chondoprotectors stimulate the restoration of cartilage structures. The most popular are Chondroitin, Arthron Complex. They should be taken in a long course, otherwise the result of therapy may not be noticed. Against the background of therapy, alcohol is excluded.

Physical activity after diagnosis
It is very important after the course of treatment (especially if there has been a surgery) to observe the regime of physical activity. Exact recommendations on the quantity and quality of physical activity can only be given by the attending physician. But all patients are forbidden to lift weights, weightlifting and strength fitness classes are prohibited.
The best types of physical activity are exercise therapy, sparing exercises from callanetics and yoga, short walks, and swimming. All movements must be performed carefully, in case of pain immediately stop the load.