A change in the color of the skin or mucous membranes is one of the body's reactions to pathology. Often, it indicates changes in the liver or the breakdown of blood cells. Such disorders are manifested by jaundice. This is one of the most common clinical syndromes. Jaundice can develop at any age and indicate a variety of pathologies. In some cases, it is considered normal. However, with diseases, this syndrome is an indicator that serious disorders have already occurred in the body. Therefore, it is important to identify the cause of the skin discoloration as soon as possible and eliminate it.
The concept of jaundice syndrome
Jaundice does not belong to a variety of diseases, as many believe. This is just one of the signs of pathology. Moreover, it can develop with many diseases. Among them - infections, cancer, parasitic infestations, genetic disorders, blood loss. To understand what is the cause of this phenomenon, a pathogenetic classification of jaundice has been developed. It is based on the mechanism of development of this syndrome. Having found out how the disorder formed, it is easier for clinicians to find the initial cause of the pathology.
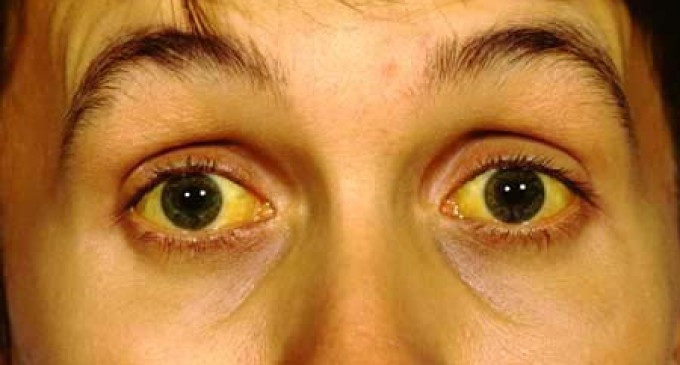
Jaundice is accompanied not only by external manifestations, but also by changes in the biochemical analysis of blood. Such a disorder is called hyperbilirubinemia. With a change in the color of the mucous membranes and skin, the level of this indicator rises by several tens of times. Bilirubin levels are also the basis for the classification of jaundice. This is another criterion that helps doctors conduct differential diagnostics for this syndrome. Jaundice is also classified by severity and etiology. Only after finding out the cause of the discoloration of the skin, the doctor will be able to prescribe an adequate treatment.
Classification of neonatal jaundice by etiology
Most parents note that their baby's skin at birth had a slightly yellowish tint. After a few days, this passes and the child turns pink. This is a completely normal reaction of the body to environmental changes. This condition is called physiological jaundice in newborns. It develops as a result of the immaturity of the liver and the breakdown of fetal hemoglobin, which is converted into bilirubin. Neonatal jaundice in the absence of disease passes on the 10-14th day. However, if skin color changes are not observed, it is worth considering the presence of pathology and contact a pediatrician.
Unfortunately, pathological jaundice syndrome is often observed in children in the first months of life. Etiological factors may be as follows:
- Prematurity.
- Diseases of the endocrine system in the mother or newborn.
- Heredity.
- Fetal hypoxia during pregnancy or childbirth.
- Hemolytic disease associated with Rh conflict in the mother and child.
- The use of certain drugs that adversely affect the baby's body.
Depending on the provoking factor, medication, hereditary, hypoxic and other types of neonatal jaundice are isolated. Regardless of the cause of the development of this syndrome, pathological hyperbilirubinemia requires treatment. Otherwise, an excess of bile pigment can lead to serious brain disorders. To avoid this, special conditions must be observed in the hospital.
Jaundice of the newborn: classification by localization
It is possible to track the degree of damage not only by laboratory indicators, but also by clinical data. This is also useful for evaluating the effectiveness of ongoing therapy. For this purpose, in pediatrics, a classification of jaundices according to a 5-point system (according to Kramer) is used. It is based on the localization of the pathological syndrome. The doctor examines the baby and conducts on his skin, revealing exactly where there is jaundice. If it is localized only on the mucous membrane of the eyes and face, then this is regarded as 1 point according to Kramer. This means the first degree of severity. With the spread of jaundice on the body, 2 points are set. The next degree is the change in skin color to the elbows and knees of the baby. With 4 points, jaundice spreads to the limbs of the child. An extreme degree is the change in the color of the skin of the palms and feet.
The more points, the higher the level of bilirubin in the blood. Thanks to Cramer's classification, it becomes easier for a doctor to evaluate the effectiveness of therapeutic measures in dynamics. This helps to avoid daily blood collection from the baby.
Types of jaundice in adults
For the adult population there is a special classification of jaundice. It is based on the pathogenesis of this syndrome. The following types of jaundice are distinguished by the development mechanism:
- Suprahepatic. Its pathogenesis is similar to the transitional syndrome of the newborn. The development of suprahepatic jaundice is associated with accelerated decay of red blood cells. Therefore, in another way it is called hemolytic.
- Hepatic (parenchymal) jaundice. It is associated with damage to hepatocytes in acute and chronic inflammatory processes. In this case, the liver can not cope with the transport and capture of bilirubin formed in the body.
