"Stoma" in Greek means "mouth." That is, all medical terms in which this Greek word is present are associated with the human oral cavity. In particular, stomatitis is a group of diseases characterized by inflammation and ulceration of the mucous membrane in the mouth. There are various types of stomatitis, depending on the reasons that caused it. Most species have similar symptoms, so many people who have encountered this disease and are self-medicating do not even suspect that their actions do not have any therapeutic effect, but only drive the disease into the body. In this article we will try to figure out how to find out what type of stomatitis takes place, how to get rid of it and what preventive measures exist so that this disease never appears at all.
How does stomatitis develop?
The human oral cavity is lined with a mucous membrane, so named because it is constantly covered with mucus secreted by epithelial cells. In a healthy state, it is pink in color, without swelling, infiltrates and ulcers. For various reasons, foci of inflammation may appear on the mucosa. This is stomatitis. The types and treatment of the disease are already well known. But the mechanism of development of stomatitis is still being studied. The main version of scientists is that the inflammatory processes in the mouth in humans are the response of the immune system to unfamiliar particles (cells, molecules). When they are detected, lymphocytes begin to be produced intensely. They pounce on unidentified substances to deal with them. The result of the active actions of the body's defenders are ulcers of the mucosa, that is, stomatitis. It can be either an independent disease, or a sign of another ailment. That is why it is so important to know what types of stomatitis are, what causes them, what are their characteristic features and consequences.

Causes
Stomatitis can occur for dozens of different reasons, each of which leads to the penetration of foreign substances into the body. In medicine, they are called irritants. They can become:
- smoking;
- pathogenic microorganisms (viruses, fungi, bacteria);
- medicines;
- excess or lack of vitamins;
- hormonal disruptions in the body (age-related, during pregnancy, from taking birth control pills).
- sodium lauryl sulfate (found in dentifrices and oral care products, helps to form a rich foam).
Some types of stomatitis are caused by injuries of the oral cavity of a different nature:
- mechanical (cuts, bites, bump);
- thermal (most often from too hot food);
- chemical (ingestion of toxic substances);
- rubbing dentures.
There are types of stomatitis in which inflammatory foci on the gums, mucous membrane, tongue, and larynx act as one of the symptoms of a disease of internal organs - the thyroid gland, gastrointestinal tract, blood, heart and blood vessels, nervous system, and connective tissues. Stomatitis can occur in HIV-infected people who have cancerous tumors on the face, nose, throat, mouth, neck, and patients whose condition is accompanied by dehydration, with anemia, and poor nutrition.
And, finally, a frequent cause of stomatitis is improper hygiene of the teeth and oral cavity, and its deficiency and overabundance are harmful when people brush their teeth many times a day or rinse their mouth with drugs that reduce saliva.
Types of stomatitis in children
Based on the above reasons, we can say that stomatitis in adults and in babies can have the same etiology (for example, viral, microbial, medication), and different. In particular, children do not have inflammation of the mucous membranes in the mouth from smoking or from improperly made dentures. But due to the fact that the kids pull everything in their mouths - pens, toys, various objects, inflammatory processes in the oral cavity occur most often. The following types of stomatitis in children are diagnosed:
- traumatic;
- infectious;
- allergic;
- aphthous;
- angular;
- vesicular;
- candidiasis;
- catarrhal;
- pellagrotic (with a deficiency of vitamin PP);
- mournful (with vitamin C deficiency);
- herpetic.
Classification of types of stomatitis in adults
In people over 18 years of age, inflammation in the mouth mainly occurs due to insufficient immunity. For example, nearly half of humanity smokes, and smokers' stomatitis develops in only 1 out of 100. Another common reason for the development of the disease in adults is their work activity associated with harmful production.
According to medical statistics, people over the age of 18 are most often diagnosed with the following types of stomatitis:
- traumatic;
- aphthous;
- infectious;
- Vincent (ulcerative necrotic, trench);
- gangrenous;
- from intoxication with salts of heavy metals (bismuth, lead, mercury);
- scurvy (similar to mournful);
- diffuse erythematous;
- radiation;
- nicotine;
- medication;
- professional.
But such types of stomatitis as candidal, herpetic, angular, in adults are rare.
Candidiasis stomatitis
From the name you can guess what causes its fungus Candida. Popularly, this disease is better known as thrush, because its main symptom is a white coating on the mucous membranes in the mouth, on the tongue, sometimes on the gums and larynx.
Candidiasis, and with it infectious, are the most common types of stomatitis in children. The photo demonstrates what the oral cavity of infants looks like when the mucous membranes are affected by Candida. In addition to white plaque, the symptoms of candidal stomatitis are:
- hyperemia of the mucous membranes;
- soreness when chewing and even when talking;
- in children - moodiness, refusal to eat, anxiety;
- in adults - a change in taste, bleeding of the affected areas when removing plaque;
- dryness and burning in the mouth.
