In this article, we will consider the symptoms and treatment of atrial fibrillation. What is this pathology?
Atrial fibrillation, which includes pathologies such as atrial fibrillation and atrial fibrillation, is one of the heart rhythm disturbances that is characterized by irregular, rapid atrial contraction at a rate of about 350-700 per minute. If the attacks of atrial fibrillation last more than 48 hours, then there is a risk of thrombosis and a severe stroke develops. The chronic form of this disease is characterized by the rapid development of persistent cardiovascular failure.
Quite often in cardiological practice, patients with atrial fibrillation are found. In the basic structure of the incidence of various forms of arrhythmia, atrial fibrillation accounts for approximately 30% of cases. Its prevalence increases with age. Therefore, in people under 60 years of age, this type of arrhythmia is diagnosed in 1%, and after 60 years, this pathology is observed in 6%.
Treatment for atrial fibrillation is presented below.
Forms of the disease
Atrial fibrillation is classified using electrophysiological mechanisms, an etiological factor, taking into account the features of clinical treatment.
By the duration of the development of pathological processes, these forms of atrial fibrillation are distinguished:
- paroxysmal form (transient) - in most cases, the attack lasts no more than a day, but can last up to a week;
- persistent form - signs of atrial fibrillation last more than a week;
- chronic form - the main feature is the inadequacy of electric cardioversion.
Paroxysmal and persistent forms of atrial fibrillation include a recurrent development, that is, such attacks of atrial fibrillation occur repeatedly.
In connection with the types of atrial rhythm disturbances, atrial fibrillation is divided into two types:
- Atrial fibrillation (flickering). There is no ordered atrial contraction because uncoordinated contractions of individual muscle fibers occur. A lot of electrical impulse accumulates in atrioventricular joints. Some of them extend to the ventricular myocardium, thereby causing contractions. Given the frequency of ventricular contractions, atrial fibrillation is divided into tachysystolic (more than 80 contractions per minute), normosystolic (50 to 90 contractions per minute), bradyssystolic (less than 50 contractions per minute).
- Atrial flutter. With this type of contraction, they reach 200-400 per minute, while maintaining their coordinated correct rhythm. With this type of pathology, there is practically no diastolic pause. They do not relax, as they are in a constant state of systole. It is difficult to fill them with blood, as a result of which insufficient blood flows into the ventricles. If every second or third impulse enters the ventricles through the atrioventricular junction, then this can provide the correct rhythm of contractions and a similar form of the disease is called correct atrial flutter. In cases when there are chaotic contractions of the ventricles, which are caused by pathologies of the atrioventricular conduction, they are called atrial flutter.
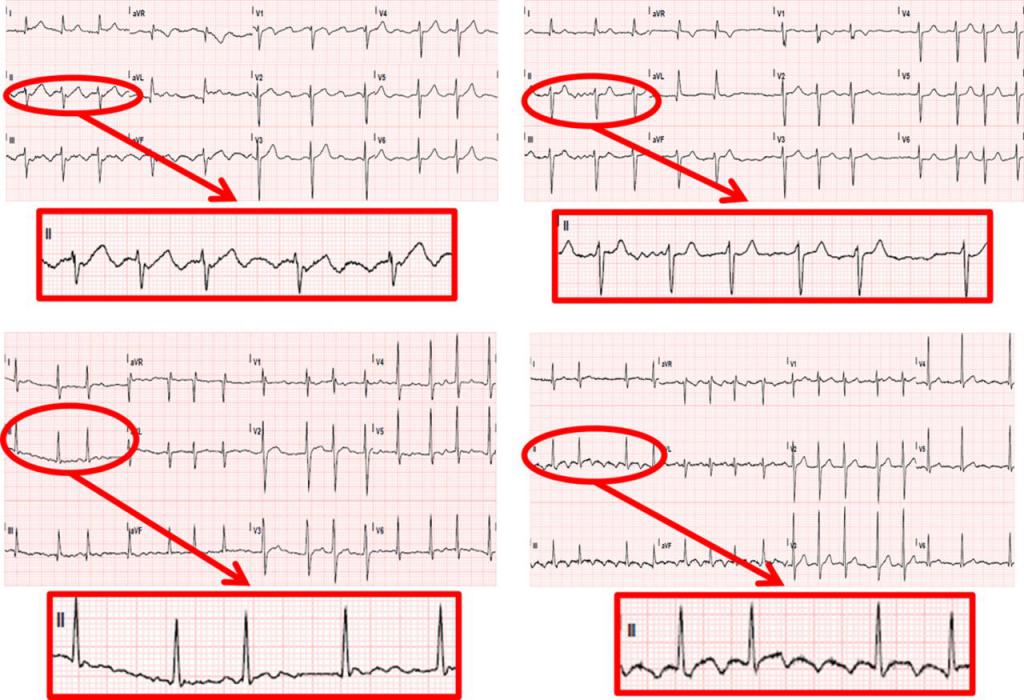
During attacks of atrial fibrillation, the atria contract unproductively. In this case, the ventricles are not completely filled with blood, and at the time of contractions, there is sometimes no emission of blood into the aorta.