- Obstructive jaundice. It occurs due to various pathologies. Among them - calculous cholecystitis, pancreatic cancer, parasites. In another way it is called subhepatic and obstructive. It develops as a result of stagnation of bile.
It is possible to determine the type of pathological syndrome using a biochemical blood test. By the level of free and conjugated (direct) bilirubin. Such a classification of jaundice helps the doctor to navigate and narrow down the range of diseases associated with this syndrome. In addition to biochemical analysis of blood, perform OAC, a study of feces and urine, as well as an ultrasound of the hepato-duodenal zone.
The concept of suprahepatic jaundice
Suprahepatic jaundice is the result of the fact that the liver does not have time to cope with its work and metabolize all bilirubin formed in large quantities. The reason for its increased production is erythrocyte hemolysis, that is, their destruction. In most cases, this happens due to congenital diseases of the hematopoietic system. In particular, with hemolytic anemia. This pathology is accompanied by the formation of antibodies to blood cells, as a result of which red blood cells are destroyed. Other causes of hemolytic jaundice can be: massive injuries, poisoning with various poisons. All this leads to the destruction of blood cells.
Hemolytic jaundice can be suspected by a lemon shade of the skin. Most often, these patients are pale due to the presence of anemia. Itching of the skin and hepatomegaly are absent. Some patients have an enlarged spleen. Urine and feces become darker due to the high content of pigments (uro and stercobilinogen).
Causes of Hepatic Jaundice
Parenchymal jaundice is one of the main syndromes that indicate liver damage. It is associated with the destruction or damage of hepatocytes. The causes of this syndrome include:
- Infectious pathologies. Among them - hepatitis, mononucleosis, leptospirosis, sepsis.
- Cirrhosis of the liver.
- Toxic effects on the body. In particular, chronic drug and alcohol intoxication.
With long-term current diseases, intrahepatic cholestasis syndrome develops. It is characterized by obstruction of the small bile ducts. At the same time, free bilirubin penetrates the lymphatic and circulatory system. This is accompanied by darkening of the urine. Feces in patients with parenchymal jaundice, on the contrary, are discolored. This is of great importance for diagnosis.
Characteristic obstructive jaundice
Subhepatic jaundice occurs due to blockage of the outflow of digestive juice. Obstacles are tumors, large parasites or calculi. The result is stagnation of bile and digestive disorders. The disease is accompanied by itchy skin, nausea, and stool disorders. Halperin's classification of obstructive jaundice includes criteria such as total protein and blood bilirubin, as well as complications that develop as a result of the underlying disease. Points are awarded depending on this. This allows you to assess the prognosis for obstructive jaundice. The classification is designed to be possible to set the severity class. The easiest is grade A, which scores up to 5 points. In the presence of complications, the prognosis worsens. Class B corresponds to 6-12 points. The patient's condition is noticeably worsening. In the presence of several complications and a deterioration in blood counts, more than 15 points are gained. Class C corresponds to severe severity.
Changes in laboratory indicators for jaundice
Assess the condition of the patient using laboratory criteria. Classification of jaundice by bilirubin level helps not only to assess the severity of the disease, but also to conduct a differential diagnosis. It is more often used in pediatrics. Clinical and laboratory classification of neonatal jaundice is evaluated in the system according to Kramer. A mild degree corresponds to a change in the color of the scalp and sclera. In this case, bilirubin is less than 80 μmol / L. The higher the pigment level, the more points according to Kramer. With jaundice of the body, the level of bilirubin is 80-150 μmol / L. This corresponds to 2 points. A third degree of jaundice develops if the level of bilirubin is between 150 and 200 μmol / L. Clinically, this corresponds to a change in skin color to the knees and elbows. With an extreme degree of severity of the syndrome, the level of bilirubin rises above 250 μmol / L.
Complications of icteric syndrome
In most cases, a high bilirubin content does not threaten the body. The pigment does not harm the skin and internal organs. The causes of the patient’s serious condition are: erythrocyte hemolysis, liver damage and impaired bile outflow. Complications of directly hyperbilirubinemia are observed when the pigment enters the brain. This condition is called nuclear jaundice. It is observed with increasing levels of indirect bilirubin hundreds of times. Nuclear jaundice develops due to hemolytic disease of newborns and various congenital pathologies of the hematopoietic system. She faces severe neurological impairment.
Differential diagnosis for jaundice syndrome
To find out the cause of jaundice, pay attention to skin color (lemon, orange) and the presence of other symptoms. Palpation of the liver and spleen is performed. It is important to determine the level of bilirubin. If only free pigment is elevated, the cause is red blood cell hemolysis. If the liver is disturbed, the level of both unconjugated and direct bilirubin changes. Urine becomes darker and feces lighter. In the blood, the level of stercobilinogen rises. Subhepatic jaundice is accompanied by itching and a worsening of the general condition. An increase in conjugated bilirubin is noted in the blood . To find out the cause of jaundice, perform various tests, ultrasound and CT scan of the abdominal cavity.