Kids can become infected with Candida from sick children through unwashed toys, from a sick mother when feeding. Very often candidal stomatitis is observed in premature infants. Adults acquire this disease as concomitant with diabetes mellitus, problems with the digestive tract, dysbiosis, HIV infection, Sjogren's syndrome, during pregnancy, taking antibiotics, and lack of hygiene. In general, Candida fungus is constantly present in the mouth, but begins to manifest itself pathologically with a decrease in immunity.
Treatment of candidal stomatitis is based on the strictest oral hygiene, and for infants it is additionally based on the thorough processing of the nipples, toys, and mother’s nipples. In addition to hygiene, treatment of the disease in children includes treatment of the oral cavity with antiseptics and antimycotic drugs, and in adults, taking antibiotics and rinsing the mouth with antiseptic solutions.
Infectious (viral) types of stomatitis in children, photos, treatment
This group includes not only thrush, but any inflammation in the oral cavity caused by the penetration of pathogenic microorganisms into the mucous membranes. In particular, viral stomatitis brings us viruses, and not necessarily parasitic in the mouth. They can affect any other organ, and viral stomatitis manifests itself as a complication of the underlying disease. The most common in this group is herpetic stomatitis. It causes herpes virus. In 100% of cases, children receive it from adults (when kissing, licking a nipple, a spoon before putting it in a child’s mouth and so on). On Earth, 9 out of 10 people are carriers of herpes, so it’s easy to imagine how often children get infected from adults.
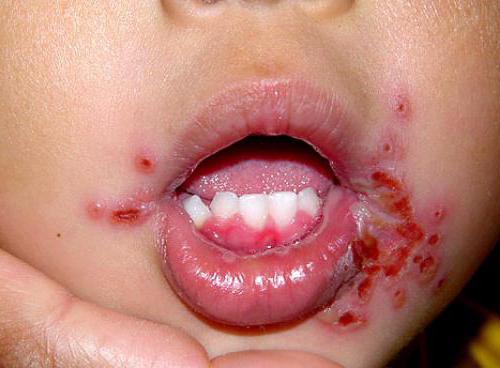
The visual symptoms of herpes infection can be not only in the mouth, but also on the face. External signs of the disease, in addition to herpetic, also have angular (formation of seizure) and vesicular types of stomatitis in children. The photo shows what rashes form in the nasal region when infected with herpes. Other symptoms of the disease:
- deterioration in well-being;
- temperature;
- hyperemia and soreness of the mucous membranes in the mouth;
- the appearance on the mucous membranes, as well as on the gums, less often on the tongue of fluid-filled bubbles that burst with the formation of small erosions.
An important feature of herpes is that once it has penetrated a person’s body, he will not be able to get out of it, but, let’s say there, he lives quietly and does not manifest himself. In these cases, they talk about the chronic course of the disease, which makes itself felt every time with stress, vitamin deficiency, infections, injuries, hypothermia. Treatment of the acute form of herpetic stomatitis is carried out according to the symptoms and includes the use of anti-inflammatory and painkillers, treatment of the oral cavity with antiseptics, heavy drinking, and elimination of toxins. In the chronic form of the disease, the main treatment method is prevention. It consists in hardening the body, eating vitamin-containing foods, the correct daily routine.
The causes of angular stomatitis are allergic reactions to certain foods and antibiotics that cause imbalance in the microflora in the mouth. Treatment is carried out locally (treats of seizures with antiseptics and keratoplastics). If an allergic cause of the appearance of a jam is established, it is important to eliminate unacceptable foods from the diet, and then restore the microflora in the oral cavity.
Vesicular stomatitis
There are non-hazardous to others and quite contagious types of stomatitis in children. Treatment in these cases should be accompanied by isolation of the sick child. Allergic stomatitis can be attributed to non-contagious, and vesicular to the most pathogenic. This disease is caused by Picornaviridae viruses, which are able to be well preserved in the environment for a long time. Children suffer from vesicular stomatitis more often, although it occurs in adults who do not follow hygiene. Characteristic symptoms:
- a rash on the arms, legs, in the mouth, sometimes on the genitals and buttocks;
- temperature;
- nausea, sometimes with vomiting;
- irritability, fatigue;
- loss of appetite;
- itching rashes (characteristic of the disease in adults);
- the appearance of blisters and painful ulcers.
Treatment is carried out by the following methods:
- taking painkillers and antiviral drugs;
- antiseptic treatment of rashes in the mouth ;
- treatment of external rashes with brilliant green;
- vitamin therapy.
There are other types of stomatitis caused by viruses. The photo shows what influenza stomatitis looks like, which by the nature of the course can manifest itself as catarrhal, aphthous, ulcerative or ulcerative necrotic stomatitis. Foci of inflammation with this complication of influenza appear in the palate, gums, inner surfaces of the cheeks, less often in the tongue, not only at the stage of the acute form of the disease, but also during the recovery period and even after it. Methods of treating influenza stomatitis depend on how it appeared. So, catarrhal requires local therapy, and aphthous along with the treatment of foci of inflammation and general therapy. With chickenpox in children, bubble rashes can appear not only on the skin, but also on the mucous membranes of the oral cavity.