Treatment of persistent atrial fibrillation is a very topical issue today.
Causes of atrial fibrillation
The causes of this disease can be both pathologies of the heart, and a number of other various diseases. Atrial fibrillation often appears due to severe heart failure, arterial hypertension, myocardial infarction, cardiosclerosis, myocarditis, cardiomyopathies, rheumatic heart disease.
The causes and treatment of atrial fibrillation are interrelated.
Other causes of atrial fibrillation:
- alcoholic cardiopathy;
- hypokalemia;
- frequent obstructive pulmonary disease;
- pulmonary embolism (pulmonary embolism);
- overdose of cardiac glycosides;
- thyrotoxicosis (thyrotoxic heart).
If it is not possible to identify the cause of atrial fibrillation, then a diagnosis of the idiopathic form of the disease is established.
How to recognize the first symptoms of atrial fibrillation?
Symptomatology
The symptomatic picture of atrial fibrillation is established depending on the conditions of the myocardium and valvular apparatus of the heart, the type of disease (paroxysmal, chronic, bradysystolic, tachysystolic), and also take into account the patient’s psychoemotional state.
Tachysystolic atrial fibrillation is not easily tolerated by patients. Signs of this pathology are:
- pains and interruptions in the heart;
- heart palpitations;
- shortness of breath, which intensifies during physical exertion.
Initially, atrial fibrillation is characterized by paroxysmal manifestations. Further development of pathology with changes in the duration and frequency of seizures in each patient occurs in different ways. In some patients, seizures appear very rarely, and there is no tendency to their progress. In others, on the contrary, after two or three episodes, the disease passes into a chronic or persistent form. Alternative treatment for atrial fibrillation can be very effective. About it further.
Patients experience various attacks and sensations. Some patients do not feel any unpleasant symptoms during attacks, and they often learn about the presence of a disease only after a medical examination. But still, most often the manifestations of atrial fibrillation are pronounced. These signs include:
- muscle tremors;
- excessive sweating;
- sensation of chaotic palpitations;
- severe general weakness;
- polyuria;
- fear of death.
In especially severe cases, fainting conditions, severe dizziness occur, an attack of Morgagni-Adams-Stokes occurs.
Timely treatment and first aid for the symptoms of atrial fibrillation are important here.
All signs end immediately after the restoration of heart rhythms. In a chronic form of pathology, patients after some time cease to notice symptoms.
During auscultation of the heart with atrial fibrillation, chaotic tones of various volumes are listened. Pulse waves are characterized by different amplitudes, the pulse is arrhythmic. Pulse deficiency is also another sign of atrial fibrillation. With such a deficiency of the pulse, the number of pulse waves becomes less than the number of heart contractions. The development of such a pathology may be due to the fact that blood is not ejected into the aorta with every contraction of the ventricle.
With atrial flutter, patients often have complaints of discomfort in the heart, a feeling of palpitations, pulsation of the cervical veins, shortness of breath.
Before talking about the methods of treating atrial fibrillation, we will find out what kind of diagnosis is needed.
Diagnostics
Atrial fibrillation is usually diagnosed easily, the diagnosis is made already during the physical examination of the patient. By palpation of the peripheral artery, irregular rhythms of pulsation of its walls are detected, but at the same time, the filling and tension of each pulse wave is different. During auscultation of the heart, irregular heart sounds and significant volume fluctuations are heard. Such a change in the volume of the first tone, which follows a diastolic pause, can be explained by different sizes of diastolic fillings of the ventricles with blood.
Before starting treatment for atrial fibrillation in the elderly, an electrocardiogram is recorded. With this ailment, the following pathologies are detected:
- absence of P waves or observation of atrial waves in their place;
- random distribution of QRS ventricular complex.
If necessary, daily ECG monitoring is performed, which will reveal the exact form of atrial fibrillation, duration of seizures, and their relationship with physical activity. In order to choose antiarrhythmic drugs and detect symptoms of myocardial ischemia, you need to perform tests with physical activity (bicycle ergometry, treadmill test).
