When a future mother finds out that she is pregnant, her life takes on a completely different meaning. Now you need to take care not only about yourself, but also a small lump that already lives under the heart. The first thing a woman should do is to register with a good specialist whom she trusts to be sure of the normal course of pregnancy.
Of course, young parents least of all want to think that their child may not develop properly. But if nevertheless problems were discovered, do not despair. Gather all your will into a fist and do everything possible so that the baby is born healthy.
Fetal neural tube - what is it?
Many expectant mothers who are just learning the good news about pregnancy are in a hurry to study all the available literature about the upcoming birth. Then they get the information that the fetal neural tube is already beginning to form on the 19-22 day from conception. What it is? After all, an adult does not have such an organ. The answer is simple: the neural tube of the fetus is the primary form of development of the nervous system, including the brain and spinal cord. Open nerve felling is a platform for the formation of the anterior, middle and posterior bladder.
Terrible diseases that are not compatible with life
As we understood, one of the most important stages in the origin of life that occurs during pregnancy is the formation of the neural tube from which the baby’s brain and spinal cord will develop very soon. But sometimes it happens that the process of closing the upper section is disturbed, as a result of which anencephaly develops (absence of the brain in the fetus). If there is a violation in closing the lower part of the neural tube, a spinal hernia occurs . Unfortunately, both of these pathologies are not compatible with life, but they are very rare. Statistics confirm that such a disease affects one out of a thousand fetuses.
Sometimes there are situations when the neural tube in the fetus begins to develop incorrectly. What does this mean and is it worth worrying about this?
What are neural tube defects?
Defects in the development of the neural tube are a number of individual defects that can develop in the fetus. Fortunately, such deviations are quite rare.
It is important to understand that the pathology of the neural tube of the fetus is not a modern disease that is caused by the current living conditions of a person. According to the records of paleontologists who conducted the relevant studies, defects in the development of the spinal cord or brain (this confirms the abnormal development of the skull and ridge) were found in the remains of a person who lived 7000 years ago.
The first mentions in scientific medical works, on the basis of which, one might say, neurosurgery began to develop, were noted in the writings of Hippocrates. The Italian anatomist Morgagni Batista, perhaps one of the first to give an approximate description of neural tube defects. Of course, such pathologies were not subject to treatment at that time, because medicine was still at a very low level of development.
The reasons for the development of such problems
Unfortunately, a defective neural tube in the fetus is sometimes observed. What is this pathology and what is it caused by? Let's find out the reasons for the deviation from the norm.
So, on the 19-20th day after conception, a specific plate is formed in each fetus - the very first form of development of the human nervous system. On day 20-22, it should begin to close, as a result of which a neural tube forms in the fetus. The fact that everything is going according to plan confirms the absence of pathologies of the nervous system in the child who is born. If, on the 23rd day from conception, the neural plate does not close completely into the tube, the fetus will develop problems with the spine. This can lead to increased pressure of the cerebrospinal larkiness, which was observed in the first trimester of pregnancy.
One of the most common causes of such pathologies are viral infections, radiation received by future matter that is sick with cancer, as well as environmental factors. But more often, such deviations are found in pregnant women who also had a neural tube defect. High risk generates genetic inheritance.
External factors that may become the root cause of the defect
Yes, a genetic predisposition to such a defect significantly increases the risk of its occurrence. But today, doctors consider radiation to be a very frequent reason for the development of such a pathology (the expectant mother can receive radiation exposure not only during treatment, but simply while living in a territory contaminated with radionuclides). Pesticides, petroleum products and various kinds of synthetic fertilizers also become the reason that the neural tube in the fetus begins to develop incorrectly.
Today it is known to many that it is very dangerous for a person to consume genetically modified food. However, not everyone knows that if the expectant mother abuses such products, she thereby increases the risk of developing a fatal pathology in her baby. Even a hot bath, which a woman takes at the beginning of pregnancy, can provoke the occurrence of such a defect.
Doctors also attribute the unbalanced nutrition of the mother to the root causes of the development of a neural tube defect. A woman should be especially attentive to herself throughout her pregnancy. In the case when several of the above factors are found in the life of a future mother, it is worthwhile to be prepared for the fact that a pregnant woman will be included in the high-risk group for having a baby who will have a neural tube defect.
Is it true that in mothers with increased body weight, the risk of a neural tube defect increases?
Not so long ago, the results of studies became known, according to which the fact was confirmed that in women who are overweight during pregnancy, the risk of developing a neural tube defect in the fetus is two times higher than in women with low body weight. It is interesting that in future mothers in whom weight is insufficient, a similar trend was not observed.
Data was compiled from California women’s case histories of a fetal neural tube defect. Cases from 1989 to 1991 were taken into account. The results of such a study showed that women with overweight have a 2.1- fold increased risk of developing the disease. But, interestingly, these data are not affected in any way by the increase in folic acid intake, the lack of which is considered one of the reasons for the development of neural tube pathologies in the fetus.
What happens to the fetus when it has a similar disorder?
In order to understand how a fetal neural tube defect develops, it is necessary to understand at least in general terms what embryogenesis is.
So, the first week of pregnancy ends with the formation of germinal nodes. The second is the period of formation of the axial organs in the fetus, when the extra-embryonic parts are actively developing. As already mentioned, the third week is the time when the neural tube is formed from a special plate. The first three weeks are a period of primary neurulation. The secondary one falls for a period of 4-7 weeks from the moment of conception.
