Keratolytic agents help preserve the beauty and youth of the skin or cure the epidermis of skin ailments accompanied by the process of hyperkeratosis. It is known that daily renewal of the skin is associated with the death of millions of cells on its surface, the accumulation of which leads to keratinization of the epidermis, uneven and dull complexion, peeling, fine wrinkles and clogged pores. Regular exfoliation of the scales stimulates the regeneration of the epidermis, gives it a healthy appearance and pleasant velvety. In the case when, due to various diseases, the process of rejection of dead cells is disrupted, hyperkeratosis develops - excessive keratinization. This phenomenon can have both a local form (in separate areas), and generalized (throughout the body).
What are keratolytic agents?
These are external medicines used for cosmetic and therapeutic purposes. This term came from the fusion of two words: “keratin” - the main structural protein that forms the epidermis (including corns and corns), hair and nails, and “lysis”, meaning “dissolution and decay”. Destroying the structure of keratin, keratolytic drugs can soften, dissolve and facilitate the rejection of the stratum corneum on the surface of the epidermis, nail plates and hair, and have a therapeutic effect in many skin diseases. Keratolytics with a low concentration have a slight exfoliating effect and perfectly cope with many cosmetic defects. Modern keratolytic agents are available in the form of ointments, plasters, powders, varnishes, collodion, solutions and pastes. In cosmetology, a similar, but less concentrated, effect is exfoliant, depilatory creams and other delicate peeling products containing acids in their composition.
Names of components that exfoliate the stratum corneum
Acids have keratolytic effects: salicylic acid (in a concentration of 5 to 60%), lactic acid (10 to 20%), benzoic acid (5 to 15%), trichloroacetic acid (10%), pyrogallic acid (10 to 20%), and also urea (from 10 to 50%), resorcinol (from 10 to 20%), potassium iodide (50%), barium sulfide (15%), thymol and phenol (5%). These keratolytic agents serve as active components of plasters, varnishes, ointments (often used for compresses or occlusive dressings), less often in pastes and solutions.
The use of keratolytic drugs
Indications for the appointment of this group of drugs are:
- Hyperkeratoses, especially palmar-plantar localization - psoriasis, tylotic eczema, mycoses and calluses.
- Onychomycosis, in which softening and removal of the nail plates affected by the fungus is a necessity.
- Skin ailments requiring exfoliating procedures - dermatoses with a characteristic excess of keratinized epithelial cells in the affected areas (psoriasis, erythroderma, chronic eczema, certain types of toxicoderma, reminiscent of the symptoms of hyper- and parakeratosis). In these cases, salicylic acid, naphthalan or tar tar of low concentration (not more than 3-5%) is used as part of special ointments, creams and emulsions with emollients and oil vitamins A and E, normalizing the process of cell regeneration.
- Hyperpigmentation (which occurs more often on the face), in which keratolytics are combined with whitening agents.
Soft peels and their concentration
Unlike mechanical scrubs that scratch the skin, keratolytic agents soften and loosen the stratum corneum, dissolve it, which favors its safe rejection. The “squamolytic effect” (exfoliation) ensures the removal of excess horn mass from problem areas of the skin (affected by acne or psoriasis), from seals on corns and corns, hair - with hypertrichosis, and also rejection of deformed nail plates. The keratolytic effect of this group of drugs manifests itself during chemical (acid) peeling procedures. In high concentration, they are used by professionals. Acid exfoliants of less saturation have a surface exfoliating effect, and in small doses they have a keratoplastic effect, that is, restoring the natural process of formation of the stratum corneum.
Pharmacodermatology in the fight against excess keratinization of the dermis
In mild forms of acne or moderate disease severity, salicylic acid and preparations based on it have the most pronounced effect: powders that contain 2-5% of the active substance, pastes and ointments with a concentration of 1-10% and alcohol solutions for home use (no more 1-2%).
Aromatic retinoids can be used to treat severe acne. The leaders among the funds of this group are Differin (gel, cream) or Isotretinoin, as well as Roaccutane.
To treat complex forms of acne, dermatologists prescribe keratolytic agents, the names of which are widely known in pharmacodermatology:
- "Baziron AS".
- Neotigazone.
- Akriderm SK.
- Vipsogal.
- Belosalik.
- “Tretinoin” (“Airol”).
- Diprosalik
- "Bensalitin."
- Lorinden A.
- "Carboderm."
These drugs, in addition to keratolytic, have anti-inflammatory properties, which well affects the result in the treatment of acne. For psoriasis, hyperkeratosis and other skin ailments, the listed keratolytic drugs, as well as Betadermic, Betnovate S, Keratolan, Lokasalen, Elokom S and Kerasal can be used in complex therapy. These ointments are anti-inflammatory non-steroidal drugs intended for external use. These drugs are also prescribed for eczema, ichthyosis, oily seborrhea and hyperhidrosis (excessive sweating).