Echocardiography (Echocardiography) can also make it possible to identify the dimensions of the cardiac cavities, detect the presence of intracardiac blood clots, symptoms of presumptive lesions of the valvular apparatus and pericardium, and evaluate contractile functions of the left ventricle. The results of echocardiography can help in choosing the right drugs for antithrombotic and antiarrhythmic therapy.
In order to examine in detail the structure of the heart, one can perform magnetic resonance or multispiral tomography of the heart.
The method of transesophageal electrophysiological examination will help to identify the mechanism of the formation of atrial fibrillation. This examination is carried out for all patients with atrial fibrillation, who are planning to implant an artificial pacemaker (pacemaker) or catheter ablation.
Atrial fibrillation treatment
Therapy involves maintaining and restoring the correct heart rhythm, preventing the occurrence of repeated attacks, eliminating the development of thromboembolic complications and the formation of blood clots.
To eliminate an attack of atrial fibrillation, an antiarrhythmic drug is administered intravenously to a patient under the control of blood pressure and ECG. Sometimes, cardiac glycosides and calcium channel blockers can be used to improve the patient’s well-being (elimination of shortness of breath, palpitations, decrease in weakness) due to a decrease in heart rate.
If conservative treatment of atrial fibrillation is ineffective, then the therapy is carried out by the method of applying electric pulsed discharges to the heart region (electric cardioversion). This method will allow you to adjust the heart rate in 80% of cases.
If the pathology lasts more than 48 hours, then there is a risk of developing thromboembolic disorders and thrombosis. For the prevention of such disorders, anticoagulant tablets are prescribed in the treatment of atrial fibrillation.
Once the heart rate has been settled, it is necessary to take antiarrhythmic drugs for a long time to prevent recurrence of the symptoms of the disease.
If chronic forms of atrial fibrillation are detected, treatment should consist of regular use of anticoagulants, cardiac glycosides, calcium antagonists and adrenergic blockers. Active treatment of the initial disease, which caused atrial fibrillation, is carried out.
In order to radically eliminate atrial fibrillation, it is necessary to perform radio-frequency isolation of the pulmonary veins. During such a minimally invasive procedure, the focus of ectopic excitation, which is located at the mouth of the pulmonary veins, is isolated. Experts identify 60% of the effectiveness of radio-frequency isolation of the pulmonary veins.
For the treatment of the chronic form of atrial fibrillation, radiofrequency ablation of the heart (RFA) is used. This procedure involves cauterization of the atrioventricular node using a special electrode, which completely leads to atrioventricular block, and then a permanent pacemaker is set.
Medication for atrial fibrillation should be selected by a doctor.
Strategy "tablet in your pocket"
This name arose as a result of tactics to combat attacks of atrial fibrillation. Doctors prescribe this method for those patients who do not often suffer from atrial fibrillation. In this case, there is no urgent need to take medications constantly in order to maintain heart rate. But you should always keep the drug with you to eliminate the attack. In such cases, usually take "Propaphenone" and "Propanorm." These drugs are antiarrhythmic and successfully eliminate seizures in most patients in 2-4 hours.
Preparations for the treatment of atrial fibrillation are now very diverse.
The most common method of combating an ailment is medication. Effective in this situation, Esmolol and Metoprolol. A particularly good result can be obtained in cases where atrial fibrillation caused an excessive activity of the sympathetic nervous system. Typically, such a pathology is associated with pathologies in the endocrine system. Beta blockers are used for patients suffering from ischemia.
Also, many patients are known drugs "Verapamil" and "Diltiazem." The use of calcium blockers makes sense to patients without symptoms of heart failure, for whom beta-blockers are contraindicated. With cardiac asthma, reception is prohibited.
Electric cardioversion
Another way to restore your normal heart rhythm is with electric cardioversion. This method is used during attacks of atrial fibrillation, when the condition deteriorates sharply, pulmonary edema, cerebral ischemia, shock begin.
In such situations, you need to act quickly. The patient is given intravenous anesthesia and the heart is launched in a normal rhythm using a high-voltage defibrillator. At the same time, strong current discharges pass through the heart, thereby causing its muscle fibers to contract at the same time. After such an impact, the ability to regulate the rhythm will return to the sinus node.
We continue to consider modern aspects of the treatment of atrial fibrillation.