Aphthous stomatitis
The name is also associated with the Greek language, in which oral ulcers sound approximately like "aphthae". The reasons for their appearance may be:
- injuries of the oral mucosa;
- diseases of some internal organs, such as the gastrointestinal tract;
- plaque;
- caries;
- gum disease;
- vitamin deficiency;
- heredity.
Aphthous stomatitis exists of two types - acute, which occurs when an infection penetrates the body, and chronic, which manifests itself when a person experiences stress, fatigue, and immunity decreases. However, during periods of remission, this is perhaps the only type of stomatitis that does not hurt. In other cases, inflammation of the mucosa always causes pain of varying intensity.
The main symptom of aphthous stomatitis is a slight reddish bloating on the mucous membrane, painful when the tongue is pressed on it. After a day, less often after two, an ulcer appears in this place, whitish in the center. Around her, the mucous membrane is inflamed and very painful. Without taking measures, aphthae can increase in size and cause a person quite tangible suffering.
The treatment of this disease is carried out in a complex:
- the use of external antiseptic and anti-inflammatory drugs (rinses, applications);
- a diet that excludes contact with ulcers of acute, salty, sour;
- according to indications, taking antipyretic medicines, painkillers, antiallergic drugs;
- strengthening immunity.
Traditional medicine recommends rinsing with decoctions of calendula, chamomile, a solution of baking soda and lubricating aphthae with sea buckthorn or rosehip oil.
Traumatic stomatitis
Of course, it is important to know how to determine the type of stomatitis. But in the case of traumatic parents, it is even more important to find out the reason why he developed. In babies, injuries in the mouth most often occur when sucking fingers with uncircumcised (and in addition dirty) nails, objects with sharp edges, bruises on the lips or cheeks. There are cases when in very small hypertrophic foci in the mouth appear from too long sucking pacifiers of an uncomfortable shape or poor quality. In older children, traumatic stomatitis can occur from malocclusion, when the teeth, when chewing or talking, cling to the inner surface of the cheeks, from too hot food, from tasting inedible objects and substances on the tooth.
The pathogenesis of traumatic stomatitis is as follows: a slight hyperemia appears in the oral cavity (swelling, redness), then quite painful erosion opens in this place. Its center may be red or have a whitish coating, the edges are usually surrounded by inflamed infiltrate. Without treatment, erosion becomes open gates for the thousands of microorganisms always present in the human mouth. As a result, purulent ulcers appear, and in some cases tissue necrosis begins. In children, symptoms of the onset of traumatic stomatitis are a refusal to eat, a tearful mood, in the future there is a high temperature, and in severe cases signs of intoxication.
People over 18 years old rarely suck their fingers and pull inedible objects into their mouths, but they can also injure mucous membranes, for example, when performing medical manipulations with a dentist.
In addition, ulcers with inflamed infiltrate of nearby tissues cause other types of stomatitis in adults. The photo shows what an ulcer looks like with radiation stomatitis.
In order not to make a mistake with the diagnosis, additional studies are conducted that exclude diseases such as syphilis, tuberculosis, Vincent’s stomatitis, and the presence of trophic ulcers.
Treatment of traumatic stomatitis begins with the elimination of the traumatic factor. Further therapy is performed in the following sequence:
1. Antiseptic treatment (rinsing with decoctions of herbs, "Chlorhexidine", a solution of baking soda).
2. Application of one of the preparations to erosion: “Iodinol”, “Fukortsin”, “Ingalipt”.
3. Applications of drugs to inflamed areas to relieve pain.
4. If necessary, tooth sanitation and taking medications that promote epithelization.
Occupational stomatitis
Whatever type of stomatitis we consider, it can be diagnosed in people of any age. This also applies to thrush - a disease of infants that the elderly often suffer from, and to infectious stomatitis, and to allergic and aphthous, even leukemic (observed with leukemia) and medication. But there are types of stomatitis in adults that are associated with the characteristics of work. If they happen to children, then in rare cases. We are talking about inflammation of the mucous membranes in the mouth during poisoning with harmful substances. This happens if a person works where it is very dusty, where you have to deal with salts of heavy metals or with radioactive substances. So, with mercury stomatitis on the mucous membranes (usually on the gums), grayish pigmentation appears, and after necrosis not only of tissues on the gums, but also on the tongue and mucous membrane of the cheeks. With lead stomatitis, there is severe hyperemia of the mucous membranes, gray spots appear on the gums. With bismuth stomatitis, gum pigmentation is also observed, only in this case it has a characteristic blue-black border. In addition to all the symptoms listed above, patients have signs of intoxication - weakness, headache, and disorders of the digestive tract. Nicotinic stomatitis can also be attributed to adult disease. Treatment consists in removing harmful substances from the body. In parallel, patients are anesthetized, rinsed and treated with antiseptics of mucous membranes, and ulcers are prescribed drugs to help restore epithelial tissue.