Already in this period of time, violations may occur, that is, spinal dysraphia. Pathology of the fetal neural tube, which becomes malformations of the lumbosacral spine of the future spine, can occur only during the period of secondary neurulation. Now it becomes clear that the abnormal development of the neural tube in the fetus begins from the first weeks of pregnancy, which is why the treatment of such diseases occurs in the form of preventing the development of serious defects. Thus, therapy should begin before pregnancy and continue during the first weeks of gestation.
Neural tube defects have their own symptoms.
As with any disease or impaired development, a defective neural tube formation in the fetus has its own symptoms.
The signs of spinal dysraphy are modern medicine that includes the following concepts:
- Latent non-closure of the spine: a similar defect is most often located in the lumbosacral region. It is quite dangerous, since it simply does not have clinical symptoms. This pathology is detected absolutely by accident, for example, after radiography of the spine. There are no special changes in the skin, occasionally there are age spots or wen. Such a hidden cleft is nothing more than a poorly closed arch of one of the vertebrae. Such a disease has a plethora of consequences, which include nighttime urinary incontinence, a significant violation of correct posture, weak leg muscles , pain in the lumbar region and even deformity of the feet. That is why it is so important to track whether the formation of the neural tube in the fetus is correct.
- Open-type cystic cleavage: they are also called true spinal hernias. They can occur in the form of a partial protrusion of the dura mater. The contents of such hernias is cerebrospinal fluid, that is, cerebrospinal fluid. This serious pathological process can spread to two or three vertebrae. Many people who were born with a similar defect lived a long and happy life perfectly. Surgical intervention in such cases, practitioners recommend using only when the growth of a true spinal hernia is observed.If a similar bone defect captures 3-5 vertebrae, then patients will already have muscle weakness and urinary incontinence. But, unfortunately, the most common disorder that captures 6-8 vertebrae. The skin on such a hernia is too thin, and a sheet of the pial sheath is visible through it. This is a very severe form of the defect, which often ends with a rupture of the hernial sac and leakage of cerebrospinal fluid.
- An extreme degree of deformity is considered to be non-closure of the spine and soft tissues, which is accompanied by an inferior formation of the spinal cord. Such a defect is practically incompatible with life.
An interesting fact is that the location of such hernias in 90% of cases falls on the lumbar region, and it is very rarely observed in the chest or cervical region. This state of affairs is explained by the fact that if the defect develops in the fetus, then pregnancy is most often pumped out by spontaneous abortion (miscarriage). Such embryos simply die, because their further formation is almost impossible.
How to diagnose a defect or pathology of the neural tube?
It is possible to see a neural tube defect in an ultrasound only in the third trimester of pregnancy. But before that there is still a lot of chances to detect a similar pathology.
To begin with, as already mentioned, it is necessary to perform a preliminary diagnosis, which is recommended even during the planning of a future pregnancy. You should also visit the obstetrician-gynecologist, urologist and genetics. If possible, it is worth passing tests that show the level of risk of having a baby with a defect in the development of the neural tube. In addition, it is recommended to read a lot of specialized literature. This will help to understand what the neural tube of the fetus is, and also will allow you to study all the recommendations of specialists that will be useful to you in the future.
After conception, you can not do without a monthly examination at the obstetrician. The second trimester of pregnancy must be accompanied by a regular blood test for the expectant mother. It is already possible to conduct an ultrasound examination of the fetus. Do not be shy to ask a specialist about the condition of the baby, especially if you are in a group of women with an increased risk of neural tube pathology.
In the third trimester, it is already possible by ultrasound to see the congenital malformation of the fetus, which arose as a result of the incorrect formation of the neural tube. A photo of the fetus in the womb can also be shown to another specialist to confirm the diagnosis.
If at one of the stages a defect in the formation of the neural tube was confirmed, this is a serious reason for raising the issue of abortion. However, first you need to find out the degree of violation, because with some of its forms a completely normal life is possible. To date, the abnormal formation of the neural tube, which is expressed in the development of malformation in the fetus, can be corrected with surgical intervention. An additional diagnosis is required after you have been given a similar diagnosis, because abortion is the very last exit.
Treatment of neural tube developmental defects
Therapy of problems that arose because the neural tube formation was impaired can be started immediately after the birth of the baby. As soon as the doctors eliminate all threats to the baby’s life, that is, they restore their independent breathing and check the body temperature of the newborn, the surface of the hernia should immediately be treated with disinfectant solutions and covered with sterile wipes. After a conversation with parents, if they agree to surgery, the born is transferred to the neurosurgical department, where they carry out all the necessary studies, because without them the operation will not be successful.
If there is a threat of rupture of a hernia, excision is performed immediately. Otherwise, you can wait a bit until the baby gets stronger. This decision is justified by the fact that gaps are “open gates” for any type of infection. Often after removal of hernias, purulent-inflammatory processes are observed. According to statistics, approximately 78% of young patients had similar complications. It should be noted that a day after the operation, the state of health in the kids is normal. However, 5% of children are still at risk.
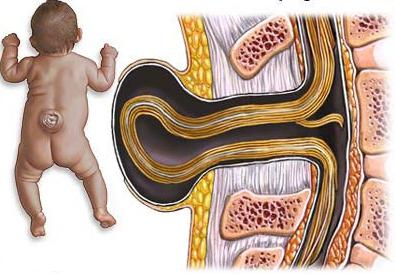
Also important is the fact that if you perform a similar operation in a newborn, you can completely restore the integrity of the meninges. That is, the child after the operation will develop absolutely normal, and he will wait for a normal full life. You must understand that preliminary studies before surgery are carried out very quickly. Only the most necessary tests are done to save the child and not allow him to remain disabled for life. It is important to take the postoperative period seriously. In order for rehabilitation to proceed easily and without complications, all the recommendations of the attending physician must be strictly observed.