Catheter ablation
This method is considered less traumatic, since it does not require a large incision. The operation is performed under local anesthesia. The doctor introduces the necessary electrodes into the heart through the subclavian or femoral vein. The surgeon at this time control everything that happens with the help of an x-ray.
First, the doctor conducts an examination. With the help of special sensors, he reveals where the zones that cause atrial fibrillation are located. An intracardiac cardiogram will show the reaction of the heart to special tests performed by a specialist.
At the next stage of the operation, doctors "neutralize" the atrial areas in which flicker occurs. This is done using radio frequency energy and electrodes. Chemicals or a laser are also used for these purposes. It can destroy small groups of cells that produce an impulse that makes the atria flutter.
What is important in the treatment of chronic atrial fibrillation?
Diet
In complex treatment, an important role is played by proper nutrition. The diet should include mainly plant and non-fat protein foods. You need to eat food as often as possible in small portions. Dinner can be no later than 2-3 hours before going to bed. This approach will eliminate excessive stimulation of the vagus nerve receptors, which affect the function of the sinus node.
Patients with atrial fibrillation must completely refrain from drinking alcohol, tea and coffee, because they can cause seizures.
A diet for atrial fibrillation should consist of a large number of foods that are rich in magnesium and potassium. These products include:
- nuts (almonds, cashews, peanuts);
- Brown rice;
- soya beans;
- wheat germ;
- beans;
- wheat bran;
- spinach;
- baked potato;
- cereals;
- bananas
- Tomatoes
- oranges.
To preserve the maximum amount of vitamins and minerals, you should steam them or bake. It will be equally useful to include fruit, berry and vegetable smoothies in the menu.
Consider methods of alternative treatment for atrial fibrillation.
ethnoscience
In order to restore the rhythm and keep it normal, medicinal herbs are used.
Hawthorn berries are very effective. They allow you to strengthen blood vessels, improve the functioning of the heart and arteries. With the help of active substances, which are found in abundance in hawthorn, blood pressure is stabilized. The excitability of the nervous system and heart is reduced. Hawthorn restores the necessary balance of potassium and sodium in the body. Namely, they are responsible for the normal conductivity of the pulses. Thus, the manifestations of arrhythmia are significantly reduced.
Treatment of atrial fibrillation with folk remedies has been used since ancient times.
Motherwort - normalizes blood pressure, prevents the formation of blood clots, soothes the nervous system. The work of the vessels that nourish the heart improves, its rhythm stabilizes. , 15 . , . 30-50 . 3-4 .
, . . . 2 . 3-4 .
Possible complications and consequences
, , . , , , , .
, . 65% , , . , , . , :
, . . , .
One of the most severe signs of heart failure in atrial fibrillation is arrhythmogenic shock, which is caused by decreased cardiac output.
Atrial fibrillation can go into ventricular fibrillation, which after will lead to death.
In many cases, atrial fibrillation is complicated by the development of constant heart failure, which tends to progress at different speeds and can lead to the formation of dilated arrhythmic cardiomyopathy.
Consider the reviews on the treatment of atrial fibrillation.
Reviews
Reviews about the treatment of this disease are in large numbers. As a rule, the disease significantly reduces the quality of life. But if you take timely measures, take it on an ongoing basis, follow the recommendations of doctors, then you can significantly improve your well-being.
Forecast
Atrial fibrillation can be predicted by identifying the cause that caused the development of heart rhythm disturbances and the appearance of complications. Heart failure develops as a result of atrial fibrillation, which occurs against a background of heart disease and other severe myocardial pathologies (large-focal myocardial infarction, dilated cardiomyopathy, general or diffuse cardiosclerosis).
The presence of atrial fibrillation in humans increases the risk of death in cardiac pathologies by more than 1.5 times.
The same unfavorable prognosis can be obtained with atrial fibrillation, which was complicated by thromboembolism.
Patients with a satisfactory condition of the myocardium and ventricles have a favorable prognosis. However, if bouts of atrial fibrillation occur very often, then the quality of life of patients is greatly impaired.
Atrial fibrillation in idiopathic form, as a rule, does not cause deterioration; patients feel completely healthy and lead a normal lifestyle.
Prevention
For the prevention of atrial fibrillation, it is necessary to detect and actively treat diseases of the respiratory systems and cardiovascular in advance.
The following prevention of atrial fibrillation prevents the occurrence of new episodes of cardiac arrhythmias. This prevention should include:
- refusal to drink alcohol;
- long-term drug therapy with antiarrhythmic drugs;
- limitation of physical and mental stress;
- cardiac surgery if indicated.
We examined the symptoms and treatment of atrial fibrillation.