Keratolytics act beneficially for any inflammatory and infectious skin lesions, in the presence of warts, corns, corns, burns and hyperpigmentation. Beauticians often recommend drugs based on glycolic acid in a concentration of 10-20% for treatment, but prescribe them individually to solve a specific aesthetic problem.
Keratolytics from corns and corns
Prolonged wearing of women's high-heeled shoes and other uncomfortable shoes provokes excessive keratinization of the skin on the feet. The need to get rid of corns and dry corns - these painful formations on the skin that arose due to mechanical irritation and pressure on the soles of the feet - is associated with the use of drugs with extreme Ph values (an indicator of the acid content in the substance).
Alkalis and acids are the main components that destroy the dense stratum corneum. On their basis, keratolytic drugs from corns are created:
- therapeutic and prophylactic foot paste “5 days”;
- Namozol 911 creams (based on tea tree extract), Super Antimozolin (the basis is lactic acid) and Green Planet (with lactic acid and oils);
- high-quality, but expensive Norwegian urea cream Neutrogena, TianDe (with snake fat);
- therapeutic and preventive tincture for pedicure Gehwol;
- Cream "Healer" (with healing urea);
- ointment "Bensalitin" (the basis is benzoic and salicylic acid);
- colorless solution for external use “Collomac” (salicylic and lactic acids together with polydocanol are the main components).
Keratolytic remedies for corns are the above drugs that cope well with corns, and salicylic acid ointment, and corn fluid (alcohol solution), and Crown of Siberia cream (with antifungal effect), as well as many others.
Popular keratoplastic remedies for corns
Compeed high-quality plasters reduce the mechanical effect on the skin, relieve pain and can be used for several days until the corns softens and comes off. Another, no less well-known remedy for corns is considered to be the Chinese corn patch “Shuyangsuan”. These red plates coated with the active substance stick on steamed and dried skin. Use them for at least six days. Salipod patch with antiseptic and antifungal effect contains salicylic acid, sulfur, which dries the skin, sticks to corn and lasts two days. After four applications, as a rule, keratinization softens and disappears. The keratolytic agent Urgo in the form of a patch is made on the basis of wheat germ oil and can be of two types: therapeutic corn patch and conventional protective.
Keratolytics for high-quality pedicure: we process the plate
Nails can deteriorate in people with diabetes, psoriasis, eczema, lichen planus, and other skin diseases. Also on the plates sometimes there are areas affected by fungus, bacteria or viruses. One of the ways to remove a deformed plate is chemical, when keratolytic agents for nails are applied to their horn parts and dissolve the defect. These properties are possessed by plasters with a concentration of 20 to 50% urea and onycholysin powder, which contains 15% barium sulfide (in talc). For example, the combined preparation "Mikospor" (ointment) contains 40% urea and 1% of the antifungal component - bifonazole. This drug is manufactured by Bayer (Germany) in the form of a cream, solution and a special kit for treating nails with the same concentration of the active component.
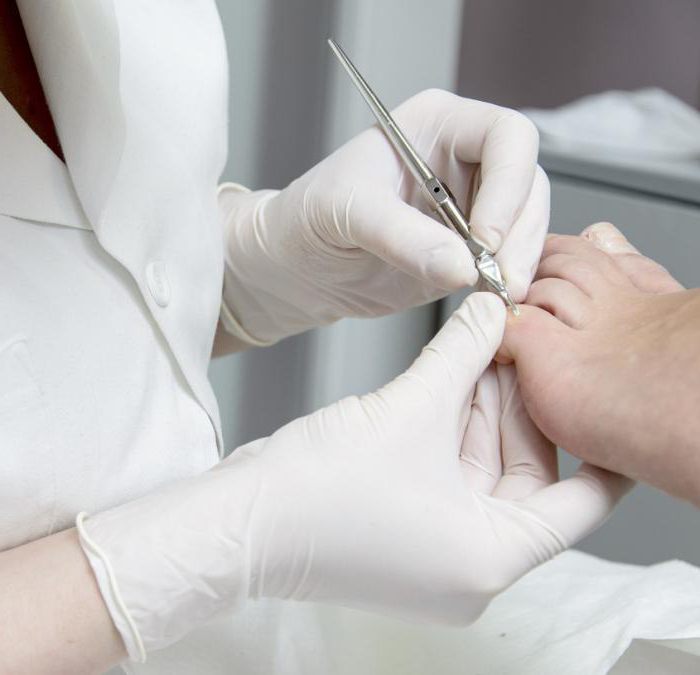
All drugs in this group contain keratolytic components (urea and salicylic acid in high concentrations), an antifungal agent (bifonazole or ketoconazole) and an antiseptic (chinosol or iodine). Fixation on the nail plate of a simple or complex lead patch, Ureaplast, trichloroacetic (CCL3COOH), salicylic or soap-salicylic patch will accelerate the destruction of the defective area of the nail, which must be periodically filed and cleaned.